Benzene
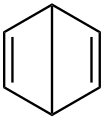
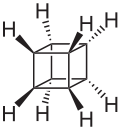
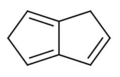
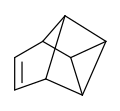
There are many valence isomers one can draw for the C6H6 formula benzene. Some were originally proposed for benzene itself before the actual structure of benzene was known. Others were later synthesized in lab. Some have been observed to isomerize to benzene, whereas others tend to undergo other reactions instead, or isomerize by ways other than pericyclic reactions.
- Some known valence isomers of benzene