Related Research Articles

A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion, the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.
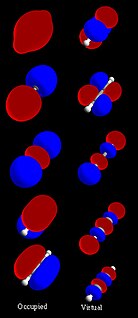
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron orbital wave functions. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the region of space in which a function has a significant amplitude.
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics.

Theoretical chemistry is the branch of chemistry which develops theoretical generalizations that are part of the theoretical arsenal of modern chemistry: for example, the concepts of chemical bonding, chemical reaction, valence, the surface of potential energy, molecular orbitals, orbital interactions, and molecule activation.

In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s and 2p subshells are occupied by 2, 2 and 6 electrons respectively.

Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones was a British mathematician and professor of theoretical physics at the University of Bristol, and then of theoretical science at the University of Cambridge. He was an important pioneer in the development of modern computational chemistry and theoretical chemistry.

The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens; although more generally the rule is applicable for the s-block and p-block of the periodic table. Other rules exist for other elements, such as the duplet rule for hydrogen and helium, or the 18-electron rule for transition metals.
Coupled cluster (CC) is a numerical technique used for describing many-body systems. Its most common use is as one of several post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods in the field of computational chemistry, but it is also used in nuclear physics. Coupled cluster essentially takes the basic Hartree–Fock molecular orbital method and constructs multi-electron wavefunctions using the exponential cluster operator to account for electron correlation. Some of the most accurate calculations for small to medium-sized molecules use this method.
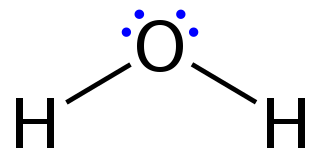
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas,Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule. Lewis structures extend the concept of the electron dot diagram by adding lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond.
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century.
In chemistry, valence bond (VBT) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule.

Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies.
In chemistry, the valence or valency of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
A basis set in theoretical and computational chemistry is a set of functions that is used to represent the electronic wave function in the Hartree–Fock method or density-functional theory in order to turn the partial differential equations of the model into algebraic equations suitable for efficient implementation on a computer.

PQS is a general purpose quantum chemistry program. Its roots go back to the first ab initio gradient program developed in Professor Peter Pulay's group but now it is developed and distributed commercially by Parallel Quantum Solutions. There is a reduction in cost for academic users and a site license. Its strong points are geometry optimization, NMR chemical shift calculations, and large MP2 calculations, and high parallel efficiency on computing clusters. It includes many other capabilities including Density functional theory, the semiempirical methods, MINDO/3, MNDO, AM1 and PM3, Molecular mechanics using the SYBYL 5.0 Force Field, the quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics mixed method using the ONIOM method, natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis and COSMO solvation models. Recently, a highly efficient parallel CCSD(T) code for closed shell systems has been developed. This code includes many other post Hartree–Fock methods: MP2, MP3, MP4, CISD, CEPA, QCISD and so on.

Water is a simple triatomic bent molecule with C2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. Despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is nonetheless complex as many of its bonding properties such as bond angle, ionization energy, and electronic state energy cannot be explained by one unified bonding model. Instead, several traditional and advanced bonding models such as simple Lewis and VSEPR structure, valence bond theory, molecular orbital theory, isovalent hybridization, and Bent's rule are discussed below to provide a comprehensive bonding model for H
2O, explaining and rationalizing the various electronic and physical properties and features manifested by its peculiar bonding arrangements.

Linnett double-quartet theory (LDQ) is a method of describing the bonding in molecules which involves separating the electrons depending on their spin, placing them into separate 'spin tetrahedra' to minimise the Pauli repulsions between electrons of the same spin. Introduced by J. W. Linnett in his 1961 monograph and 1964 book, this method expands on the electron dot structures pioneered by G. N. Lewis. While the theory retains the requirement for fulfilling the octet rule, it dispenses with the need to force electrons into coincident pairs. Instead, the theory stipulates that the four electrons of a given spin should maximise the distances between each other, resulting in a net tetrahedral electronic arrangement that is the fundamental molecular building block of the theory.
References
- ↑ Alia, Joseph (2010). "Chemical Reasoning Based on an Invariance Property: Bond and Lone Pair Pictures in Quantum Structural Formulas". Symmetry. MDPI. 2 (3): 1559–1590. doi: 10.3390/sym2031559 . Retrieved 15 March 2018.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(October 2012) |