Related Research Articles

Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2.
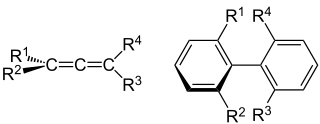
In chemistry, axial chirality is a special case of chirality in which a molecule contains two pairs of chemical groups in a non-planar arrangement about an axis of chirality so that the molecule is not superposable on its mirror image. The axis of chirality is usually determined by a chemical bond that is constrained against free rotation either by steric hindrance of the groups, as in substituted biaryl compounds such as BINAP, or by torsional stiffness of the bonds, as in the C=C double bonds in allenes such as glutinic acid. Axial chirality is most commonly observed in substituted biaryl compounds wherein the rotation about the aryl–aryl bond is restricted so it results in chiral atropisomers, as in various ortho-substituted biphenyls, and in binaphthyls such as BINAP.
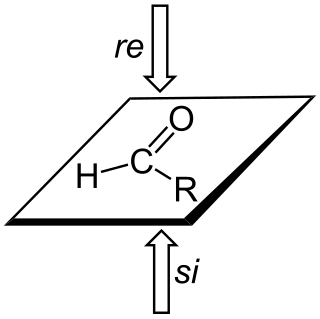
In stereochemistry, prochiral molecules are those that can be converted from achiral to chiral in a single step. An achiral species which can be converted to a chiral in two steps is called proprochiral.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.

Mostafa A. El-Sayed is an Egyptian-American physical chemist, a leading nanoscience researcher, a member of the National Academy of Sciences and a US National Medal of Science laureate. He was the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Physical Chemistry during a critical period of growth. He is also known for the spectroscopy rule named after him, the El-Sayed rule.

Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, also known as the Green Book, is a compilation of terms and symbols widely used in the field of physical chemistry. It also includes a table of physical constants, tables listing the properties of elementary particles, chemical elements, and nuclides, and information about conversion factors that are commonly used in physical chemistry. The Green Book is published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is based on published, citeable sources. Information in the Green Book is synthesized from recommendations made by IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), including recommendations listed in the IUPAP Red Book Symbols, Units, Nomenclature and Fundamental Constants in Physics and in the ISO 31 standards.
Steven Victor Ley is Professor of Organic Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Cambridge, and is a Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge. He was President of the Royal Society of Chemistry (2000–2002) and was made a CBE in January 2002, in the process. In 2011, he was included by The Times in the list of the "100 most important people in British science".
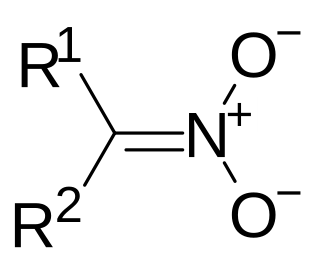
A nitronate (IUPAC: azinate) in organic chemistry is a functional group with the general structure R1R2C=NO−
2. It is the anion of nitronic acid (sometimes also called an aci, or an azinic acid), a tautomeric form of a nitro compound. Just as ketones and aldehydes can exist in equilibrium with their enol tautomer, nitro compounds exist in equilibrium with their nitronate tautomer under basic conditions. In practice they are formed by the deprotonation of the α-carbon, the pka of which is typically around 17.
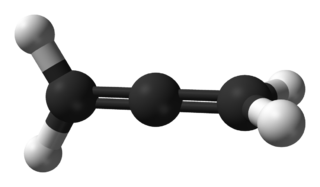
Propadiene or allene is the organic compound with the formula H2C=C=CH2. It is the simplest allene, i.e. a compound with two adjacent carbon double bonds. As a constituent of MAPP gas, it has been used as a fuel for specialized welding.
In mass spectrometry, resolution is a measure of the ability to distinguish two peaks of slightly different mass-to-charge ratios ΔM, in a mass spectrum.

Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, commonly referred to by chemists as the Blue Book, is a collection of recommendations on organic chemical nomenclature published at irregular intervals by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). A full edition was published in 1979, an abridged and updated version of which was published in 1993 as A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Both of these are now out-of-print in their paper versions, but are available free of charge in electronic versions. After the release of a draft version for public comment in 2004 and the publication of several revised sections in the journal Pure and Applied Chemistry, a fully revised edition was published in print in 2013 and its online version is also available.

The Compendium of Analytical Nomenclature is an IUPAC nomenclature book published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) containing internationally accepted definitions for terms in analytical chemistry. It has traditionally been published in an orange cover, hence its informal name, the Orange Book.
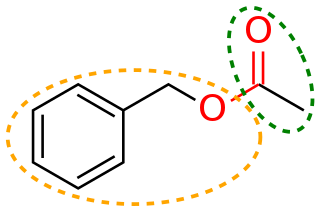
In organic chemistry, a moiety is a part of a molecule that is given a name because it is identified as a part of other molecules as well.
In chemistry, a ring is an ambiguous term referring either to a simple cycle of atoms and bonds in a molecule or to a connected set of atoms and bonds in which every atom and bond is a member of a cycle. A ring system that is a simple cycle is called a monocycle or simple ring, and one that is not a simple cycle is called a polycycle or polycyclic ring system. A simple ring contains the same number of sigma bonds as atoms, and a polycyclic ring system contains more sigma bonds than atoms.

Norman Neill Greenwood FRS CChem FRSC was an Australian-British chemist and Emeritus Professor at the University of Leeds. Together with Alan Earnshaw, he wrote the textbook Chemistry of the Elements, first published in 1984.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and Red. There is also an eighth book, the "Silver Book".
The Compendium of Macromolecular Nomenclature, by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), provides definition of polymer related terms and rules of nomenclature of polymers. It is referred to as the Purple Book. It was published in 1991 (ISBN 0-63202-8475) by Blackwell Science. The author of this book is W.V. Metanomski.
A ring forming reaction or ring-closing reaction in organic chemistry is a general term for a variety of reactions that introduce one or more rings into a molecule. A heterocycle forming reaction is such a reaction that introduces a new heterocycle. Important classes of ring forming reactions include annulations and cycloadditions.
In chemical nomenclature, a descriptor is a notational prefix placed before the systematic substance name, which describes the configuration or the stereochemistry of the molecule. Some listed descriptors are only of historical interest and should not be used in publications anymore as they do not correspond with the modern recommendations of the IUPAC. Stereodescriptors are often used in combination with locants to clearly identify a chemical structure unambiguously.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Albery, W. J. (1987). "Victor Gold. 29 June 1922-29 September 1985". Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society . 33: 262–288. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1987.0010. JSTOR 769953. S2CID 73043269.
- ↑ Carsten Reinhardt (2001), Chemical sciences in the 20th century , page 20. Wiley-VCH, ISBN 3-527-30271-9, ISBN 978-3-527-30271-0
- ↑ "UCL Aberystwyth Prospectus, 1942". Collecting: Knowledge in Motion. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ ‘GOLD, Prof. Victor’, Who Was Who, A & C Black, an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing plc, 1920–2016
- 1 2 Colin Archibald Russell and Gerrylynn K. Roberts (2005) Chemical history: reviews of the recent literature, Royal Society of Chemistry, ISBN 0-85404-464-7, ISBN 978-0-85404-464-1
- ↑ Advances in Physical Organic Chemistry , Google Books website
- ↑ IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
- ↑ From the Editor, Chemistry International, Vol. 28 No. 6, November–December 2006