
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 252 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 20,000 species having been described.

Xiphosura is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are sometimes called horseshoe crabs. They first appeared in the Hirnantian. Currently, there are only four living species. Xiphosura contains one suborder, Xiphosurida, and several stem-genera.

Dalmanites is a genus of trilobite in the order Phacopida. They lived from the Late Ordovician to Middle Devonian.

Paradoxides is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of Paradoxides davidis, described by John William Salter in 1863, is 37 cm (15 in). The cephalon was semicircular with free cheeks ending in long, narrow, recurved spines. Eyes were crescent shaped providing an almost 360° view, but only in the horizontal plane. Its elongate thorax was composed of 19-21 segments and adorned with longish, recurved pleural spines. Its pygidium was comparatively small. Paradoxides is a characteristic Middle-Cambrian trilobite of the 'Atlantic' (Avalonian) fauna. Avalonian rocks were deposited near a small continent called Avalonia in the Paleozoic Iapetus Ocean. Avalonian beds are now in a narrow strip along the East Coast of North America, and in Europe.

Asaphus is a genus of trilobites that is known from the Lower and Middle Ordovician of northwestern Europe.
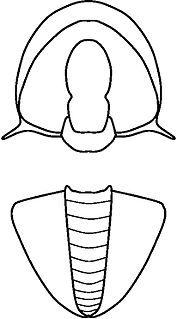
Acidiscus Rasetti, 1966, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.

Erbenochile is a genus of spinose phacopid trilobite, of the family Acastidae, found in Lower to Middle Devonian age rocks from Algeria and Morocco. Originally described from an isolated pygidium, the first complete articulated specimen of E. erbeni revealed the presence of extraordinarily tall eyes:
"Straight-sided towers of lenses... with [up to] 18 lenses in a vertical file"

Pagetia Walcott, 1916. is a small genus of trilobite, assigned to the Eodiscinid family Pagetiidae and which had global distribution during the Middle Cambrian. The genus contains 55 currently recognized species, each with limited spatial and temporal ranges.
Yukoniidae S. Zhang, 1980 [nom. transl. et emend. Jell, in Whittington et al., 1997 ex Yukoniinae S. Zhang in W. Zhang, Lu et al., 1980] is a small family of trilobites, belonging to the Eodiscina.

Odontochile is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Dalmanitidae.
Bolbolenellus is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with five species attributed to it currently. It can be easily distinguished from all other trilobites by the combination of the absence of dorsal sutures in the head shield like all Olenellina, and a distinctly bulbous frontal lobe (L4) of the raised axial area in the head called glabella. The species lived at the end of the Lower Cambrian.
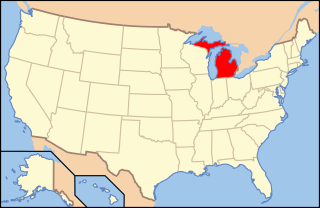
Paleontology in Michigan refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Michigan. During the Precambrian, the Upper Peninsula was home to filamentous algae. The remains it left behind are among the oldest known fossils in the world. During the early part of the Paleozoic Michigan was covered by a shallow tropical sea which was home to a rich invertebrate fauna including brachiopods, corals, crinoids, and trilobites. Primitive armored fishes and sharks were also present. Swamps covered the state during the Carboniferous. There are little to no sedimentary deposits in the state for an interval spanning from the Permian to the end of the Neogene. Deposition resumed as glaciers transformed the state's landscape during the Pleistocene. Michigan was home to large mammals like mammoths and mastodons at that time. The Holocene American mastodon, Mammut americanum, is the Michigan state fossil. The Petoskey stone, which is made of fossil coral, is the state stone of Michigan.

Paleontology in Indiana refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Indiana. Indiana's fossil record stretches all the way back to the Precambrian, when the state was inhabited by microbes. More complex organisms came to inhabit the state during the early Paleozoic era. At that time the state was covered by a warm shallow sea that would come to be inhabited by creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, cephalopods, crinoids, and trilobites. During the Silurian period the state was home to significant reef systems. Indiana became a more terrestrial environment during the Carboniferous, as an expansive river system formed richly vegetated deltas where amphibians lived. There is a gap in the local rock record from the Permian through the Mesozoic. Likewise, little is known about the early to middle Cenozoic era. During the Ice Age however, the state was subject to glacial activity, and home to creatures like short-faced bears, camels, mammoths, and mastodons. After humans came to inhabit the state, Native Americans interpreted the fossil proboscidean remains preserved near Devil's Lake as the bones of water monsters. After the advent of formal scientific investigation one paleontological survey determined that the state was home to nearly 150 different kinds of prehistoric plants.

Paleontology in Oklahoma refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Oklahoma has a rich fossil record spanning all three eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Oklahoma is the best source of Pennsylvanian fossils in the United States due to having an exceptionally complete geologic record of the epoch. From the Cambrian to the Devonian, all of Oklahoma was covered by a sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, graptolites and trilobites. During the Carboniferous, an expanse of coastal deltaic swamps formed in areas of the state where early tetrapods would leave behind footprints that would later fossilize. The sea withdrew altogether during the Permian period. Oklahoma was home a variety of insects as well as early amphibians and reptiles. Oklahoma stayed dry for most of the Mesozoic. During the Late Triassic, carnivorous dinosaurs left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Cretaceous, however, the state was mostly covered by the Western Interior Seaway, which was home to huge ammonites and other marine invertebrates. During the Cenozoic, Oklahoma became home to creatures like bison, camels, creodonts, and horses. During the Ice Age, the state was home to mammoths and mastodons. Local Native Americans are known to have used fossils for medicinal purposes. The Jurassic dinosaur Saurophaganax maximus is the Oklahoma state fossil.

Kendallina is a genus of trilobite with an inverted egg-shaped outline, a wide headshield, small eyes, small deflected spines, 12 thorax segments and a small, short tailshield. It lived during the Upper Cambrian in what are today Canada and the United States.

Orygmaspis is a genus of asaphid trilobite with an inverted egg-shaped outline, a wide headshield, small eyes, long genal spines, 12 spined thorax segments and a small, short tailshield, with four pairs of spines. It lived during the Upper Cambrian in what are today Canada and the United States.

Tricrepicephalus is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae with species of average size. Its species lived from 501 to 490 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Tricrepicephalus are widespread in Late Cambrian deposits in North America, but is also known from one location in South-America. Tricrepicephalus has an inverted egg-shaped exoskeleton, with three characteristic pits in the fold that parallels the margin of the headshield just in front of the central raised area. The articulating middle part of the body has 12 segments and the tailshield carries two long, tubular, curved pygidial spines that are reminiscent of earwig's pincers that rise backwards from the plain of the body at approximately 30°.
Triroetus is a genus of proetid trilobite found in Upper Carboniferous-aged marine strata in Russia, and Lower Permian-aged strata of Thailand, Malaysia, Spitzbergen, Yukon Territory, and Middle Permian-aged marine strata of Oman and Texas.
Ditomopyge is an extinct genus of trilobite belonging to the family Proetidae. It was extant during the Carboniferous and Permian and is widely distributed, with fossils found in Europe, southwest Asia, southeast Asia, Australia, North America, and South America.

Anisopyge is an extinct genus of trilobite belonging to the order Proetida and family Phillipsiidae. Specimens have been found in Permian beds in North and Central America.

















