Related Research Articles

The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 230 BCE to 1206 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, from 230 BCE. The "middle" period lasted for almost 1436 years and ended in 1206 CE, with the rise of the Delhi Sultanate, founded in 1206, and the end of the Later Cholas.

The history of southern India covers a span of over four thousand years during which the region saw the rise and fall of a number of dynasties and empires.

Western Ganga was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India which lasted from about 350 to 1000 CE. They are known as "Western Gangas" to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over Kalinga. The general belief is that the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later, moving their capital to Talakadu on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district.

Vishnuvardhana was a king of the Hoysala Empire in what is today the state of Karnataka, India. He ascended the Hoysala throne after the death of his elder brother Veera Ballala I in c.1108. Originally a follower of Jainism and known as Bitti Deva, he came under the influence of the Hindu philosopher Ramanuja, converted to Hindu Vaishnavism and took the name "Vishnuvardhana". His queen Shanthala however remained a Jain. This was the transition period from Jainism to Hinduism. Vishnuvardhana took the first steps in creating an independent Hoysala Empire in South India through a series of battles against his overlord, the Western Chalukya King Vikramaditya VI, and the Chola Empire to the south. He recovered parts of Gangavadi province from the hegemony of the Cholas in the battle of Talakad, and parts of Nolambavdi. According to historian Coelho, the Hoysalas gained the dignity of a kingdom due to the efforts of Vishnuvardhana, whose rule was packed with "glorious" military campaigns. According to historians Sen, Chopra et al., and Sastri, Vishnuvardhana was a "great soldier" and an "ambitious monarch".

Dhruva was one of the most notable rulers of the Rashtrakuta Empire. He ascended the imperial throne after replacing his elder brother Govinda II. Govinda II had become unpopular among his subjects on account of his various misconducts as a monarch, including excessive indulgence in sensual pleasures. This according to the historian Kamath is evident from the Karhad plates of Krishna III. The Dhulia grant of 779 and Garugadahalli inscription of 782 proclaim Dhruva the emperor. Though some historians claim that Dhruva revolted and grabbed the throne, other historians feel the transition of the throne from Govinda II to Dhruva was peaceful and may have happened willingly. He earned titles like Kalivallabha, Srivallabha, Dharavarsha, Maharajadhiraja and Parameshvara.

Vikramaditya VI became the Western Chalukya King after deposing his elder brother Someshvara II, a political move he made by gaining the support of Chalukya vassals during the Chola invasion of Chalukya territory. Vikramaditya's reign is marked with the abolishment of the Saka era and the start of the Chalukya-Vikrama era. He was the greatest of the Western Chalukya kings and had the longest reign in the dynasty. He earned the title Permadideva and Tribhuvanamalla. He had several queens who ably assisted him in administration. One of his queens, Chandala Devi, a princess from the Shilahara ruling family of Karad was called Abhinava Saraswati for her skills as an artist. Queen Kethala Devi administered the Siruguppa region and Savala Devi was in charge of an Agrahara in Naregal. According to the historian Kamath, Vikramaditya VI was a "great king who ruled over South India" and he finds a "pride of place in Karnataka history". More inscriptions in Kannada are attributed to Vikramaditya VI than any other king prior to the Vijayanagara era.
Vikramaditya I was the third son and followed his father, Pulakeshi II on to the Chalukya throne. He restored order in the fractured empire and made the Pallavas retreat from the capital Vatapi.
Satyashraya, also known as Sattiga or Irivabedanga, was a king of the Western Chalukya Empire. During a time of consolidation of the empire in the early 11th century, Satyashraya was involved in several battles with the Chola dynasty of Thanjavur, the Paramara dynasty and Chedi Kingdom of central India, and the Chaulukyas of Gujarat. The results of these wars were mixed, with victories and defeats. Even as a prince, during the rule of his father Tailapa II, Satyashraya had established himself as an ambitious warrior. Satyashraya patronised the great Kannada poet Ranna who compared his patron favourably to the Pandava prince Bhima for his strength and valor in his epic poem Sahasabhimavijaya. Satyashraya held such titles as Akalavarsha, Akalankacharita and Sahasabhima.

Jayasimha II succeeded his brother Vikramaditya V on the Western Chalukya throne. He had to fight on many fronts, against the Cholas of Tanjore in the south and the Paramara dynasty in the north, to protect his kingdom. His rule however was an important period of development of Kannada literature. The Brahmin Kannada writers Durgasimha, Chavundaraya II and Kavitavilasa were in his patronage. Chandraraja, a Brahmin writer on erotics was in the court of Machiraja, a vassal of Jayasimha II. The Jain Sanskrit scholar Vadiraja was in Jayasimha II's court and wrote two epics, on logic, and a commentary on an earlier Jain text. His queen Suggaladevi was a disciple of the Kannada saint-poet Devara Dasimayya.

Someshvara I was a king of the Western Chalukyas. Also known as "Ahavamalla" or "Trilokamalla", Someshvara succeeded his father Jayasimha II to the throne.
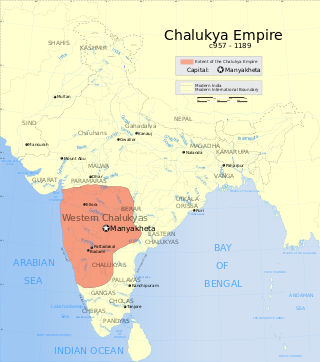
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada-speaking dynasty is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the modern Bidar district of Karnataka state, and alternatively the Later Chalukya from its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called Western Chalukyas to differentiate from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Before the rise of these Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta Empire of Manyakheta controlled most of the Deccan Plateau and Central India for over two centuries. In 973, seeing confusion in the Rashtrakuta empire after a successful invasion of their capital by the ruler of the Paramara dynasty of Malwa, Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta dynasty ruling from Bijapur region defeated his overlords and made Manyakheta his capital. The dynasty quickly rose to power and grew into an empire under Someshvara I who moved the capital to Kalyani.
Ereyanga was the son of Vinayaditya and distinguished himself as a Chalukya feudatory during their campaigns against Dhara of Malwa. Though he remained the Yuvaraja or crown prince for several decades, his rule as a monarch of Hoysala Empire was short. He was a Jain by faith and took the title 'Vira Ganga'.

Veera Ballala II was the most notable monarch of the Hoysala Empire. His successes against the Yadavas of Devagiri, the Southern Kalachuris, the Pandyas of Madurai and the waning Western Chalukya Empire, and his domination over the diminishing Cholas of Tanjore took the Hoysalas to the peak of their power. The historian Chaurasia claims that by the end of the 12th century, Ballala II's conquests had made the Hoysalas the most powerful dynasty of Deccan. According to historian Derrett, Ballala II was "the most outstanding among Hoysala kings", and historian William Coelho in comparing Ballala II to King Vishnuvardhana writes, "he vied in glory with his grandfather".

Krishna I, an uncle of Dantidurga, took charge of the growing Rashtrakuta Empire by defeating the last Badami Chalukya emperor Kirtivarman II in 757. This is known from the copper plate grant of Emperor Govinda III of 807 and a copper plate grant of the Gujarat Rashtrakuta ruler Karka from Baroda. He is also known as Kannara or Kannesvara and took the titles Akalavarsha, Shubatunga, Prithvivallabha and Shrivallabha.He patronised the famous Jain logician Akalanka Bhatta, the author of Rajavartika.

Krishna III whose Kannada name was Kannara was the last great warrior and able Rashtrakuta Emperor. He was a shrewd administrator and skillful military campaigner. He waged many wars to restore the glory of the Rashtrakutas and played an important role in rebuilding the Rashtrakuta empire. He patronised the famous Kannada poets Sri Ponna, who wrote Shanti Purana, Gajankusha, also known as Narayana, who wrote on erotics, and the Apabhramsha poet Pushpadanta who wrote Mahapurana and other works. His queen was a Chedi princess and his daughter Bijjabbe was married to a Western Ganga prince. During his rule he held titles such as Akalavarsha, Maharajadhiraja, Parameshvara, Paramamaheshvara, Shri Prithvivallabha etc. At his peak, he reigned over a vast empire stretching from at least the Narmada river in the north to at least the Kaveri river delta in the south. A copper grant of 993 issued by the Shilahara king of Thana states that the Rashtrakuta control extended from the Himalayas in the north to Ceylon in the south and from the eastern sea to the western seas. This grant also states that when the emperor Krishna III mobilised his armies, the kings of Chola, Bengal, Kannauj, Andhra and Pandya regions used to quiver.

Balligavi a town in Shikaripura taluk Shivamogga district of Karnataka state, India, is today known as Belagami or Balagame. Its ancient names are Baligrama, Dakshina Kedara, Valliggame and Valligrame. Dakshina Kedara means Kedarnath of the South. A place of antiquity, it is known for its ancient monuments. Balligavi is located 72 km from Shivamogga city and 21 km from Shikaripura town and 2.3 km from Shiralakoppa in Shikaripura taluk. Balli in Kannada means creeper or vine.
The History of Karnataka goes back several millennia. Several great empires and dynasties have ruled over Karnataka and have contributed greatly to the history, culture and development of Karnataka as well as the entire Indian subcontinent. The Chindaka Nagas of central India Gangas, Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, Chalukyas of Vengi, Yadava Dynasty of Devagiri were all of Kannada origin who later took to encouraging local languages.
The political history of medieval Karnataka spans the 4th to the 16th centuries in Karnataka region of India. The medieval era spans several periods of time from the earliest native kingdoms and imperialism; the successful domination of the Gangetic plains in northern India and rivalry with the empires of Tamilakam over the Vengi region; and the domination of the southern Deccan and consolidation against Muslim invasion. The origins of the rise of the Karnataka region as an independent power date back to the fourth-century birth of the Kadamba Dynasty of Banavasi which was the earliest of the native rulers to conduct administration in the native language of Kannada in addition to the official Sanskrit.
The Western Ganga Dynasty ruled large parts of southern Karnataka from the fourth century CE till the late tenth century CE with their regal capital initially at Kolar and later at Talakad in Mysore district, Karnataka. The origin of the Ganga clan prior to the fourth century is shrouded in legends and myths. Clarity into their history comes from such contemporaneous writings as Chavundaraya Purana in Kannada and Lokhavibhaga in Prakrit and from numerous inscriptions excavated in the Mysore, Bangalore and Kolar districts and Anantapur district. The Western Gangas played a pivotal role in the development of polity, culture and literature during their long rule in the region, at times as independent monarchs and at other times as subordinates of their larger neighbors: the Badami Chalukyas and later the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta. Their patronage to literature in Kannada and Sanskrit, their achievements in architecture including the famous monolith of Gomateshwara, their Hindu temples in the southern Karnataka, and their Jain Basadi's of Shravanabelagola and Kambadahalli are testimony to the rich contribution they made to the region.

The Chalukya dynasty was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani until the end of the 12th century.
References
- Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise History of Karnataka from Pre-historic Times to the Present, Jupiter books, MCC, Bangalore, 1980 (Reprinted 2001, 2002) OCLC: 7796041