
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability.

Etruscan was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually completely superseded by it. The Etruscans left around 13,000 inscriptions that have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Greek, or Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study, with it mostly being referred to as one of the Tyrsenian languages, at times as an isolate and a number of other less well-known theories.

The Etruscan civilization was developed by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in ancient Italy, with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania.

Veii was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and 16 km (9.9 mi) north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-state of Veii are in Formello, immediately to the north. Formello is named after the drainage channels that were first created by the Veians.

Etruscan religion comprises a set of stories, beliefs, and religious practices of the Etruscan civilization, heavily influenced by the mythology of ancient Greece, and sharing similarities with concurrent Roman mythology and religion. As the Etruscan civilization was gradually assimilated into the Roman Republic from the 4th century BC, the Etruscan religion and mythology were partially incorporated into ancient Roman culture, following the Roman tendency to absorb some of the local gods and customs of conquered lands. The first attestations of an Etruscan religion can be traced back to the Villanovan culture.

Ancient art refers to the many types of art produced by the advanced cultures of ancient societies with different forms of writing, such as those of ancient China, India, Mesopotamia, Persia, Palestine, Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The art of pre-literate societies is normally referred to as prehistoric art and is not covered here. Although some pre-Columbian cultures developed writing during the centuries before the arrival of Europeans, on grounds of dating these are covered at pre-Columbian art and articles such as Maya art, Aztec art, and Olmec art.

Volterra is a walled mountaintop town in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its history dates from before the 8th century BC and it has substantial structures from the Etruscan, Roman, and Medieval periods.

The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family.

Caere is the Latin name given by the Romans to one of the larger cities of southern Etruria, the modern Cerveteri, approximately 50–60 kilometres north-northwest of Rome. To the Etruscans it was known as Cisra, to the Greeks as Agylla and to the Phoenicians as 𐤊𐤉𐤔𐤓𐤉𐤀.

Vulci or Volci was a rich Etruscan city in what is now northern Lazio, central Italy.

Situla, from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Bronze Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in bands or friezes running round the vessel.

San Casciano dei Bagni is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Siena in the Italian region of Tuscany, located about 110 km (68 mi) southeast of Florence and about 70 km (43 mi) southeast of Siena. It is a member of the I Borghi più belli d'Italia association.

Etruscan art was produced by the Etruscan civilization in central Italy between the 10th and 1st centuries BC. From around 750 BC it was heavily influenced by Greek art, which was imported by the Etruscans, but always retained distinct characteristics. Particularly strong in this tradition were figurative sculpture in terracotta, wall-painting and metalworking especially in bronze. Jewellery and engraved gems of high quality were produced.
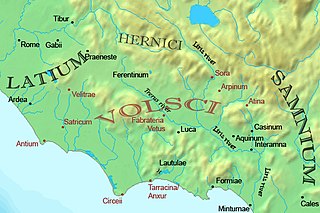
The Latins, sometimes known as the Latials or Latians, were an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. From about 1000 BC, the Latins inhabited the small region known to the Romans as Old Latium, that is, the area between the river Tiber and the promontory of Mount Circeo 100 km (62 mi) southeast of Rome. Following the Roman expansion, the Latins spread into the Latium adiectum, inhabited by Osco-Umbrian peoples.

The Monteleone chariot is an Etruscan chariot dated to c. 530 BC, considered one of the world's great archaeological finds. It was originally uncovered at Monteleone di Spoleto and is currently a major attraction in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City.

Narce was a Faliscan settlement in Italy located 5 kilometers south of Falerii. Its residents spoke an Italic language related to Latin. It was inhabited from the 2nd millennium to the 3rd century B.C. The ancient name of the settlement is uncertain, but it may have been called Fescennium.

In ancient Rome, a tintinnabulum was a wind chime or assemblage of bells. A tintinnabulum often took the form of a bronze ithyphallic figure or of a fascinum, a magico-religious phallus thought to ward off the evil eye and bring good fortune and prosperity.

The tomb known as the Regolini-Galassi tomb is one of the wealthiest Etruscan family tombs in Caere, an ancient city in Italy approximately 50–60 kilometres (31–37 mi) north-northwest of Rome. The tomb dates to between 680/675-650 BC. Based on the evidence of the tomb's architecture and its contents, it was built by a wealthy family of Caere. The grave goods included with the two decedents included bronze cauldrons and gold jewellery of Etruscan origin in the Oriental style. The tomb was discovered in 1836 in modern-day Cerveteri in an undisturbed condition and named after the excavators, general Vincenzo Galassi and the archpriest of Cerveteri, Alessandro Regolini. Both of these men had previous experience opening and excavating tombs in the area of Caere.
Lucus Pisaurensis is a sacred grove or lucus of ancient Pisaureum, modern Pesaro in Italy. It is just outside the coastal comune of Pesaro, between the Colle della Salute and the Collina in Santa Veneranda. It is in the Pesaro e Urbino Province of Marche, a pre-Imperium Romanum region of the Sabines and Latins peoples.

















