
Afro Celt Sound System is a European and African group who fuse electronic music with traditional Gaelic and West African music. Afro Celt Sound System was formed in 1995 by producer-guitarist Simon Emmerson, and feature a wide range of guest artists. In 2003, they temporarily changed their name to Afrocelts before reverting to their original name.
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification System is a drug classification system that classifies the active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties. Its purpose is an aid to monitor drug use and for research to improve quality medication use. It does not imply drug recommendation or efficacy. It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology (WHOCC), and was first published in 1976.

Pathology is the study of disease and injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases. The suffix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.
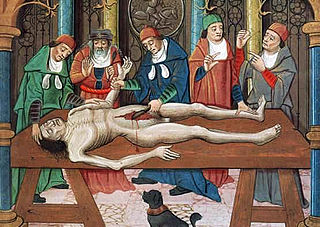
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern anatomists and scientists. Written descriptions of human organs and parts can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Egyptian papyri, where attention to the body was necessitated by their highly elaborate burial practices.

Anatomical pathology (Commonwealth) or anatomic pathology (U.S.) is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the 20th century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovanni Battista Morgagni from Forlì.

Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes.

The macula (/ˈmakjʊlə/) or macula lutea is an oval-shaped pigmented area in the center of the retina of the human eye and in other animals. The macula in humans has a diameter of around 5.5 mm (0.22 in) and is subdivided into the umbo, foveola, foveal avascular zone, fovea, parafovea, and perifovea areas.
Dead space is the volume of air that is inhaled that does not take part in the gas exchange, because it either remains in the conducting airways or reaches alveoli that are not perfused or poorly perfused. It means that not all the air in each breath is available for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Mammals breathe in and out of their lungs, wasting that part of the inhalation which remains in the conducting airways where no gas exchange can occur.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones, which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans, it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species have only the scapula.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.

This glossary of entomology describes terms used in the formal study of insect species by entomologists.

ITK-SNAP is an interactive software application that allows users to navigate three-dimensional medical images, manually delineate anatomical regions of interest, and perform automatic image segmentation. The software was designed with the audience of clinical and basic science researchers in mind, and emphasis has been placed on having a user-friendly interface and maintaining a limited feature set to prevent feature creep. ITK-SNAP is most frequently used to work with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and computed tomography (CT) data sets.

The iliolumbar vein is the vena comitans of the iliolumbar artery.

Justus Ferdinand Christian Loder was a German anatomist and surgeon who was a native of Riga.
Physoclisti are, collectively, fishes that lack a connection between the gas bladder and the alimentary canal, with the bladder serving only as a buoyancy organ.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors, physicians, and pharmacists.
A drug class is a group of medications and other compounds that have similar chemical structures, the same mechanism of action, similar modes of action, and/or are used to treat the similar diseases. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has worked on classifying and licensing new medications for many years. However, the FDA's Drug Evaluation and Research Center categorizes these new medications based on both their chemical and therapeutic class.

Krapina Neanderthal site, also known as Hušnjakovo Hill is a Paleolithic archaeological site located near Krapina, Croatia.
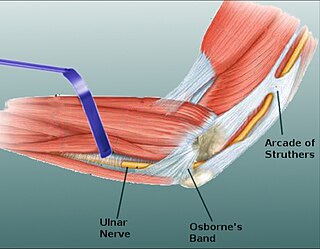
Osborne's ligament, also Osborne's band, Osborne's fascia, Osborne's arcade, arcuate ligament of Osborne, or the cubital tunnel retinaculum, refers to either the connective tissue which spans the humeral and ulnar heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) or another distinct tissue located between the olecranon process of the ulna and the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It is named after Geoffrey Vaughan Osborne, a British orthopedic surgeon, who described the eponymous tissue in 1957.















