
The 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. The Republican nominee, Governor George W. Bush of Texas, the eldest son of George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections, with long-standing controversy about the result. Gore conceded the election on December 13.
Bush v. Gore, 531 U.S. 98 (2000), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court on December 12, 2000, that settled a recount dispute in Florida's 2000 presidential election between George W. Bush and Al Gore. On December 8, the Florida Supreme Court had ordered a statewide recount of all undervotes, over 61,000 ballots that the vote tabulation machines had missed. The Bush campaign immediately asked the U.S. Supreme Court to stay the decision and halt the recount. Justice Antonin Scalia, convinced that all the manual recounts being performed in Florida's counties were illegitimate, urged his colleagues to grant the stay immediately. On December 9, the five conservative justices on the Court granted the stay, with Scalia citing "irreparable harm" that could befall Bush, as the recounts would cast "a needless and unjustified cloud" over Bush's legitimacy. In dissent, Justice John Paul Stevens wrote that "counting every legally cast vote cannot constitute irreparable harm." Oral arguments were scheduled for December 11.

The 2000 United States presidential election recount in Florida was a period of vote recounting in Florida that occurred during the weeks after Election Day in the 2000 United States presidential election between George W. Bush and Al Gore. The Florida vote was ultimately settled in Bush's favor by a margin of 537 votes when the U.S. Supreme Court, in Bush v. Gore, stopped a recount that had been initiated upon a ruling by the Florida Supreme Court. Bush's win in Florida gave him a majority of votes in the Electoral College and victory in the presidential election.

The 2000 presidential campaign of George W. Bush, the then-governor of Texas, was formally launched on June 14, 1999 as Governor Bush, the eldest son of former President George H. W. Bush, announced his intention to seek the Republican Party nomination for the presidency of the United States in the 2000 presidential election.
The following is a timeline of events during the 2004 U.S. presidential election:
An election exit poll is a poll of voters taken immediately after they have exited the polling stations. A similar poll conducted before actual voters have voted is called an entrance poll. Pollsters – usually private companies working for newspapers or broadcasters – conduct exit polls to gain an early indication as to how an election has turned out, as in many elections the actual result may take many hours to count.
The National Election Pool (NEP) is a consortium of American news organizations formed in 2003 to provide exit polling information for US elections, replacing the Voter News Service following the latter's disbandment the same year.
During the 2004 United States elections, concerns were raised about various aspects of the voting process, including whether voting had been made accessible to all those entitled to vote, whether ineligible voters were registered, whether voters were registered multiple times, and whether the votes cast had been correctly counted. More controversial was the charge that these issues might have affected the reported outcome of the presidential election, in which the incumbent, Republican President George W. Bush, defeated the Democratic challenger, Senator John Kerry. Despite the existing controversies, Kerry conceded the election the following day on November 3.
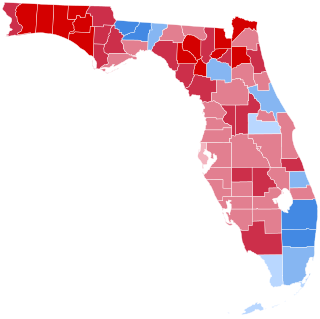
The 2004 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 2, 2004, as part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 27 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
The Volusia error was an incident that occurred during the 2000 United States presidential election in Florida.

The 1998 Texas gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1998, to elect the governor of Texas. Incumbent Republican Governor George W. Bush was re-elected in a landslide over 4-term Democratic Texas Land Commissioner Garry Mauro, winning 68% of the vote to Mauro's 31%. Bush carried 239 counties, while Mauro carried just 15. Exit polls revealed that Bush won 27% of the African-American vote, which was the highest percentage for any Republican statewide candidate, and 49% of the Latino vote. Bush was sworn in for a second term as Governor on January 19, 1999.
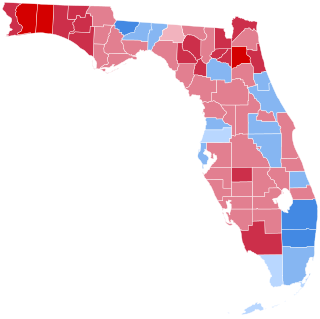
The 2000 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 7, 2000, as part of the nationwide presidential election. Florida, a swing state, had a major recount dispute that took center stage in the election. The outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election was not known for more than a month after balloting because of the extended process of counting and recounting Florida's presidential ballots. State results tallied on election night gave 246 electoral votes to Republican nominee Texas Governor George W. Bush and 255 to Democratic nominee Vice President Al Gore, with New Mexico (5), Oregon (7), and Florida (25) too close to call that evening. Gore won New Mexico and Oregon over the following few days; but the result in Florida was to be decisive, regardless of how those two states had voted.
An election verification exit poll (EVEP) is a relatively new concept in polling, intended to improve the accuracy of exit polls to such an extent that they can be used to verify election results. Traditional (media) exit polling relies on small samples, wheres EVEPs propose to use larger samples.

The 2008 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 4, 2008, and was part of the 2008 United States presidential election. Voters chose 27 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2000 United States presidential election in New Mexico took place on November 7, 2000, and was part of the 2000 United States presidential election. Voters chose five electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. New Mexico was won by Vice President Al Gore by a 0.06 percent margin. It was the closest state in the entire presidential election by raw vote margin, which was even closer than Florida. News outlets called New Mexico for Gore at approximately 10:21 p.m. (EST), but later retracted the call when it was determined to be too close to call.

The 2000 presidential campaign of Pat Buchanan, conservative pundit and advisor to both President Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan, was formally launched on March 2, 1999, as Buchanan announced his intention to seek the Republican Party nomination for the presidency of the United States in the 2000 presidential election. It marked Buchanan's third primary campaign for the presidency, following his bids in 1992 and 1996. Although he had not attained the nomination either time, he had been regarded as a consequential figure within the party. Early primary surveys found Buchanan polling in the single digits, and following the publication of his book A Republic, Not an Empire, which generally advocated for noninterventionist and "America first" foreign policy, some within the Republican Party condemned Buchanan's foreign policy views. There began to be speculation that Buchanan would leave the Republican Party in favor of the Reform Party, a third party which qualified for matching federal campaign funds.

The 2012 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 6, 2012, as part of the 2012 general election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Florida voters chose 29 electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, Vice President Joe Biden, against Republican challenger and former Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney and his running mate, Congressman Paul Ryan.

The 2016 Florida Democratic presidential primary took place on March 15 in the U.S. state of Florida as one of the Democratic Party's primaries ahead of the 2016 presidential election.
A decision desk is a team of experts that one or many US news organizations assemble to analyze incoming data about election results and project winners on election day. Decision desks use exit polling data as well as officially reported results as they come in, to project and then "call" the winners of elections on election night. "Projected winners" are only unofficial; depending on state or local laws, election officials may still have days or weeks after election day to complete counting votes and certifying winners.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Iowa was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Iowa voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Iowa has six electoral votes in the Electoral College.











