
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg in Russia to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn. The eastern parts of the Gulf of Finland belong to Russia, and some of Russia's most important oil harbors are located farthest in, near Saint Petersburg. As the seaway to Saint Petersburg, the Gulf of Finland has been and continues to be of considerable strategic importance to Russia. Some of the environmental problems affecting the Baltic Sea are at their most pronounced in the shallow gulf. Proposals for a tunnel through the gulf have been made.
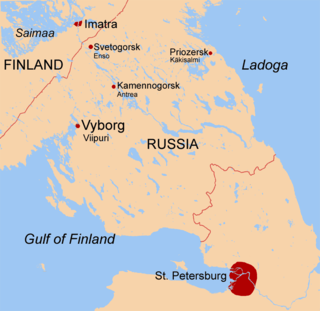
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110-kilometre-wide (30–70 mi) stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about 15,000 km2 (5,800 sq mi).
Vesikko is a submarine, which was launched on 10 May 1933 at the Crichton-Vulcan dock in Turku. Until 1936 it was named by its yard number CV 707. Vesikko was ordered by a Dutch engineering company Ingenieurskantoor voor Scheepsbouw in 1930 as a commercial submarine prototype, being the prototype for the German Type II submarines. Purchased by the Finnish before World War II, she saw service in the Winter War and Continuation War, sinking the Soviet merchant ship Vyborg as her only victory. After the cease-fire with the Allies in 1944, Vesikko was retired. Finland was banned from operating submarines after the war and she was kept in storage until she was turned into a museum ship.

Vyborg Castle is a fortress in Vyborg, Russia. It was built by the Swedes during the Middle Ages around which the town of Vyborg evolved. The castle became the stronghold of the Swedish realm in the Karelian region. Throughout the centuries, it was the first defense of the kingdom against the Russians. Its military and strategic status in the late Middle Ages was second only to the fortified capital Stockholm. Currently it serves as the site of Vyborg Regional Museum.
The history of the Jews in Finland goes back to the late 18th century. Many of the first Jews to arrive were nineteenth-century Russian soldiers who stayed in Finland after their military service ended. The two synagogues in active use today in Finland were built by Jewish congregations in Helsinki and Turku in 1906 and 1912, respectively. The Vyborg Synagogue was destroyed by Russian air bombings on 30 November 1939, the first day of the Winter War. Today, Finland is home to around 1,800 Jews, of which 1,400 live in the Greater Helsinki area and 200 in Turku. Finnish and Swedish are the most common mother tongues of Jews in Finland, and many also speak Yiddish, German, Russian or Hebrew. Since data collection began in 2008, incidents of antisemitism have been on the rise in Finland. The number of incidents are likely under-reported, as Finland does not have a systematic method for recording specific forms of hate speech that incite violence or hatred.

The Great Synagogue, was a synagogue of the Jewish Community of Danzig in the city of Danzig, Germany. It was built in 1885–1887 on Reitbahnstraße, now Bogusławski Street. It was the largest synagogue in the city, and was demolished by the Free City authorities in May 1939.

The Ezras Izrael Synagogue, also known as Wołyńska Shul, was a former Orthodox Jewish congregation and synagogue or shul, located at ul. Wólczańska 6 Street, in Łódź, in the Łódź Voivodeship of Poland. Designed by Gustaw Landau-Gutenteger and completed in 1904, the synagogue served as a house of prayer until World War II when it was destroyed by Nazis in November 1939.

Vyborg is a railway station, located in the town of Vyborg in Leningrad Oblast, Russia.

The Saint Petersburg–Hiitola railway is a 170-kilometer (110 mi) long railway with 1,520 mm broad gauge located in St. Petersburg, Leningrad Oblast and Republic of Karelia, which links Finlyandsky Rail Terminal to Khiytola through Devyatkino, Vaskelovo, Sosnovo, Priozersk and Kuznechnoye. Originally built by Finnish State Railways in the Grand Duchy of Finland, the railway was part of a trunk line from Vaasa by the Gulf of Botnia to St. Petersburg. In the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty the territory was ceded by Finland to the Soviet Union. The railroad is now operated by the Russian Railways. The railroad is used by passenger trains between St. Petersburg and Sortavala. The track between Khiytola and Sortavala is a part of the Vyborg–Joensuu railroad completed in 1894.

Sommers is an islet and a lighthouse in the eastern part of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea, just outside the Gulf of Vyborg, about 19 kilometres south of Virolahti, Finland, but it is now possessed by Russia. The lighthouse is situated on a rocky skerry, which is elevated a maximum of 16 metres above the Baltic Sea.

Viipuri Province was a historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945.

The Königsberg Synagogue, called at the time, the New Synagogue, was a former Orthodox Jewish congregation and synagogue, located in Königsberg in Prussia, East Prussia, Germany.
The history of rail transport in Finland began on January 31, 1862, with the opening of the railway line between Helsinki and Hämeenlinna. By 1900 most of the future main lines had been constructed, including the line to St. Petersburg. By the time of the birth of the new Finnish Republic in 1917 lines connected all major cities, major ports, and reached as far as the Swedish border, and inner Finland as far north as Kontiomäki in Paltamo region, as well as eastwards into Karelia.

The Stara Synagogue, also known as Alte Szil and Alt Stodt Shul meaning Old Town Synagogue, was a former Orthodox Jewish congregation and synagogue, located at 20 Wolborska Street, in Łódź, in the Łódź Voivodeship of Poland. Designed by Adolf Zeligson in the Moorish Revival style and completed in 1900, the synagogue served as a house of prayer until World War II when it was destroyed by Nazis on November 15–16, 1939. It was the third synagogue built in Łódź by the congregation.

The Łańcut Synagogue is a former Jewish congregation and synagogue, located in Łańcut, in Podkarpackie Voivodeship, Poland. Completed in 1761, it served as a house of prayer until World War II; subsequently used for profane purposes, and as a Jewish museum since 1981. The Łańcut Synagogue is a rare surviving example of the vaulted synagogues with a bimah-tower, that were built throughout the Polish lands in masonry from the sixteenth through the early nineteenth centuries.

Vyborg is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, 130 km northwest of St. Petersburg, 245 km east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and 38 km south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The most recent census population of Vyborg is 72,530 (2021 Census).

George Wylie Easton (1883–1966) was a Scottish businessman, footballer and sportsperson. He lived in Finland from 1903 to 1939 and worked on the timber trade mostly in the city of Vyborg. Easton was an enthusiast sportsman who was interested in football, athletics and curling.

Hjalmar Fabian Parikka was a Finnish revolutionary soldier, actor and artistic director.

The Battle of Porlampi, also known as the Battle of Porlammi, was a military engagement fought between the Finnish Army and Red Army from 30 August to 1 September 1941 on the Karelian Isthmus. The battle was fought near the town of Porlampi during the second month of the Continuation War. The battle was a Finnish victory and effectively ended the reconquest of Karelia.

The Vyborg (Viipuri) railway station built in 1913 was the second railway station built in Vyborg, Grand Duchy of Finland. The station, which had replaced Vyborg's first railway station was almost completely destroyed in 1941 during the Continuation War, and only the part that had acted as a cargo office remains. The present Vyborg railway station was built in 1953.



















