
Erfurt (German pronunciation:[ˈɛʁfʊʁt] ) is the capital and largest city of the Central German state of Thuringia. It lies in the wide valley of the River Gera, in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest, and in the middle of a line of the six largest Thuringian cities, stretching from Eisenach in the west, via Gotha, Erfurt, Weimar and Jena, to Gera in the east, close to the geographic centre of Germany. Erfurt is 100 km (62 mi) south-west of Leipzig, 250 km (155 mi) north-east of Frankfurt, 300 km (186 mi) south-west of Berlin and 400 km (249 mi) north of Munich.

Jena is a city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a population of about 110,000. Jena is a centre of education and research; the university was founded in 1558 and had 18,000 students in 2017 and the Ernst-Abbe-Fachhochschule Jena counts another 5,000 students. Furthermore, there are many institutes of the leading German research societies.
Gleichen is the name of two groups of castles in Germany, thus named from their resemblance to each other.

Bad Blankenburg is a spa town in the district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated 6 km southwest of Rudolstadt, and 37 km southeast of Erfurt. It is most famous for being the location of the first kindergarten of Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel, in 1837.

Gotha is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, 20 kilometres west of Erfurt and 25 km east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal and Bulgaria.
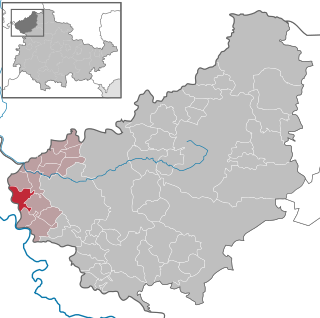
Bornhagen is a municipality in the district of Eichsfeld in Thuringia, Germany, located at the foot of the ruins of Hanstein Castle. The town district Rimbach is positioned directly south of the castle citadel at an elevation of 370 m. Bornhagen is located 22 km south of Göttingen, 85 km northwest of the state capital Erfurt and 270 km southwest of Berlin. It is the westernmost settlement in Thuringia but does not contain the westernmost point which is 75 km south near Geisa.

Arnstadt is a town in Ilm-Kreis, Thuringia, Germany, on the river Gera about 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Erfurt, the capital of Thuringia. Arnstadt is one of the oldest towns in Thuringia, and has a well-preserved historic centre with a partially preserved town wall. The town is nicknamed Das Tor zum Thüringer Wald because of its location on the northern edge of that forest. Arnstadt has a population of approximately 27,000.

Greiz is a town in the state of Thuringia, Germany, and is the capital of the district of Greiz. Greiz is situated in eastern Thuringia, 100 kilometres (62 mi) east of the state capital Erfurt, on the White Elster river.

Coburg is a town located on the Itz river in the Upper Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. Long part of one of the Thuringian states of the Wettin line, it joined Bavaria by popular vote only in 1920. Until the revolution of 1918, it was one of the capitals of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha and the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld.

Feldkirch is a town in the western Austrian state of Vorarlberg, bordering on Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is the administrative centre of the Feldkirch district. After Dornbirn, it is the second most populous town in Vorarlberg. The westernmost point in Austria lies in Feldkirch on the river Rhine, at the tripoint between Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein.

Artern is a town in the Kyffhäuserkreis district, Thuringia, Germany. The former municipalities Heygendorf and Voigtstedt were merged into Artern in January 2019.

Weißensee is a town in the district of Sömmerda, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated 6 km northwest of Sömmerda, and 25 km north of Erfurt. The former municipality Herrnschwende was merged into Weißensee in January 2019.

The Krämerbrücke is a medieval arch bridge in the city of Erfurt, in Thuringia, central Germany, which is lined with half-timbered shops and houses on both sides of a cobblestone street. It is one of the few remaining bridges in the world that have inhabited buildings. It has been continuously inhabited for over 500 years, longer than any other bridge in Europe. The stone, pedestrian bridge, which dates from 1325, is one of the oldest secular structures in Erfurt. It spans the Breitstrom, a branch of Gera River, and connects two town squares – Benediktsplatz and Wenigemarkt.

Alkersleben is a municipality in the Ilm-Kreis district in Thuringia, Germany. The municipality is a member of the collective municipality Riechheimer Berg.
Hasso Spode is a German historian and sociologist.

Amt Wachsenburg is a municipality in the district Ilm-Kreis, in Thuringia, Germany. The municipality is named after the Wachsenburg Castle which is located in its center. It was formed on 31 December 2012 from the former municipalities Wachsenburggemeinde and Ichtershausen. The former municipality Kirchheim was merged into Amt Wachsenburg in January 2019, and Rockhausen in December 2019. It consists of the villages Bechstedt-Wagd, Bittstädt, Eischleben, Haarhausen, Holzhausen, Ichtershausen, Kirchheim, Rehestädt, Rockhausen, Röhrensee, Sülzenbrücken, Thörey and Werningsleben.

Bützow Castle is a castle in Bützow, Germany.

A coercion castle or coercive castle was a heavily fortified, medieval castle built to dominate the surrounding land. Such castles were built mainly in the High and Late Middle Ages in order to protect those territories in areas where the population was not assessed as being entirely loyal to the sovereign. Because of the poor infrastructure of medieval Europe, the construction of castles was one of the most important ways of exercising power, which is why it was governed by royal rights. Examples of coercive castles are the Moritzburg in Halle, which was built in the late 15th century, and the Alte Burg in Koblenz.

Petersberg Citadel in Erfurt, central Germany, is one of the largest and best-preserved town fortresses in Europe. The citadel was built on Petersberg hill, in the north-western part of the old town centre from 1665, when Erfurt was governed by the Electorate of Mainz. It is surrounded by over two kilometres of stone walls and is 36 hectares in size.
Erfurt I is an electoral constituency represented in the Landtag of Thuringia. It elects one member via first-past-the-post voting. Under the current constituency numbering system, it is designated as constituency 24. It contains northern parts of Erfurt, the capital and largest city of Thuringia.



















