
Basel Convention, is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries (LDCs). It does not, however, address the movement of radioactive waste. The convention is also intended to minimize the rate and toxicity of wastes generated, to ensure their environmentally sound management as closely as possible to the source of generation, and to assist LDCs in environmentally sound management of the hazardous and other wastes they generate.

Palau, officially the Republic of Palau and historically Belau, Palaos or Pelew, is an island country in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caroline Islands with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia. It has a total area of 466 square kilometers. The most populous island is Koror, home to the country's most populous city of the same name. The capital Ngerulmud is located on the nearby island of Babeldaob, in Melekeok State. Palau shares maritime boundaries with international waters to the north, Micronesia to the east, Indonesia to the south, and the Philippines to the north west.

The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation between countries and territories of the Pacific Ocean, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
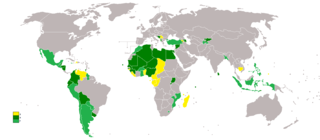
The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of August 2021 in 56 countries.

The Forced Labour Convention, the full title of which is the Convention Concerning Forced or Compulsory Labour, 1930 (No.29), is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization. Its object and purpose is to suppress the use of forced labour in all its forms irrespective of the nature of the work or the sector of activity in which it may be performed. The Convention defines forced labour as "all work or service which is exacted from any person under the menace of any penalty and for which the said person has not offered himself voluntarily", with few exceptions like compulsory military service. The convention excludes "adult able-bodied males", to whom legal imposition of forced labour is allowed.
The Convention concerning Equal Remuneration for Men and Women Workers for Work of Equal Value, or Equal Remuneration Convention is the 100th International Labour Organization Convention and the principal one aimed at equal remuneration for work of equal value for men and women. States parties may accomplish this through legislation, introduction of a system for wage determination and/or collective bargaining agreements. It is one of 8 ILO fundamental conventions.
The Convention concerning Discrimination in Respect of Employment and Occupation or Discrimination Convention is an International Labour Organization Convention on anti-discrimination. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. The convention requires states to enable legislation which prohibits all discrimination and exclusion on any basis including of race or colour, sex, religion, political opinion, national or social origin in employment and repeal legislation that is not based on equal opportunities.

The Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP) is an intergovernmental organisation based in Apia, Samoa with more than 90 staff members. The organisation is held accountable by the governments and administrations of the Pacific region to ensure the protection and sustainable development of the region's natural resources. The organisation actively promotes the understanding of the connection between Pacific island people and their natural environment and the impact that these have on their sustenance and livelihoods. The organisation was established in 1982. Previously "South Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP)", the word "South" was replaced with "Secretariat" in 2004, in recognition of the Members north of the equator. The French equivalent name is PROE, Programme régional océanien de l’environnement.

Ngerulmud is the seat of government of the Republic of Palau, an island nation in the Pacific Ocean. It replaced Koror City, Palau's largest city, as capital in 2006. The settlement is located in the state of Melekeok on Babeldaob, the country's largest island, located 20 kilometers northeast of Koror City and 2 km northwest of Melekeok City. It is the least-populous capital city in the world.

Waste management laws govern the transport, treatment, storage, and disposal of all manner of waste, including municipal solid waste, hazardous waste, and nuclear waste, among many other types. Waste laws are generally designed to minimize or eliminate the uncontrolled dispersal of waste materials into the environment in a manner that may cause ecological or biological harm, and include laws designed to reduce the generation of waste and promote or mandate waste recycling. Regulatory efforts include identifying and categorizing waste types and mandating transport, treatment, storage, and disposal practices.
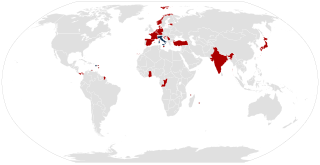
The Hong Kong International Convention for the safe and environmentally sound recycling of ships, or Hong Kong Convention is a mulitateral convention adopted in 2009, which has not entered into force. The conference that created the convention was attended by 63 countries, and overseen by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
The Niue Treaty on Cooperation in Fisheries Surveillance and Law Enforcement in the South Pacific Region or Niue Treaty is a multilateral treaty of members of the Pacific Islands Forum Fisheries Agency to enhance their ability to enforce effectively their fisheries laws, and deter breaches.

The Pacific Islands Forum Fisheries Agency (FFA) is an intergovernmental agency established in 1979 to facilitate regional co-operation and co-ordination on fisheries policies between its member states in order to achieve conservation and optimum utilisation of living marine resources, in particular highly migratory fish stocks, for the benefit of the peoples of the region, in particular the developing countries. The office campus is located in Honiara, Solomon Islands
The Constitution and Convention of the International Telecommunication Union is an international treaty, signed and ratified by almost all countries of the world. The treaty is the founding document of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations. The convention was concluded on 22 December 1992 in Geneva. The ITU Constitution and Convention succeeded and replaced the 1865 International Telegraph Convention.
The Wellington Convention is a 1989 multilateral treaty whereby states agreed to prohibit the use of fishing driftnets longer than 2.5 kilometres in the South Pacific. The Wellington Convention played a role in the 1991 United Nations General Assembly's resolution calling for a global moratorium of driftnet fishing on the high seas.
The Republic of Palau has had a turbulent history over the last 450 years, with many states claiming ownership over them. Since World War II, the Islands came under United Nation’s (UN) trusteeship and were administered by the United States. After becoming a sovereign state in 1994, Palau joined the UN and ratified the Convention on the Rights of a Child (CRC) in 1995, the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) and the Optional Protocol to the CRPD in 2013. In 2011, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) in 2011 and other core human rights treaties were signed. These treaties are yet to be ratified.
The 45th Pacific Islands Forum was held from 29 July to 1 August 2014 in Palau. The forum's official opening was held in the capital Ngerulmud, in Melekeok State, but the majority of events were held in Koror, Palau's largest city and former capital. The official theme of the meeting was "The Ocean: Life & Future". Topics under discussion include climate change, commercial fishing, non-communicable diseases and the possibility of readmitting Fiji to the forum.

India–Palau relations refers to the international relations that exist between India and Palau. The Embassy of India in Manila, Philippines is concurrently accredited to Palau.










