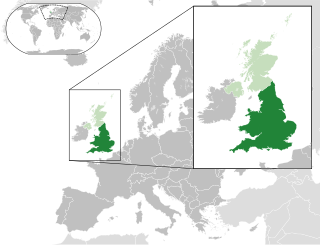
England and Wales is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is English law.

The British Islands is a term within the law of the United Kingdom which refers collectively to the following four polities:

The Sexual Offences Act 2003 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.

The Act of Supremacy 1558, sometimes referred to as the Act of Supremacy 1559, is an act of the Parliament of England, which replaced the original Act of Supremacy 1534, and passed under the auspices of Elizabeth I. The 1534 act was issued by Elizabeth's father, Henry VIII, which arrogated ecclesiastical authority to the monarchy, but which had been repealed by Mary I. Along with the Act of Uniformity 1558, the act made up what is generally referred to as the Elizabethan Religious Settlement.

The Treason Act 1351 is an Act of the Parliament of England wherethrough, according to William Blackstone, common law treason offences were enumerated and no new offences were, by statute, created. It is one of the earliest English statutes still in force, although it has been very significantly amended. It was extended to Ireland in 1495 and to Scotland in 1708. The Act was passed at Westminster in the Hilary term of 1351, in the 25th year of the reign of Edward III and was entitled "A Declaration which Offences shall be adjudged Treason". It was passed to clarify precisely what was treason, as the definition under common law had been expanded rapidly by the courts until its scope was controversially wide. The Act was last used to prosecute William Joyce in 1945 for collaborating with Germany in World War II.

The Municipal Corporations Act 1835, sometimes known as the Municipal Reform Act, was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in the incorporated boroughs of England and Wales. The legislation was part of the reform programme of the Whigs and followed the Reform Act 1832, which had abolished most of the rotten boroughs for parliamentary purposes.
In law, coming into force or entry into force is the process by which legislation, regulations, treaties and other legal instruments come to have legal force and effect. The term is closely related to the date of this transition. The point at which such instrument comes into effect may be set out in the instrument itself, or after the lapse of a certain period, or upon the happening of a certain event, such as a proclamation or an objective event, such as the birth, marriage, reaching a particular age or death of a certain person. On rare occasions, the effective date of a law may be backdated to a date before the enactment.

The Welsh Language Act 1967 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which gave some rights to use the Welsh language in legal proceedings in Wales and gave the relevant minister the right to authorise the production of a Welsh version of any documents required or allowed by the Act. The act repealed a part of the Wales and Berwick Act 1746, which defined England as including Wales.

The Suffragan Bishops Act 1534 is an Act of the Parliament of England that authorised the appointment of suffragan bishops in England and Wales. The tradition of appointing suffragans named after a town in the diocese other than the town the diocesan bishop is named after can be dated from this act.

The Coronation Oath Act 1688 is an Act of the Parliament of England. It was passed in 1689.

The Anglo-Scottish border is an internal border of the United Kingdom separating Scotland and England which runs for 96 miles (154 km) between Marshall Meadows Bay on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west.

The Treason Act 1708 is an act of the Parliament of Great Britain which harmonised the law of high treason between the former kingdoms of England and Scotland following their union as Great Britain in 1707.

The Interpretation Act 1978 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act makes provision for the interpretation of Acts of Parliament, Measures of the General Synod of the Church of England, Measures of the Church Assembly, subordinate legislation, "deeds and other instruments and documents", Acts of the Scottish Parliament and instruments made thereunder, and Measures and Acts of the National Assembly for Wales and instruments made thereunder. The Act makes provision in relation to: the construction of certain words and phrases, words of enactment, amendment or repeal of Acts in the Session they were passed, judicial notice, commencement, statutory powers and duties, the effect of repeals, and duplicated offences.

The Scottish Episcopalians Act 1711 is an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain. Its purpose was "to prevent the disturbing those of the Episcopal Communion in Scotland in the Exercise of their Religious Worship and in the Use of the Liturgy of the Church of England and for repealing the Act passed in the Parliament of Scotland intituled Act against irregular Baptisms and Marriages".
In British law and in some related legal systems, an enactment is spent if it is "exhausted in operation by the accomplishment of the purposes for which it was enacted".

The Interpretation Act 1889 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that consolidated enactments relating to statutory construction and provided definitions to shorten the language used in acts of Parliament.

The Marriage Act 1836, also known as the Act for Marriages in England 1836 or the Broomstick Marriage Act, was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that legalised civil marriage in what is now England and Wales from 30 June 1837.

The Punishment of Offences Act 1837 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It abolished the death penalty for a number of statutory offences and replaced it with transportation for life.
A collective title is an expression by which two or more pieces of legislation may, under the law of the United Kingdom, be cited together. A famous example is the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949.

The Duchy of Cornwall Act 1844, sometimes called the Duchy of Cornwall Act 1844, is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.












