
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was an American political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789, as the Tammany Society. It became the main local political machine of the Democratic Party and played a major role in controlling New York City and New York State politics. It helped immigrants, most notably the Irish, rise in American politics from the 1850s into the 1960s. Tammany usually controlled Democratic nominations and political patronage in Manhattan for over 100 years following the mayoral victory of Fernando Wood in 1854, and used its patronage resources to build a loyal, well-rewarded core of district and precinct leaders; after 1850, the vast majority were Irish Catholics due to mass immigration from Ireland during and after the Irish Famine of the late 1840s.

The City of Greater New York was the consolidation of the City of New York with Brooklyn, western Queens County, and Staten Island, which took effect on January 1, 1898. New York had already annexed the Bronx, so the consolidated city sprawled across five counties, which became the five Boroughs of modern New York. Eastern Queens County was excluded and later became Nassau County.

The New York City Council is the lawmaking body of New York City in the United States. It has 51 members from 51 council districts throughout the five boroughs.
The borough presidents are the chief executives of the five boroughs of New York City. For most of the city's history, the office exercised significant executive powers within each borough, and the five borough presidents also sat on the New York City Board of Estimate. Since 1990, the borough presidents have been stripped of a majority of their powers in the government of New York City.

The New York City Board of Estimate was a governmental body in New York City responsible for numerous areas of municipal policy and decisions, including the city budget, land-use, contracts, franchises, and water rates. Under the amendments effective in 1901, to the charter of the then-recently-amalgamated City of Greater New York, the Board of Estimate and Apportionment was composed of eight ex officio members: the Mayor of New York City, the New York City Comptroller and the President of the New York City Board of Aldermen, each of whom had three votes; the borough presidents of Manhattan and Brooklyn, each having two votes; and the borough presidents of the Bronx, Queens, and Richmond, each having one vote. The 1897 charter effective on amalgamation had had a five-member Board of Estimate and Apportionment. The La Guardia Reform Charter of 1938 simplified its name and enhanced its powers.

The boroughs of New York City are the five major governmental districts that compose New York City. The boroughs are the Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island. Each borough is coextensive with a respective county of the State of New York: The Bronx is Bronx County, Brooklyn is Kings County, Manhattan is New York County, Queens is Queens County, and Staten Island is Richmond County.

The community boards of the New York City government are the appointed advisory groups of the community districts of the five boroughs. There are currently 59 community districts: twelve in the Bronx, eighteen in Brooklyn, twelve in Manhattan, fourteen in Queens, and three in Staten Island.
The Dongan Charter is the 1686 document incorporating Albany, New York, as a city. Albany's charter was issued by Governor Thomas Dongan of the Province of New York, a few months after Governor Dongan issued a similarly worded, but less detailed charter for the city of New York. The city of Albany was created three years after Albany County. The charter is the oldest existing city charter still in force in the United States. According to Stefan Bielinski, former senior historian of the New York State Museum, the charter is also "arguably the longest-running instrument of municipal government in the Western Hemisphere." In 1936 the United States Congress commemorated the charter's 250th anniversary by minting a half dollar coin.
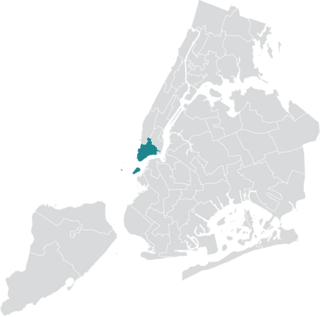
New York City's 1st City Council district is one of 51 districts in the New York City Council. It is currently represented by Democrat Christopher Marte, who took office in 2022.

The 121st New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 5 to July 16, 1898, during the second year of Frank S. Black's governorship, in Albany.

The 122nd New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 4 to April 28, 1899, during the first year of Theodore Roosevelt's governorship, in Albany.

The 127th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 6 to April 15, 1904, during the fourth year of Benjamin B. Odell Jr.'s governorship, in Albany.

The 129th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 3 to May 3, 1906, during the second year of Frank W. Higgins's governorship, in Albany.

The Morse Building, also known as the Nassau–Beekman Building and 140 Nassau Street, is a residential building in the Financial District of Manhattan in New York City, at the northeast corner of Nassau and Beekman Streets. The Morse Building, designed by Benjamin Silliman Jr. and James M. Farnsworth, contains elements of the Victorian Gothic, Neo-Grec, and Rundbogenstil style.

The New York City Board of Aldermen was a body that was the upper house of New York City's Common Council from 1824 to 1875, the lower house of its Municipal Assembly upon consolidation in 1898 until the charter was amended in 1901 to abolish the Municipal Assembly and its upper house, and its unicameral legislature from 1875 to 1897 and 1902 to 1937. The corresponding lower house was known as the Board of Assistants or the Board of Assistant Aldermen from 1824 to 1875, while the upper house was known as the Council from 1898 to 1901. In 1938 a new charter came into effect that replaced the Board of Aldermen with the New York City Council.
Martin F. Tanahey was an American politician who was the alderman of New York City's 1st district from 1922 to his death in 1930. A Democrat, he served much of the Lower East Side and Financial District in Manhattan.

Elections were held on November 2, 1937 to fill the New York City Council, which had just been formed to replace the New York City Board of Aldermen. The new Council comprised 26 members elected via proportional representation by borough, in contrast to the 65-member Board of Aldermen elected by district. This was done in response to the large majorities the Democrats often received in the Board of Aldermen. Each borough was entitled to one member of the council for each 75,000 votes cast, and an additional member for each remainder greater than 50,000. Due to voter turnout, Brooklyn was entitled to nine members of the Council, Manhattan six, Queens and The Bronx five each, and Richmond one.

An election was held in New York City to election the President of its Council on November 2, 1897. The charter of the new City of Greater New York had created a bicameral Municipal Assembly, comprising an upper Council and a lower Board of Aldermen. The Council president was elected citywide while the Board of Aldermen elected its own president.

An election was held to fill the Municipal Assembly of the newly created City of Greater New York on November 2, 1897. The charter of the new city had created a bicameral Municipal Assembly, consisting of an upper Council and a lower Board of Aldermen. Each chamber was elected from specially-made districts. In addition, the president of the Council was elected in a separate election on the same day.













