
The letter yogh (ȝogh) was used in Middle English and Older Scots, representing y and various velar phonemes. It was derived from the Insular form of the letter g, Ᵹᵹ.
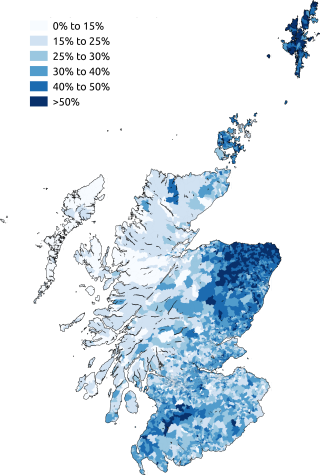
Scots is a language variety descended from Early Middle English in the West Germanic language family. Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, the Northern Isles of Scotland, and northern Ulster in Ireland, it is sometimes called: Lowland Scots, to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides, and Galloway after the sixteenth century; or Broad Scots, to distinguish it from Scottish Standard English. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged from the same medieval form of English.

Ulster Scots or Ulster-Scots, also known as Ulster Scotch and Ullans, is the dialect spoken in parts of Ulster, being almost exclusively spoken in parts of Northern Ireland and County Donegal. It is normally considered a dialect or group of dialects of Scots, although groups such as the Ulster-Scots Language Society and Ulster-Scots Academy consider it a language in its own right, and the Ulster-Scots Agency and former Department of Culture, Arts and Leisure have used the term Ulster-Scots language.

Every June the town of Lanark in Scotland celebrates Lanimer Week. The festivities reach a high point on the Thursday of Lanimer Week which is the gala day, when the town's schoolchildren parade in fancy dress with decorated vehicles, pipe bands, and a Lanimer Queen and her Court, who have been selected from local schools.

A farl is any of various quadrant-shaped flatbreads and cakes, traditionally made by cutting a round into four pieces. In Ulster, the term generally refers to soda bread and, less commonly, potato bread, which are also ingredients of an Ulster fry.

Stovies is a Scottish dish based on potatoes. Recipes and ingredients vary widely but the dish contains potatoes, fat, usually onions and often pieces of meat. In some versions, other vegetables may be added.

"I that in Heill wes and Gladnes", also known as "The Lament for the Makaris", is a poem in the form of a danse macabre by the Scottish poet William Dunbar. Every fourth line repeats the Latin refrain timor mortis conturbat me, a litanic phrase from the Office of the Dead.

East Craigs is a residential district of Edinburgh located in the north-west of the city, on the western flanks of Corstorphine Hill. It lies next to what remains of the green belt, and prior to development was a working farm.

Adam Jack Aitken was a Scottish lexicographer and leading scholar of the Scots language.
Penge Common was an area of north east Surrey and north west Kent which now forms part of London, England; covering most of Penge, all of Anerley, and parts of surrounding suburbs including South Norwood. It abutted the Great North Wood and John Rocque's 1745 map of London and its environs showed that Penge Common now included part of that wood.
Central Scots is a group of dialects of Scots.
Southern Scots is the dialect of Scots spoken in the Scottish Borders counties of mid and east Dumfriesshire, Roxburghshire and Selkirkshire, with the notable exception of Berwickshire and Peeblesshire, which are, like Edinburgh, part of the SE Central Scots dialect area. It may also be known as Border Scots, the Border tongue or by the names of the towns inside the South Scots area, for example Teri in Hawick from the phrase Teribus ye teri odin. Towns where Southern Scots dialects are spoken include Earlston, Galashiels, Hawick, Jedburgh, Kelso, Langholm, Lockerbie, Newcastleton, St. Boswells and Selkirk.

Bere, pronounced "bear," is a six-row barley cultivated mainly on 5-15 hectares of land in Orkney, Scotland. It is also grown in Shetland, Caithness and on a very small scale by a few crofters on some of the Western Isles, such as North Uist, Benbecula, South Uist, Islay and Barra. It is probably Britain's oldest cereal in continuous commercial cultivation.

The University of Aberdeen School of Law is the law school of University of Aberdeen, located in Aberdeen, Scotland. Established in 1495, it is consistently ranked among the top 10 law schools in the United Kingdom.

Ben Cleuch is a hill in the Ochil Hills range, part of the Central Lowlands of Scotland. It is the highest point in the range, Clackmannanshire and the Central Belt of Scotland; the summit is marked by a trig point within a stone windshelter and a viewpoint indicator.

The Howff is a burial ground in the city of Dundee, Scotland. Established in 1564, it has one of the most important collections of tombstones in Scotland, and is protected as a category A listed building.

Cauldcleuch Head is a hill in an unnamed range of Roxburghshire hills north of Langholm, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. The highest hill in this range, it has an isolation of approximately 26 km. Parts of the Gorrenberry Jubilee Wood can be found in the Billhope glen to its southwest, where the easiest line of ascent is found.
The Riggin o Fife is an upland area of Fife, Scotland which runs eastward from the Markinch Gap and the Howe of Fife to form the elevated hinterland to the coastal villages of the East Neuk. At 290 m, Largo Law is the highest hill, with other high points including Clatto Hill, Drumcarrow Craig, Flagstaff Hill, Kellie Law and Hill of Tarvit. The area is rural, populated by farms and hamlets, with a few small villages, such as Largoward and Peat Inn.
The tattie holidays are a school holiday in Scotland typically falling around October. The holiday started in the 1930s, when children would be taken out of school to help with the local potato harvest, with other children just not turning up for class. The tradition continued into the 1980s, when the advent of new farm machinery such as potato harvesters made hand picking potatoes obsolete. The word "tattie" comes from the Scots word for potato.















