In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder.
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification, storage, and communication of information. The field was established and put on a firm footing by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering.

In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means that the logarithm of a number x to the base b is the exponent to which b must be raised to produce x. For example, since 1000 = 103, the logarithm base of 1000 is 3, or log10 (1000) = 3. The logarithm of x to base b is denoted as logb (x), or without parentheses, logb x. When the base is clear from the context or is irrelevant it is sometimes written log x.
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistical redundancy. By contrast, lossy compression permits reconstruction only of an approximation of the original data, though usually with greatly improved compression rates.

Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)—unofficially, the initials PNG stood for the recursive acronym "PNG's not GIF".
PCX, standing for PiCture eXchange, is an image file format developed by the now-defunct ZSoft Corporation of Marietta, Georgia, United States. It was the native file format for PC Paintbrush and became one of the first widely accepted DOS imaging standards, although it has since been succeeded by more sophisticated image formats, such as BMP, JPEG, and PNG. PCX files commonly store palette-indexed images ranging from 2 or 4 colors to 16 and 256 colors, although the format has been extended to record true-color (24-bit) images as well.

Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior results compared with generic data compression methods which are used for other digital data.
Golomb coding is a lossless data compression method using a family of data compression codes invented by Solomon W. Golomb in the 1960s. Alphabets following a geometric distribution will have a Golomb code as an optimal prefix code, making Golomb coding highly suitable for situations in which the occurrence of small values in the input stream is significantly more likely than large values.
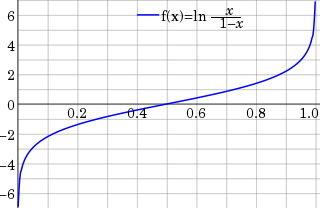
In statistics, the logit function is the quantile function associated with the standard logistic distribution. It has many uses in data analysis and machine learning, especially in data transformations.
OpenEXR is a high-dynamic range, multi-channel raster file format, released as an open standard along with a set of software tools created by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM), under a free software license similar to the BSD license.
WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format and application implementing the format. It is unique in the way that it supports hybrid audio compression alongside normal compression which is similar to how FLAC works. It also supports compressing a wide variety of lossless formats, including various variants of PCM and also DSD as used in SACDs, together with its support for surround audio.
In information theory, redundancy measures the fractional difference between the entropy H(X) of an ensemble X, and its maximum possible value . Informally, it is the amount of wasted "space" used to transmit certain data. Data compression is a way to reduce or eliminate unwanted redundancy, while forward error correction is a way of adding desired redundancy for purposes of error detection and correction when communicating over a noisy channel of limited capacity.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
Lossless JPEG is a 1993 addition to JPEG standard by the Joint Photographic Experts Group to enable lossless compression. However, the term may also be used to refer to all lossless compression schemes developed by the group, including JPEG 2000, JPEG-LS, and JPEG XL.

A Phred quality score is a measure of the quality of the identification of the nucleobases generated by automated DNA sequencing. It was originally developed for the computer program Phred to help in the automation of DNA sequencing in the Human Genome Project. Phred quality scores are assigned to each nucleotide base call in automated sequencer traces. The FASTQ format encodes phred scores as ASCII characters alongside the read sequences. Phred quality scores have become widely accepted to characterize the quality of DNA sequences, and can be used to compare the efficacy of different sequencing methods. Perhaps the most important use of Phred quality scores is the automatic determination of accurate, quality-based consensus sequences.
FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a biological sequence and its corresponding quality scores. Both the sequence letter and quality score are each encoded with a single ASCII character for brevity.

Silicon Valley is an American comedy television series created by Mike Judge, John Altschuler and Dave Krinsky. It premiered on HBO on April 6, 2014, and concluded on December 8, 2019, running for six seasons for a total of 53 episodes. Parodying the culture of the technology industry in Silicon Valley, the series focuses on Richard Hendricks, a programmer who founds a startup company called Pied Piper, and chronicles his struggles to maintain his company while facing competition from larger entities. Co-stars include T.J. Miller, Josh Brener, Martin Starr, Kumail Nanjiani, Zach Woods, Amanda Crew, Matt Ross, and Jimmy O. Yang.

An audio coding format is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital audio. Examples of audio coding formats include MP3, AAC, Vorbis, FLAC, and Opus. A specific software or hardware implementation capable of audio compression and decompression to/from a specific audio coding format is called an audio codec; an example of an audio codec is LAME, which is one of several different codecs which implements encoding and decoding audio in the MP3 audio coding format in software.
Tsachy (Itschak) Weissman is a professor of Electrical Engineering at Stanford University. He is the founding director of the Stanford Compression Forum. His research interests include information theory, statistical signal processing, their applications, with recent emphasis on biological applications, in genomics in particular, lossless compression, lossy compression, delay-constrained and complexity-constrained compression and communication, network information theory, feedback communications, directed information, the interplay between estimation theory and information theory, entropy, noise reduction (denoising), filtering, prediction, sequential decision making, learning, and connections with probability, statistics, and computer science.






