
West Nile sub-region, previously known as West Nile Province and West Nile District, is a sub-region in north-western Uganda, in the Northern Region of Uganda.

Burning of renewable resources provides approximately 90 percent of the energy in Uganda, though the government is attempting to become energy self-sufficient. While much of the hydroelectric potential of the country is untapped, the government decision to expedite the creation of domestic petroleum capacity coupled with the discovery of large petroleum reserves holds the promise of a significant change in Uganda's status as an energy-importing country.

Aga Khan Fund for Economic Development SA is a Swiss for-profit entity and international development finance institution which invests in countries of East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. It is based in Geneva, Switzerland.
Industrial Promotion Services(IPS) is the industrial development arm of the Aga Khan Fund for Economic Development (AKFED). AKFED is a member of the Aga Khan Development Network.

The Bujagali Power Station is a hydroelectric power station across the Victoria Nile that harnesses the energy of its namesake; the Bujagali Falls, in Uganda. Construction began in 2007 and concluded in 2012. It was officially inaugurated on 8 October 2012 by Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni and Aga Khan IV in the presence of African politicians and investors.
Nyagak Power Station is a 3.5 megawatts (4,700 hp) mini hydroelectric power plant in Uganda.
Bondo is a town in Uganda.
Paidha is a town in the Northern Region of Uganda.
Tororo Thermal Power Station is a 89 MW (119,000 hp) heavy fuel oil-fired thermal power plant located in the town of Tororo in Tororo District in the Eastern Region of Uganda.
The Muzizi Power Station is a proposed 45 megawatts (60,000 hp) hydroelectric power project in Uganda. The project, which has been planned for several years, has received a funding commitment from KfW and the French Development Agency.
Ayago Hydroelectric Power Station, also Ayago Power Station, is a planned 840 megawatt hydroelectric power project to be constructed in Uganda. If it is built, Ayago would be the largest power station in Uganda, based on generating capacity.
Energy in Sudan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and imports in Sudan. The chief sources of energy in 2010 were wood and charcoal, hydroelectric power, and oil. Sudan is a net energy exporter. Primary energy use in Sudan was 179 TWh and 4 TWh per million persons in 2008.
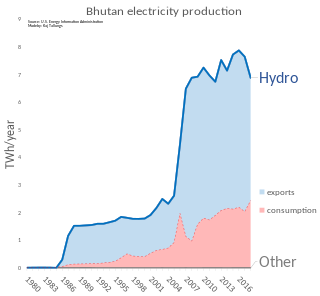
Energy in Bhutan has been a primary focus of development in the kingdom under its Five-Year Plans. In cooperation with India, Bhutan has undertaken several hydroelectric projects whose output is traded between the countries. Though Bhutan's many hydroelectric plants provide energy far in excess of its needs in the summer, dry winters and increased fuel demand makes the kingdom a marginal net importer of energy from India.
Nyagak III Power Station is a 6.6 megawatts (8,900 hp) mini hydroelectric power project, under construction in Uganda, the third-largest economy in the East African Community.
Nyagak II Power Station is a 5 megawatts (6,700 hp) proposed mini hydroelectric power project in Uganda.
Muvumbe Hydroelectric Power Station is a 6.5 megawatts (8,700 hp) hydroelectric power station in the Western Region of Uganda.
Bujagali Energy Limited (BEL), is an electric energy generating company in Uganda. The company owns and operates the Bujagali Power Station, which was the largest hydropower plant in the country as of July 2014.
The Lira–Gulu–Nebbi–Arua High Voltage Power Line is a high voltage electricity power line, under construction in Uganda. It connects the high voltage substation at Lira, in Lira District, to another high voltage substation at Arua, in Arua District, all in the Northern Region of the country.
Nyapea, is a town in Zombo District, West Nile sub-region, in the Northern Region of Uganda.




