
The Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome located primarily in Central Africa. It includes four woodland savanna ecoregions characterized by the dominant presence of Brachystegia and Julbernardia species of trees, and has a range of climates ranging from humid to semi-arid, and tropical to subtropical or even temperate. The trees characteristically shed their leaves for a short period in the dry season to reduce water loss and produce a flush of new leaves just before the onset of the wet season with rich gold and red colours masking the underlying chlorophyll, reminiscent of autumn colours in the temperate zone.
Lukulu is a market town in the Western Province of Zambia, on the Zambezi River, and headquarters of a district of the same name. Access to the town is limited to only a few graded roads with traffic running through it from Kaoma town to Watopa town. Fish from the river provide most of the local diet, and some are exported to other parts of Zambia away from the river. The town has very beautiful Zambezi River water front and sandy beaches.

Mongu is the capital of Western Province in Zambia and was the capital of the formerly-named province and historic state of Barotseland. Its population is 179,585, and it is also the headquarters of Mongu District. Mongu is the home of the Litunga, King of the Lozi people.

Sioma Ngwezi National Park is a 5,000-square-kilometre park in the south west corner of Zambia. It is undeveloped and rarely visited, lacking roads and being off the usual tourist tracks, but this may change in the future.

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater ecoregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Zambezian region of the Afrotropical biogeographic realm. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.

The Barotse Floodplain, also known as the Bulozi Plain, Lyondo or the Zambezi Floodplain, is one of Africa's great wetlands, on the Zambezi River in the Western Province of Zambia. It is a designated Ramsar site, regarded as being of high conservation value.

The South Malawi montane forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion of Malawi.

Angolan miombo woodlands cover most of central Angola and extend into the Democratic Republic of Congo. They are part of the larger miombo ecosystem that covers much of eastern and southern Africa.

The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands ecoregion spans southern central Africa. Miombo woodland is the predominant plant community. It is one of the largest ecoregions on the continent, and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals.
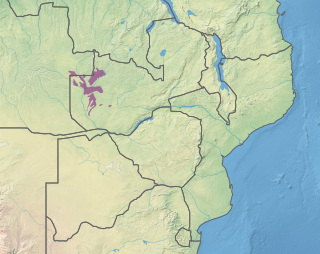
The Zambezian dry evergreen forest, also known as the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.

The Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.

The Itigi-Sumbu thicket is an ecoregion consisting of two small areas of thick shrubland in Tanzania, Zambia and the adjacent Democratic Republic of the Congo, in East Africa. The floral community of dense deciduous brush is unique, with many endemic species, and almost no transition zone between it and the surrounding dry miombo woodlands. The distinctive nature of this small region is partly due to its setting on dry alluvial soil over a hard duricrust, while the surrounding areas are rocky hills and plateaus.

The southern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is an ecoregion that covers a large area of the southern Democratic Republic of the Congo and northeastern Angola. Its rich blend of habitats provides key insights into the biogeography of central Africa with the extensive climatic variation that it has been experiencing for the last 10 million years. The human population is not high.
The Cheringoma Plateau is a low plateau in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It lies mostly within Cheringoma, Muanza, and Marromeu districts.

The East European forest steppe ecoregion is a patchwork of broadleaf forest stands and grasslands (steppe) that stretches 2,100 km across eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains in Ural, through Povolzhye, Central Russia to the middle of Ukraine. There are isolated areas of similar character off the western end in eastern Romania, Moldova, and Bulgaria.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
The Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.

The Baluchistan xeric woodlands ecoregion covers the middle elevations of a series of mountain ranges of western Pakistan and northeastern Afghanistan, reaching 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) from the Arabian Sea in the south to the Hindu Kush Mountains and the Himalayas in the north. The characteristic vegetation is xeric (dry) woodlands of shrubs and herbaceous cover. The region has rich biodiversity but relatively few endemic species.

















