Related Research Articles

Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer science and engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers.

Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary field of science that focuses on living systems and organisms, and it applies engineering principles to develop new biological parts, devices, and systems or to redesign existing systems found in nature.
E-Science or eScience is computationally intensive science that is carried out in highly distributed network environments, or science that uses immense data sets that require grid computing; the term sometimes includes technologies that enable distributed collaboration, such as the Access Grid. The term was created by John Taylor, the Director General of the United Kingdom's Office of Science and Technology in 1999 and was used to describe a large funding initiative starting in November 2000. E-science has been more broadly interpreted since then, as "the application of computer technology to the undertaking of modern scientific investigation, including the preparation, experimentation, data collection, results dissemination, and long-term storage and accessibility of all materials generated through the scientific process. These may include data modeling and analysis, electronic/digitized laboratory notebooks, raw and fitted data sets, manuscript production and draft versions, pre-prints, and print and/or electronic publications." In 2014, IEEE eScience Conference Series condensed the definition to "eScience promotes innovation in collaborative, computationally- or data-intensive research across all disciplines, throughout the research lifecycle" in one of the working definitions used by the organizers. E-science encompasses "what is often referred to as big data [which] has revolutionized science... [such as] the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN... [that] generates around 780 terabytes per year... highly data intensive modern fields of science...that generate large amounts of E-science data include: computational biology, bioinformatics, genomics" and the human digital footprint for the social sciences.
Modelling biological systems is a significant task of systems biology and mathematical biology. Computational systems biology aims to develop and use efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization and communication tools with the goal of computer modelling of biological systems. It involves the use of computer simulations of biological systems, including cellular subsystems, to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes.
The Gene Ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and gene product attributes; 2) annotate genes and gene products, and assimilate and disseminate annotation data; and 3) provide tools for easy access to all aspects of the data provided by the project, and to enable functional interpretation of experimental data using the GO, for example via enrichment analysis. GO is part of a larger classification effort, the Open Biomedical Ontologies, being one of the Initial Candidate Members of the OBO Foundry.
United States federal research funders use the term cyberinfrastructure to describe research environments that support advanced data acquisition, data storage, data management, data integration, data mining, data visualization and other computing and information processing services distributed over the Internet beyond the scope of a single institution. In scientific usage, cyberinfrastructure is a technological and sociological solution to the problem of efficiently connecting laboratories, data, computers, and people with the goal of enabling derivation of novel scientific theories and knowledge.

Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blanket terms for various related technologies.
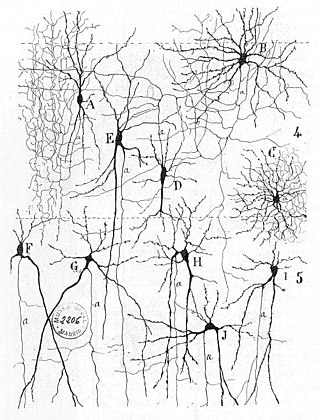
A wetware computer is an organic computer composed of organic material "wetware" such as "living" neurons. Wetware computers composed of neurons are different than conventional computers because they use biological materials, and offer the possibility of substantially more energy-efficient computing. While a wetware computer is still largely conceptual, there has been limited success with construction and prototyping, which has acted as a proof of the concept's realistic application to computing in the future. The most notable prototypes have stemmed from the research completed by biological engineer William Ditto during his time at the Georgia Institute of Technology. His work constructing a simple neurocomputer capable of basic addition from leech neurons in 1999 was a significant discovery for the concept. This research was a primary example driving interest in creating these artificially constructed, but still organic brains.
Rahul Sarpeshkar is the Thomas E. Kurtz Professor and a professor of engineering, professor of physics, professor of microbiology & immunology, and professor of molecular and systems biology at Dartmouth. Sarpeshkar, whose interdisciplinary work is in bioengineering, electrical engineering, quantum physics, and biophysics, is the inaugural chair of the William H. Neukom cluster of computational science, which focuses on analog, quantum, and biological computation. The clusters, designed by faculty from across the institution to address major global challenges, are part of President Philip Hanlon's vision for strengthening academic excellence at Dartmouth. Prior to Dartmouth, Sarpeshkar was a tenured professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and led the Analog Circuits and Biological Systems Group. He is now also a visiting scientist at MIT's Research Laboratory of Electronics.
An artificial cell, synthetic cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, liposomes, polymersomes, nanoparticles, microcapsules and a number of other particles can qualify as artificial cells.

Paul M. Rabinow was a professor of anthropology at the University of California (Berkeley), director of the Anthropology of the Contemporary Research Collaboratory (ARC), and former director of human practices for the Synthetic Biology Engineering Research Center (SynBERC). He worked with, and wrote extensively about, the French philosopher Michel Foucault.
The Alan T. Waterman Award, named after Alan Tower Waterman, is the United States's highest honorary award for scientists no older than 40, or no more than 10 years past receipt of their Ph.D. It is awarded on a yearly basis by the National Science Foundation. In addition to the medal, the awardee receives a grant of $1,000,000 to be used at the institution of their choice over a period of five years for advanced scientific research.
Biological computers use biologically derived molecules — such as DNA and/or proteins — to perform digital or real computations.

BioBrick parts are DNA sequences which conform to a restriction-enzyme assembly standard. These building blocks are used to design and assemble larger synthetic biological circuits from individual parts and combinations of parts with defined functions, which would then be incorporated into living cells such as Escherichia coli cells to construct new biological systems. Examples of BioBrick parts include promoters, ribosomal binding sites (RBS), coding sequences and terminators.

Do-it-yourself biology is a biotechnological social movement in which individuals, communities, and small organizations study biology and life science using the same methods as traditional research institutions. DIY biology is primarily undertaken by individuals with limited research training from academia or corporations, who then mentor and oversee other DIY biologists with little or no formal training. This may be done as a hobby, as a not-for-profit endeavor for community learning and open-science innovation, or for profit, to start a business.
Agrobiology is defined by Merriam-Webster as a field that studies how plant or crop nutrition, growth, and yield or production relate to soil management (Merriam-Webster). Agrobiology is an interdisciplinary field of study that provides a comprehensive understanding of the complex relationships between crops, soils, and the environment. Agrobiology consists of several science-based disciplines including, plant biology and nutrition, agronomy, ecology, genetics, molecular biology, and soil science. Prominent topics that involve agrobiology practices include the following but are not limited to, the role of soil microbiota in both conventional and sustainable agriculture systems, the effects of integrating livestock in sustainable agriculture systems, and the use of biotechnology and its relationship to agrobiology.

Artificial life is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American theoretical biologist, in 1986. In 1987, Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: soft, from software; hard, from hardware; and wet, from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena.
The concept of biological computation proposes that living organisms perform computations, and that as such, abstract ideas of information and computation may be key to understanding biology. As a field, biological computation can include the study of the systems biology computations performed by biota the design of algorithms inspired by the computational methods of biota, the design and engineering of manufactured computational devices using synthetic biology components and computer methods for the analysis of biological data, elsewhere called computational biology or bioinformatics.
ATUM is an American biotechnology company. ATUM provides tools for the design and synthesis of optimized DNA, as well as protein production and GMP cell line development.
Karmella Ann Haynes is a biomedical engineer and associate professor at the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University. She researches how chromatin is used to control cell development in biological tissue.