Related Research Articles
Boyden Observatory is an astronomical research observatory and science education centre located in Maselspoort, 20 kilometres (12 mi) north-east of the city of Bloemfontein in Free State, South Africa. The observatory is managed by the Physics Department of the University of the Free State (UFS). The Friends of Boyden assist the observatory as a public support group, organising open evenings and protecting its public interest. Boyden also makes use of members of ASSA Bloemfontein Centre, the amateur astronomy club of the city, for presenters and telescope assistants.

The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an astronomical observatory located on the summit of Mt. Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Mt. Cerro Pachón about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) to the southeast. It is approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) east of La Serena, where support facilities are located. The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel Blanco, and the 4.1 m Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, which is situated on Cerro Pachón. Other telescopes on Cerro Tololo include the 1.5 m, 1.3 m, 1.0 m, and 0.9 m telescopes operated by the SMARTS consortium. CTIO also hosts other research projects, such as PROMPT, WHAM, and LCOGTN, providing a platform for access to the southern hemisphere for U.S. and worldwide scientific research.

A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.

Space Place at Carter Observatory is an observatory in Wellington, New Zealand, located at the top of the Wellington Botanic Garden.
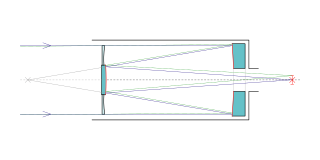
The Schmidt–Cassegrain is a catadioptric telescope that combines a Cassegrain reflector's optical path with a Schmidt corrector plate to make a compact astronomical instrument that uses simple spherical surfaces.

The Orange County Astronomers (OCA) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit, civilian-led astronomy organization in Orange County, southern California. It was formed in 1967 and currently operates with around 800 concurrent members; they offer beginner courses in astronomy, and have meetings on the second Friday of every month at Chapman University. Currently, the OCA offers a dark-sky site to viewers, which includes a 22-inch Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope and public-use observation areas. In addition, the OCA has been registered as an affiliate of the Astronomers Without Borders program since March of 2012.

The Royal Observatory, Edinburgh (ROE) is an astronomical institution located on Blackford Hill in Edinburgh. The site is owned by the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC). The ROE comprises the UK Astronomy Technology Centre (UK ATC) of STFC, the Institute for Astronomy of the School of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Edinburgh, and the ROE Visitor Centre.

Bowman Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Greenwich, Connecticut Board of Education.
Naylor Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Astronomical Society of Harrisburg. It is located near Lewisberry, Pennsylvania, United States.
The William G. and Retha Stone Baker Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Missouri State University. It is located in Marshfield, Missouri.

The Hamilton Astronomical Society Observatory is located next to the Hamilton Zoo in Brymer Road to the west of Hamilton City, New Zealand. The Hamilton Astronomical Society was founded on 3 July 1933 and is one of New Zealand's oldest astronomical societies.
R. F. Joyce Observatory is the home observatory of the Canterbury Astronomical Society (CAS) and is situated near West Melton, Christchurch, New Zealand.

The Hirsch Observatory is an astronomical observatory at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, New York. It is located on the roof of the Jonsson-Rowland Science Center and is used by members of the Rensselaer Astrophysical Society as well as astronomy students in laboratory exercises. It is frequently opened to the community for public viewing sessions. The observatory's main dome contains a 16" Cassegrain Reflector, with a CCD camera and fully computerized controls. The observatory also owns a variety of smaller scopes and a SBIG Spectrograph. The spectrograph has been used to catalog bright solar spectrum as part of an effort to create an online digital database for astrophysical research. The current director of the observatory is Professor Heidi Newberg.

The Givatayim Observatory is a public observatory that was founded in 1968 by the Israeli Astronomical Association and the Givatayim municipality.

The Heights Observatory is an Astronomical Observatory at The Heights School in Modbury Heights, Adelaide, South Australia.

Table Mountain Observatory (TMO) is an astronomical observation facility operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It is located in Big Pines, California, in the Angeles National Forest near Wrightwood, north-northeast of Los Angeles, California.

The Southland Astronomical Society is the southernmost astronomical society in the world. Based in Invercargill at the southern tip of New Zealand's South Island, its small, active group of about 36 amateur astronomer members participate in a variety of astronomical activities including education with groups and school children, deep sky observing, astrophotography and aurora observation.
Mount Burnett Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Mount Burnett, Victoria, Australia.

The Eileen M. Collins Observatory is a small astronomical observatory operated by Corning Community College in Corning, New York, United States. It is named for astronaut Eileen Collins. The observatory is primarily used to teach astronomy classes, but the college also provides monthly viewing sessions for the public.

Bayfordbury Observatory is the University of Hertfordshire's astronomical and atmospheric physics remote sensing observatory, and one of the largest teaching observatories in the UK. It is located in the relatively dark countryside of Bayfordbury, Hertfordshire, 6 miles from the main university campus in Hatfield. The first telescope was built in 1969, and since then has been used as a teaching observatory for undergraduate students, staff and student research as well as for public outreach activities.
References
- ↑ Whakatane Astronomical Society. "Sky of Plenty" . Retrieved 2010-03-09.
- ↑ Royal Astronomical Society of New Zealand. "Affiliated Societies" . Retrieved 2010-03-09.