Related Research Articles

Francis Harry Compton Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule.
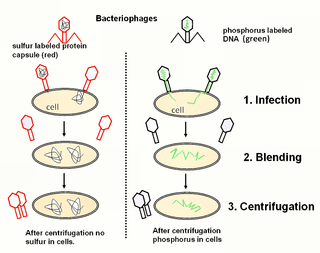
The Hershey–Chase experiments were a series of experiments conducted in 1952 by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase that helped to confirm that DNA is genetic material.

James Dewey Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material".
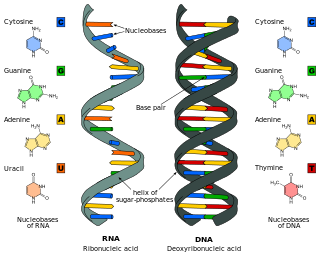
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA.
The central dogma of molecular biology deals with the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It is often stated as "DNA makes RNA, and RNA makes protein", although this is not its original meaning. It was first stated by Francis Crick in 1957, then published in 1958:
The Central Dogma. This states that once "information" has passed into protein it cannot get out again. In more detail, the transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid is impossible. Information here means the precise determination of sequence, either of bases in the nucleic acid or of amino acid residues in the protein.

Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins was a New Zealand-born British biophysicist and Nobel laureate whose research spanned multiple areas of physics and biophysics, contributing to the scientific understanding of phosphorescence, isotope separation, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction. He is known for his work at King's College London on the structure of DNA.

Sydney Brenner was a South African biologist. In 2002, he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with H. Robert Horvitz and Sir John E. Sulston. Brenner made significant contributions to work on the genetic code, and other areas of molecular biology while working in the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England. He established the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans as a model organism for the investigation of developmental biology, and founded the Molecular Sciences Institute in Berkeley, California, United States.

The Astonishing Hypothesis is a 1994 book by scientist Francis Crick about consciousness. Crick, one of the co-discoverers of the molecular structure of DNA, later became a theorist for neurobiology and the study of the brain. The Astonishing Hypothesis is mostly concerned with establishing a basis for scientific study of consciousness; however, Crick places the study of consciousness within a larger social context. Human consciousness according to Crick is central to human existence and so scientists find themselves approaching topics traditionally left to philosophy and religion.

The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA is an autobiographical account of the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA written by James D. Watson and published in 1968. It has earned both critical and public praise, along with continuing controversy about credit for the Nobel award and attitudes towards female scientists at the time of the discovery.

Life Story is a 1987 television historical drama which depicts the progress toward, and the competition for, the discovery of the structure of DNA in the early 1950s. It was directed by Mick Jackson for the BBC's Horizon science series, and stars Jeff Goldblum, Tim Pigott-Smith, Juliet Stevenson, and Alan Howard. It won several awards in the UK and U.S., including the 1988 BAFTA TV Award for Best Single Drama.

"Molecular Structure of Nucleic Acids: A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid" was the first article published to describe the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA, using X-ray diffraction and the mathematics of a helix transform. It was published by Francis Crick and James D. Watson in the scientific journal Nature on pages 737–738 of its 171st volume.
Alexander Rawson Stokes was a British physicist at Royal Holloway College, London and later at King's College London. He was most recognised as a co-author of the second of the three papers published sequentially in Nature on 25 April 1953 describing the correct molecular structure of DNA. The first was authored by Francis Crick and James Watson, and the third by Rosalind Franklin and Raymond Gosling.
The history of molecular biology begins in the 1930s with the convergence of various, previously distinct biological and physical disciplines: biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, virology and physics. With the hope of understanding life at its most fundamental level, numerous physicists and chemists also took an interest in what would become molecular biology.

The adaptor hypothesis is a theoretical scheme in molecular biology to explain how information encoded in the nucleic acid sequences of messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to specify the amino acids that make up proteins during the process of translation. It was formulated by Francis Crick in 1955 in an informal publication of the RNA Tie Club, and later elaborated in 1957 along with the central dogma of molecular biology and the sequence hypothesis. It was formally published as an article "On protein synthesis" in 1958. The name "adaptor hypothesis" was given by Sydney Brenner.
Odile Crick was a British artist best known for her drawing of the double helix structure of DNA discovered by her husband Francis Crick and his partner James D. Watson in 1953.
Leslie Barnett was a British biologist who worked with Francis Crick, Sydney Brenner, and Richard J. Watts-Tobin to genetically demonstrate the triplet nature of the code of protein translation through the Crick, Brenner, Barnett, Watts-Tobin et al. experiment of 1961, which discovered frameshift mutations; this insight provided early elucidation of the nature of the genetic code.
The RNA Tie Club was an informal scientific club, meant partly to be humorous, of select scientists who were interested in how proteins were synthesised from genes, specifically the genetic code. It was created by George Gamow upon a suggestion by James Watson in 1954 when the relationship between nucleic acids and amino acids in genetic information was unknown. The club consisted of 20 full members, each representing an amino acid, and four honorary members, representing the four nucleotides. The function of the club members was to think up possible solutions and share with the other members.
Natural genetic engineering (NGE) is a class of process proposed by molecular biologist James A. Shapiro to account for novelty created in the course of biological evolution. Shapiro developed this work in several peer-reviewed publications from 1992 onwards, and later in his 2011 book Evolution: A View from the 21st Century, which has been updated with a second edition in 2022. He uses NGE to account for several proposed counterexamples to the central dogma of molecular biology. Shapiro drew from work as diverse as the adaptivity of the mammalian immune system, ciliate macronuclei and epigenetics. The work gained some measure of notoriety after being championed by proponents of Intelligent Design, despite Shapiro's explicit repudiation of that movement.
Martynas Yčas was an American microbiologist of Lithuanian descent. He co-authored the book Mr. Tompkins: Inside Himself with physicist George Gamow.

Rosalind Franklin and DNA is a biography of an English chemist Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958) written by her American friend Anne Sayre in 1975. Franklin was a physical chemist who made pivotal research in the discovery of the structure of DNA, known as "the most important discovery" in biology. DNA itself had become "life's most famous molecule". While working at the King's College London in 1951, she discovered two types of DNA called A-DNA and B-DNA. Her X-ray images of DNA indicated helical structure. Her X-ray image of B-DNA taken in 1952 became the best evidence for the structure of DNA. For the discovery of the correct chemical structure of DNA, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1962 was shared by her colleagues and close researchers James Watson, Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins; she had died four years earlier in 1958 making her ineligible for the award.
References
- ↑ Crick, Francis (1988). What Mad Pursuit: A Personal View of Scientific Discovery . New York: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-09137-7.
- ↑ Anderson PW (Feb 1990). "Some thoughtful words (not mine) on research strategy for theorists". Physics Today . 43 (2): 9. doi:10.1063/1.2810433.
- ↑ Nanjundiah, Vidyanand (Dec 1989). "What Mad Pursuit: BOOK REVIEW" (PDF). J. Genet. 68 (3): 197–200. doi:10.1007/bf02927862.