Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when standing up or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. The drop in blood pressure may be sudden, within 3 minutes or gradual. It is defined as a fall in systolic blood pressure of at least 20 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of at least 10 mmHg after 3 minutes of standing. It occurs predominantly by delayed constriction of the lower body blood vessels, which is normally required to maintain adequate blood pressure when changing the position to standing. As a result, blood pools in the blood vessels of the legs for a longer period, and less is returned to the heart, thereby leading to a reduced cardiac output and inadequate blood flow to the brain.

The effects of cannabis are caused by chemical compounds in the cannabis plant, including 113 different cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and 120 terpenes, which allow its drug to have various psychological and physiological effects on the human body. Different plants of the genus Cannabis contain different and often unpredictable concentrations of THC and other cannabinoids and hundreds of other molecules that have a pharmacological effect, so the final net effect cannot reliably be foreseen.
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have many possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs.
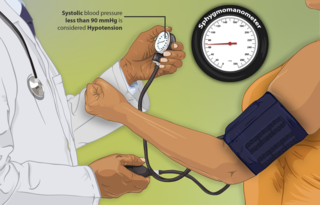
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure and the diastolic blood pressure, which are the maximum and minimum blood pressures within the cardiac cycle, respectively. A systolic blood pressure of less than 90 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or diastolic of less than 60 mmHg is generally considered to be hypotension. Different numbers apply to children. However, in practice, blood pressure is considered too low only if noticeable symptoms are present.

Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.

Reflex syncope is a brief loss of consciousness due to a neurologically induced drop in blood pressure and/or a decrease in heart rate. Before an affected person passes out, there may be sweating, a decreased ability to see, or ringing in the ears. Occasionally, the person may twitch while unconscious. Complications of reflex syncope include injury due to a fall.
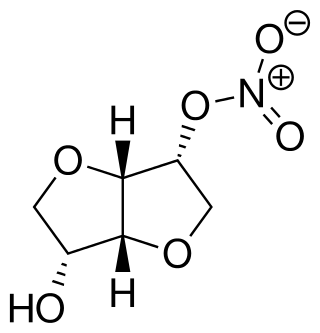
Isosorbide mononitrate, sold under many brand names, is a medication used for heart-related chest pain (angina), heart failure and esophageal spasms. It can be used both to treat and to prevent heart-related chest pain; however, it is generally less preferred than beta blockers or calcium channel blockers. It is taken by mouth.

Familial dysautonomia (FD), also known as Riley-Day syndrome, is a rare, progressive, recessive genetic disorder of the autonomic nervous system that affects the development and survival of sensory, sympathetic, and some parasympathetic neurons in the autonomic and sensory nervous system.
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may feel as though their head is weightless. The individual may also feel as though the room is "spinning" or moving (vertigo). Most causes of lightheadedness are not serious and either cure themselves quickly or are easily treated.

A tilt table test (TTT), occasionally called upright tilt testing (UTT), is a medical procedure often used to diagnose dysautonomia or syncope. Patients with symptoms of dizziness or lightheadedness, with or without a loss of consciousness (fainting), suspected to be associated with a drop in blood pressure or positional tachycardia are good candidates for this test.

Cannabis smoking is the inhalation of smoke or vapor released by heating the flowers, leaves, or extracts of cannabis and releasing the main psychoactive chemical, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is absorbed into the bloodstream via the lungs. Archaeological evidence indicates cannabis with high levels of THC was being smoked at least 2,500 years ago. As of 2021, cannabis is the most commonly consumed federally illegal drug in the United States, with 36.4 million people consuming it monthly.

Isradipine is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine class. It is usually prescribed for the treatment of high blood pressure in order to reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack.

Vomiting is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.

Dimethylheptylpyran is a synthetic analog of THC, which was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of Cannabis. DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents.

Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.

A nitrovasodilator is a pharmaceutical agent that causes vasodilation by donation of nitric oxide (NO), and is mostly used for the treatment and prevention of angina pectoris.

Syncope, commonly known as fainting or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event, usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presyncope. It is recommended that presyncope be treated the same as syncope.

Dopamine beta (β)-hydroxylase deficiency is a human medical condition involving inadequate dopamine beta-hydroxylase. It is characterized by increased amounts of serum dopamine and the absence of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine.
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) is recurrent nausea, vomiting, and cramping abdominal pain that can occur due to prolonged, high-dose cannabis use. These symptoms may be relieved temporarily by taking a hot shower or bath. Complications are related to persistent vomiting and dehydration which may lead to kidney failure and electrolyte problems.
Orthostatic syncope refers to syncope resulting from a postural decrease in blood pressure, termed orthostatic hypotension.














