
A turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a combination of the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet, and a reference to the additional fan stage added. It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust.

The Rolls-Royce RB211 is a British family of high-bypass turbofan engines made by Rolls-Royce. The engines are capable of generating 41,030 to 59,450 lbf of thrust. The RB211 engine was the first production three-spool engine and turned Rolls-Royce from a significant player in the aero-engine industry into a global leader.

The Rolls-Royce Trent is a family of high-bypass turbofans produced by Rolls-Royce. It continues the three spool architecture of the RB211 with a maximum thrust ranging from 61,900 to 97,000 lbf . Launched as the RB-211-524L in June 1988, the prototype first ran in August 1990. Its first variant is the Trent 700 introduced on the Airbus A330 in March 1995, then the Trent 800 for the Boeing 777 (1996), the Trent 500 for the A340 (2002), the Trent 900 for the A380 (2007), the Trent 1000 for the Boeing 787 (2011), the Trent XWB for the A350 (2015), and the Trent 7000 for the A330neo (2018). It has also marine and industrial variants like the RR MT30.

The Engine Alliance GP7000 is a turbofan jet engine manufactured by Engine Alliance, a joint venture between General Electric and Pratt & Whitney. It is one of the powerplant options available for the Airbus A380, along with the Rolls-Royce Trent 900.

The Rolls-Royce BR700 is a family of turbofan engines for regional jets and corporate jets. It is manufactured in Dahlewitz, Germany, by Rolls-Royce Deutschland: this was initially a joint venture of BMW and Rolls-Royce plc established in 1990 to develop this engine. The BR710 first ran in 1995. The United States military designation for the BR725 variant is F130.

The Rolls-Royce RB.183 Tay is a medium-bypass turbofan engine, developed from the RB.183 Mk 555 Spey core and using a fan scaled directly from the Rolls-Royce RB.211-535E4 to produce versions with a bypass ratio of 3.1:1 or greater. The IP compressor and LP turbine were designed using technology from the RB.211 programme. The engine was first run in August 1984. The Tay 650 had a new HP turbine which incorporated new technology which had been proven with the RB.211-535E4. This engine also had a new combustor for improved durability. The Tay family is used on a number of airliners and larger business jets, including the Gulfstream IV family, Fokker 70 and Fokker 100, with a later version being used to re-engine Boeing 727-100s.

The Pratt & Whitney F135 is an afterburning turbofan developed for the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II, a single-engine strike fighter. It has two variants; a Conventional Take-Off and Landing (CTOL) variant used in the F-35A and F-35C, and a two-cycle Short Take-Off Vertical Landing (STOVL) variant used in the F-35B that includes a forward lift fan. The first production engines were delivered in 2009.
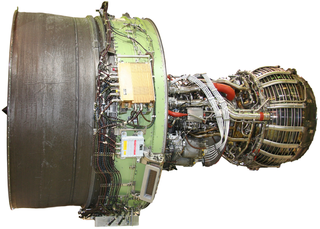
The General Electric GEnx is an advanced dual rotor, axial flow, high-bypass turbofan jet engine in production by GE Aerospace for the Boeing 747-8 and 787. The GEnx succeeded the CF6 in GE's product line.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 500 is a high-bypass turbofan produced by Rolls-Royce to power the larger A340-500/600 variants. It was selected in June 1997, first ran in May 1999, first flew in June 2000, and achieved certification on 15 December 2000. It entered service in July 2002 and 524 engines were delivered on-wing until the A340 production ended in 2012.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 700 is a high-bypass turbofan aircraft engine produced by Rolls-Royce plc to power the Airbus A330. Rolls-Royce was studying a RB211 development for the A330 at its launch in June 1987. It was first selected by Cathay Pacific in April 1989, first ran in summer 1992, was certified in January 1994 and was put into service on 24 March 1995. Keeping the characteristic three-shaft architecture of the RB211, it is the first variant of the Trent family. With its 97.4 in (247 cm) fan for a 5:1 bypass ratio, it produces 300.3 to 316.3 kN of thrust and reaches an overall pressure ratio of 36:1. It competes with the General Electric CF6-80E1 and the PW4000 to power the A330.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 800 is a high-bypass turbofan produced by Rolls-Royce plc, one of the engine options for the early Boeing 777 variants. Launched in September 1991, it first ran in September 1993, was granted EASA certification on 27 January 1995, and entered service in 1996. It reached a 40% market share, ahead of the competing PW4000 and GE90, and the last Trent 800-powered 777 was delivered in 2010. The Trent 800 has the Trent family three shaft architecture, with a 280 cm (110 in) fan. With a 6.4:1 bypass ratio and an overall pressure ratio reaching 40.7:1, it generates up to 413.4 kN of thrust.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 900 is a high-bypass turbofan produced by Rolls-Royce plc to power the Airbus A380, competing with the Engine Alliance GP7000. Initially proposed for the Boeing 747-500/600X in July 1996, this first application was later abandoned but it was offered for the A3XX, launched as the A380 in December 2000. It first ran on 18 March 2003, made its maiden flight on 17 May 2004 on an A340 testbed, and was certified by the EASA on 29 October 2004. Producing up to 374 kN (84,000 lbf), the Trent 900 has the three shaft architecture of the Rolls-Royce Trent family with a 2.95 m (116 in) fan. It has a 8.5–8.7:1 bypass ratio and a 37–39:1 overall pressure ratio.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 is a high-bypass turbofan engine produced by Rolls-Royce, one of the two engine options for the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, competing with the General Electric GEnx. It first ran on 14 February 2006 and first flew on 18 June 2007 before a joint EASA/FAA certification on 7 August 2007 and entered service on 26 October 2011. Corrosion-related fatigue cracking of intermediate pressure (IP) turbine blades was discovered in early 2016, grounding up to 44 aircraft and costing Rolls-Royce at least £1.3 billion.

A blisk is a turbomachine component comprising both rotor disk and blades as a single part instead of a disk assembled with individual removable blades. Blisks generally have better aerodynamics than conventional rotors with single blades and are lighter. They may be additively manufactured, integrally cast, machined from a solid piece of material, or made by welding individual blades to a rotor disk. The term is used mainly in aerospace engine design. Blisks may also be known as integrally bladed rotors (IBR).

The Rolls-Royce LiftSystem, together with the F135 engine, is an aircraft propulsion system designed for use in the STOVL variant of the F-35 Lightning II. The complete system, known as the Integrated Lift Fan Propulsion System (ILFPS), was awarded the Collier Trophy in 2001.

The General Electric Passport is a turbofan developed by GE Aerospace for large business jets. It was selected in 2010 to power the Bombardier Global 7500 and 8000, first run on June 24, 2013, and first flown in 2015. It was certified in April 2016 and powered the Global 7500 first flight on November 4, 2016, before its 2018 introduction. It produces 14,000 to 20,000 lbf of thrust, a range previously covered by the General Electric CF34. A smaller scaled CFM LEAP, it is a twin-spool axial engine with a 5.6:1 bypass ratio and a 45:1 overall pressure ratio and is noted for its large one-piece 52 in (130 cm) fan 18-blade titanium blisk.

The Rolls-Royce RB.203 Trent was a British medium-bypass turbofan engine of around 10,000lb thrust designed for production in the late 1960s, bearing no relation to the earlier Rolls-Royce RB.50 Trent turboprop or the later high-bypass Rolls-Royce Trent turbofan.
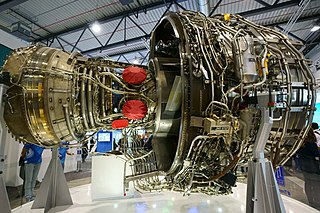
The Rolls-Royce Trent XWB is a high-bypass turbofan produced by Rolls-Royce Holdings. In July 2006, the Trent XWB was selected to power exclusively the Airbus A350. The first engine was run on 14 June 2010, it first flew on an A380 testbed on 18 February 2012, it was certified in early 2013, and it first flew on an A350 on 14 June 2013. It had its first in-flight shutdown on 11 September 2018 as the fleet accumulated 2.2 million flight hours. It keeps the characteristic three-shaft layout of the Rolls-Royce Trent, with a 3.00 m (118 in) fan, an IP and HP spool. The 84,200–97,000 lbf (375–431 kN) engine has a 9.6:1 bypass ratio and a 50:1 pressure ratio. It is the most powerful member of the Trent family.

The Rolls-Royce Trent 7000 is a high-bypass turbofan engine produced by Rolls-Royce, an iteration of the Trent family powering exclusively the Airbus A330neo. Announced on 14 July 2014, it first ran on 27 November 2015. It made its first flight on 19 October 2017 aboard on the A330neo. It received its EASA type certification on 20 July 2018 as a Trent 1000 variant. It was first delivered on 26 November, and was cleared for ETOPS 330 by 20 December. Compared to the A330's Trent 700, the 68,000–72,000 lbf (300–320 kN) engine doubles the bypass ratio to 10:1 and halves emitted noise. Pressure ratio is increased to 50:1, and it has a 112 in (280 cm) fan and a bleed air system. Fuel consumption is improved by 11%.

The General Electric Affinity was a turbofan developed by GE Aviation for supersonic transports. Conceived in May 2017 to power the Aerion AS2 supersonic business jet, initial design was completed in 2018 and detailed design in 2020 for the first prototype production. GE Aviation discontinued development of the engine in May 2021. Its high-pressure core is derived from the CFM56, matched to a new twin fan low-pressure section for a reduced bypass ratio better suited to supersonic flight.




















