
The AD Flying Boat was designed by the British Admiralty's Air Department to serve as a patrol aircraft that could operate in conjunction with Royal Navy warships. Intended for use during the First World War, production of the aircraft was terminated as the end of the war came into sight, and the type saw little operational use. A number were repurchased after the end of the war by Supermarine Aviation and rebuilt as civil transports, becoming known as the Supermarine Channel.
The AD Seaplane Type 1000 also known as the Admiralty Type 1000 and the AD.1 was a British seaplane of the First World War designed to attack German warships. When it first flew, it was the largest British aircraft yet to take to the air.

The Handley Page V/1500 was a British night-flying heavy bomber built by Handley Page towards the end of the First World War. It was a large four-engined biplane, which resembled a larger version of Handley Page's earlier O/100 and O/400 bombers, intended to bomb Berlin from East Anglian airfields. The end of the war stopped the V/1500 being used against Germany, but a single aircraft was used to carry out the first flight from England to India, and later carried out a bombing raid on Kabul during the Third Anglo-Afghan War. It was colloquially known within the fledgling Royal Air Force as the "Super Handley". The V/1500 which was shipped to Canada to attempt a transatlantic flight was flown in the US, and in 1919 crash-landed in a field at Mount Jewett, Pennsylvania. Photos appeared in the 20 February 1919 issue of the Bradford Journal newspaper.

The Fairey Aviation Company Fairey III was a family of British reconnaissance biplanes that enjoyed a very long production and service history in both landplane and seaplane variants. First flying on 14 September 1917, examples were still in use during the Second World War.
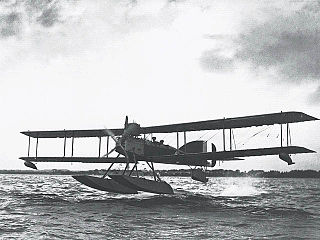
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It was first flown in 1915 and remained in service until after the armistice in 1918. A Short 184 was the first aircraft to sink a ship using a torpedo, and another was the only British aircraft to take part in the Battle of Jutland.

The Short Bomber was a British two-seat long-range reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying aircraft designed by Short Brothers as a land-based development of the very successful Short Type 184.

The Blackburn T.3 Velos was a 1920s British two-seat coastal defence seaplane built by Blackburn Aeroplane & Motor Company Limited, Brough Aerodrome and the Greek National Aircraft Factory.

The Fairey Campania was a British ship-borne, patrol and reconnaissance aircraft of the First World War and Russian Civil War. It was a single-engine, two-seat biplane with twin main floats and backward-folding wings. The Campania was the first aeroplane ever designed specifically for carrier operations.
The Avro 519 was a British bomber aircraft of the First World War, a development of the Avro 510 seaplane. They were two-bay biplanes of conventional configuration with greatly uneven span. Two single-seat examples, powered by a single 150 hp (110 kW) Sunbeam water-cooled engine, were ordered by the RNAS in early 1916. This was soon followed by orders for two modified aircraft for the Royal Flying Corps. These were fitted with seats for a crew of two and had more powerful (225 hp/168 kW) Sunbeam engines

The Avro 523 Pike was a British multi-role combat aircraft of the First World War that did not progress past the prototype stage. It was intended to provide the Royal Naval Air Service with an anti-Zeppelin fighter that was also capable of long-range reconnaissance and bombing.

The Wight Converted Seaplane was a British twin-float patrol seaplane produced by John Samuel White & Company Limited.

The Wight Pusher Seaplane, or Navyplane, was a British twin-float patrol seaplane produced by John Samuel White & Company Limited.

The Bréguet Bre.4, also known variously as the Type IV and BUM, was a French biplane bomber of World War I. A fighter version of it was also produced as the BUC and BLC; some of these saw service with the British Royal Navy, which called them 'the Bréguet de Chasse.

The Airco DH.3 was a British bomber aircraft of the First World War. The DH.3 was designed in 1916 as a long-range day bomber by Geoffrey de Havilland, chief designer at the Aircraft Manufacturing Company. It was a large biplane with wide-span three-bay wings, slender fuselage, and a curved rudder. It was powered by two 120 hp (89 kW) Beardmore engines, mounted as pushers between the wings. In addition to tailskid landing gear, two wheels were placed under the nose to prevent it from tipping over on the nose.

The Sopwith Admiralty Type 860 was a 1910s British biplane seaplane torpedo bomber designed and built for the Admiralty by the Sopwith Aviation Company.

The Short Type 827 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance floatplane. It was also known as the Short Admiralty Type 827.
The Beardmore W.B.1 was a British single-engine bomber biplane of World War I developed by Beardmore.

The Short Type 320, also known as the Short Admiralty Type 320, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying "folder" seaplane of the First World War.

The Norman Thompson N.T.2B was a British single-engined flying boat trainer of the First World War. A single-engined biplane, the N.T.2B was adopted as a standard flying boat trainer by the Royal Naval Air Service, training pilots for larger patrol flying boats such as the Felixstowe F.2.
The Grahame-White Ganymede was a prototype British heavy night bomber intended to serve with the Royal Air Force in the First World War. A large, three-engined, twin-boom biplane, the sole prototype Ganymede did not fly until after the war had ended, and although an attempt was made to convert the aircraft to an airliner, it was unsuccessful.
















