
The Wingst is a ridge, up to 74 metres high, [1] in northern Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Wingst is a ridge, up to 74 metres high, [1] in northern Lower Saxony, Germany.
The ridge is located in northeast part of the district of Cuxhaven, just a few kilometres south of the mouth of the River Elbe on the North Sea coast, and west of the lower reaches of the Oste between Cadenberge to the north and Hemmoor to the south. It is surrounded by villages in the borough of Wingst. Some distance to the south-southwest of the Wingst is the lake of Balksee; south of which is the Varrel Moor.
The Wingst is a small geest ridge, covered by mixed woods, that was formed by an ice age moraine. It is surrounded by flat, divided marsh and bog landscapes, that are sometimes only 1 metre above sea level. Dolmens situated within the Wingst indicate that there were early settlements in the local area.
The Wingst may be reached via the B 73 federal highway, that grazes the area to the east, as well as its side roads, and also via the Green Coast Road (Grüne Küstenstraße), which passes the ridge to the northwest. The Wingst is crossed by the E9 European long-distance path and also by regional walking trails. The Neuhaus-Bülkau Canal runs in a north-south direction just beyond the western fringes of the Wingst. On the northeastern edge of the Wingst is the Zoo in the Wingst.
The highest elevation in the Wingst is the Silberberg (74 m). Amongst its sub-peaks is the Deutscher Olymp (61 m), which has an observation tower of the same name. The other elevations in the Wingst are (in alphabetical order):
|
|

Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea, just a few degrees north of the equator.

Jamaica lies 140 km (90 mi) south of Cuba and 190 km (118 mi) west of Haiti. At its greatest extent, Jamaica is 235 km (146 mi) long, and its width varies between 34 and 84 km. Jamaica has a small area of 10,992 km2 (4,244 sq mi). However, Jamaica is the largest island of the Commonwealth Caribbean and the third largest of the Greater Antilles, after Cuba and Hispaniola. Many small islands are located along the south coast of Jamaica, such as the Port Royal Cays. Southwest of mainland Jamaica lies Pedro Bank, an area of shallow seas, with a number of cays, extending generally east to west for over 160 km (99 mi). To the southeast lies Morant Bank, with the Morant Cays, 51 km (32 mi) from Morant Point, the easternmost point of mainland Jamaica. Alice Shoal, 260 km (160 mi) southwest of the main island of Jamaica, falls within the Jamaica–Colombia Joint Regime. It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 258,137 km2 (99,667 sq mi).

The Caucasus Mountains is a mountain system at the intersection of Europe and Asia. Stretching between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, it is surrounded by the Caucasus region and is home to Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe at 5,642 metres (18,510 ft) above sea level.

The Weser Uplands is a hill region in Germany, between Hannoversch Münden and Porta Westfalica, along the river Weser. The area reaches into three states, Lower Saxony, Hesse, and North Rhine-Westphalia. Important towns of this region include Bad Karlshafen, Holzminden, Höxter, Bodenwerder, Hameln, Rinteln, and Vlotho.

Macquarie River a watercourse that is part of the Macquarie–Barwon catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is one of the main inland rivers in New South Wales, Australia.
This article lists extreme locations on Earth that hold geographical records or are otherwise known for their geophysical or meteorological superlatives. All of these locations are Earth-wide extremes; extremes of individual continents or countries are listed in separate articles under the Extreme points by region section. For other lists of extreme places on Earth, see Lists of extreme points. For more detailed meteorological and climatic records, see List of weather records.

Rivelin Rocks are a gritstone edge or escarpment in the upper Rivelin Valley at grid reference SK279873, 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) west of Sheffield just off the A57 road in the county of South Yorkshire, England.

Ciste Dhubh is a mountain in the Scottish Highlands between Glen Shiel and Glen Affric. It is far from any centres of population, with Kyle of Lochalsh being almost 30 kilometres (19 mi) away to the west-northwest.

The Greensand Ridge, also known as the Wealden Greensand is an extensive, prominent, often wooded, mixed greensand/sandstone escarpment in south-east England. Forming part of the Weald, a former dense forest in Sussex, Surrey and Kent, it runs to and from the East Sussex coast, wrapping around the High Weald and Low Weald. It reaches its highest elevation, 294 metres (965 ft), at Leith Hill in Surrey—the second highest point in south-east England, while another hill in its range, Blackdown, is the highest point in Sussex at 280 metres (919 ft). The eastern end of the ridge forms the northern boundary of Romney Marsh.

Balsam Lake Mountain is one of the Catskill Mountains, located in the Town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States. It is the westernmost of the range's 35 High Peaks. Its exact height has not been determined, but the highest contour line on topographic maps, 3,720 feet (1,130 m), is usually given as its elevation.

Brace Mountain is the peak of a ridge in the southern Taconic Mountains, near the tripoint of the U.S. states of New York, Connecticut and Massachusetts. Its 2,311-foot (704 m) main summit is located in New York; it is the highest point in that state's Dutchess County.

Sgùrr Ghiubhsachain is a mountain in the Lochaber area in the west of Scotland. Its summit is the highest point in a group of mountains that stand south of Glenfinnan, to the south east of the northern part of Loch Shiel. It is considerably lower than the nearby Nevis range, but it is a long way from a public road. Its slopes are steep and rugged on all sides and are devoid of paths. Despite easy access to the trail head from the road from Fort William to Mallaig, an individual or party that climbs this mountain may be alone there, even on a fine day in the summer.
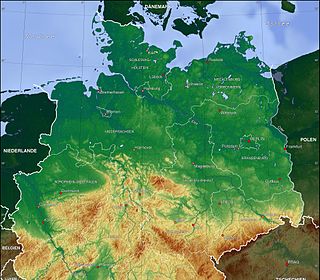
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east.

The region between the Elbe and Weser rivers forms the Elbe–Weser triangle, also rendered Elbe-Weser Triangle, in northern Germany. It is also colloquially referred to as the Nasses Dreieck or "wet triangle".

The Silberberg is a low hill, 74 metres high, in the Wingst ridge in the district of Cuxhaven in the north German state of Lower Saxony.

The Deutscher Olymp is a 62-metre-high elevation on the Wingst ridge within the boundary of the homonymous municipality in the district of Cuxhaven in the German state of Lower Saxony.
The Wildeshausen Geest is part of the northwest Germany's geest ridge, that begins near Meppen on the river Ems with the Hümmling, is broken by the Weser depression, continues with the Osterholz Geest and reaches the marshes of Kehdingen by the river Elbe with the ridges of the Wingst and Stade Geest. It gives its name to the eponymous nature park.

The Westerberg in Rahden is a low ridge in Northern Germany in the north of the collective municipality of Börde Lamstedt in the state of Lower Saxony. It is covered with mixed forest and, like the nearby Wingst ridge, it is an end moraine from the Saale glaciation period. Together with the Wingst it forms part of the eastern boundary of Land Hadeln.
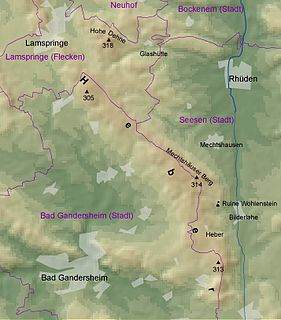
The Heber is a hogback ridge, relatively small in area and up to 313.5 metres high, in the Lower Saxon Hills within the districts of Goslar, Northeim and Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.

Seana Bhràigh is a mountain east of Ullapool, in the Highlands of Scotland.