Related Research Articles
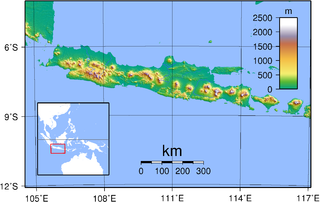
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 147.7 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, constituting approximately 55% of the Indonesian population.

East Java is a province of Indonesia. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern and southern coasts, respectively, while the narrow Bali Strait to the east separates Java from Bali. Located in eastern Java, the province also includes the island of Madura, as well as the Kangean islands and other smaller island groups located further east and Masalembu archipelagos in the north. Its capital is Surabaya, the second largest city in Indonesia, a major industrial center and also a major business center. Banyuwangi is the largest regency in East Java and the largest on the island of Java.

Javanese is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. There are also pockets of Javanese speakers on the northern coast of western Java. It is the native language of more than 98 million people.
Kawi or Old Javanese is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the islands of Madura, Bali and Lombok. It had a sizable vocabulary of Sanskrit loanwords but had not yet developed the formal krama language register, to be used with one's social superiors that is so characteristic of modern Javanese.

Central Java is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakarta in the south, East Java in the east, and the Java Sea in the north. It has a total area of 32,800.69 km², with a population of 36,516,035 at the 2020 Census making it the third-most populous province in both Java and Indonesia after West Java and East Java. The province also includes the island of Nusakambangan in the south, and the Karimun Jawa Islands in the Java Sea. Central Java is also a cultural concept that includes the Special Region and city of Yogyakarta. However, administratively the city and its surrounding regencies have formed a separate special region since the country's independence, and is administrated separately. Although known as the "heart" of Javanese culture, there are several other non-Javanese ethnic groups, such as the Sundanese on the border with West Java. Chinese Indonesians, Arab Indonesians, and Indian Indonesians are also scattered throughout the province.

The Javanese people are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to the Indonesian island of Java. With approximately 100 million people, they form the largest ethnic group in Indonesia. They are predominantly located in the central to eastern parts of the island. There are also significant numbers of people of Javanese descent in most provinces of Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Suriname, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Yemen and the Netherlands.

The kris or keris in the Indonesian and Malay languages, is an asymmetrical dagger with distinctive blade-patterning achieved through alternating laminations of iron and nickelous iron (pamor). Of Javanese origin, the kris is famous for its distinctive wavy blade, although many have straight blades as well, and is one of the weapons commonly used in the pencak silat martial art native to Indonesia, Malaysia, & Brunei.

Wayang, also known as wajang, is a traditional form of puppet theatre play originated on the Indonesian island of Java. Wayang refers to the entire dramatic show. Sometimes the leather puppet itself is referred to as wayang. Performances of wayang puppet theatre are accompanied by a gamelan orchestra in Java, and by gender wayang in Bali. The dramatic stories depict mythologies, such as episodes from the Hindu epics the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, as well as local adaptations of cultural legends. Traditionally, a wayang is played out in a ritualized midnight-to-dawn show by a dalang, an artist and spiritual leader; people watch the show from both sides of the screen.

Prince Diponegoro, also known as Dipanegara, was a Javanese prince who opposed the Dutch colonial rule. The eldest son of the Yogyakartan Sultan Hamengkubuwono III, he played an important role in the Java War between 1825 and 1830. After his defeat and capture, he was exiled to Makassar, where he died, 69 years old.

Hinduism in Indonesia, as of the 2018 census, is practised by about 1.74% of the total population, and almost 87% of the population in Bali. Hinduism is one of the six official religions of Indonesia. Hinduism came to Indonesia in the 1st-century through traders, sailors, scholars and priests. A syncretic fusion of pre-existing Javanese folk religion, culture and Hindu ideas, that from the 6th-century also synthesized Buddhist ideas as well, evolved as the Indonesian version of Hinduism. These ideas continued to develop during the Srivijaya and Majapahit empires. About 1400 CE, these kingdoms were introduced to Islam from coast-based Muslim traders, and thereafter Hinduism mostly vanished from many of the islands of Indonesia.

Priyayi was the Dutch-era class of the nobles of the robe, as opposed to royal nobility or ningrat (Javanese), in Java, Indonesia, the world's most populous island.

The Mataram Kingdom or also known as Medang Kingdom was a Javanese Hindu–Buddhist kingdom that flourished between the 8th and 11th centuries. It was based in Central Java, and later in East Java. Established by King Sanjaya, the kingdom was ruled by the Shailendra dynasty.

Kejawèn or Javanism, also called Kebatinan, Agama Jawa, and Kepercayaan, is a Javanese religious tradition, consisting of an amalgam of animistic, Buddhist, and Hindu aspects. It is rooted in Javanese history and religiosity, syncretizing aspects of different religions.

Yogyakarta is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, on the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an important centre for classical Javanese fine arts and culture such as ballet, batik textiles, drama, literature, music, poetry, silversmithing, visual arts, and wayang puppetry. Renowned as a centre of Indonesian education, Yogyakarta is home to a large student population and dozens of schools and universities, including Gadjah Mada University, the country's largest institute of higher education and one of its most prestigious.
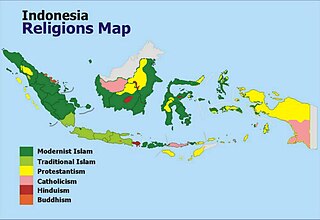
Indonesia is officially a republic with a compromise made between the ideas of a secular state and an Islamic state. Indonesia has the world's largest Muslim population and the first principle of Indonesia's philosophical foundation, Pancasila requires its citizens to "believe in the one and only God". Consequently, atheists in Indonesia experience official discrimination in the context of registration of births and marriages and the issuance of identity cards. In addition, Aceh officially enforces Sharia law and is notorious for its discriminatory practices towards religious and sexual minorities. There are also pro-Sharia and fundamentalist movements in several parts of the country with overwhelming Muslim majorities.

The history of arrival and spread of Islam in Indonesia is unclear. One theory states it arrived directly from Arabia before the 9th century, while another credits Sufi merchants and preachers for bringing Islam to Indonesian islands in the 12th or 13th century either from Gujarat in India or directly from the Middle East. Before the arrival of Islam, the predominant religions in Indonesia were Hinduism and Buddhism.

Javanese culture is the culture of the Javanese people. Javanese culture is centered in the provinces of Central Java, Yogyakarta and East Java in Indonesia. Due to various migrations, it can also be found in other parts of the world, such as Suriname, the broader Indonesian archipelago region, Cape Malay, Malaysia, Singapore, Netherlands and other countries. The migrants bring with them various aspects of Javanese cultures such as Gamelan music, traditional dances and art of Wayang kulit shadow play.

Peter Carey is a British historian and author who specialises in the modern history of Indonesia, Java in particular, and has also written on East Timor and Myanmar. He was the Laithwaite fellow of Modern History at Trinity College, Oxford, from 1979 to 2008. His major early work concentrated on the history of Diponegoro, the British in Java, 1811–16 and the Java War (1825–30), on which he has published extensively. His biography of Diponegoro, The Power of Prophecy, appeared in 2007, and a succinct version, Destiny; The Life of Prince Diponegoro of Yogyakarta, 1785–1855, was published in 2014. He has conducted research in Lisbon and the United Kingdom amongst the exile East Timorese student community for an oral history of the Indonesian occupation of East Timor, 1975–99, part of which was published in the Cornell University journal Indonesia.

The East Sumatra revolution, also known as the East Sumatra Social Revolution, began on 3 March 1946. Across 25 "native states", many sultanates were overthrown and mass killing of members of the aristocratic families were performed by armed pergerakan groups. To the opportunistic pergerakan militants, the revolutionary movement was seen as one of the means for East Sumatra to be freed from colonial overlordship and to join the larger Indonesian National Revolution. Participants of the revolution were believed to be provoked by leaders to kill aristocrats and create violence. These belligerents had three prime objectives: to eliminate the sultans and aristocrats, to seize their wealth and to eliminate the region's feudal social structure. The revolution brought about the formation of the State of East Sumatra), which was dissolved when the region became part of the Indonesian republic.

Javanisation or Javanization is the process in which Javanese culture dominates, assimilates, or influences other cultures in general. The term "Javanise" means "to make or to become Javanese in form, idiom, style, or character." This domination could take place in various aspects; such as cultural, language, politics and social.
References
- ↑ Eklof, Stefan (2004). Power and Political Culture in Suharto's Indonesia: The Indonesian Democratic Party (PDI) and Decline of the New Order (1986-98). NIAS Press. p. 119. ISBN 9788791114502.
- ↑ Berman, Laine A. (1998). Speaking through the Silence: Narratives, Social Conventions, and Power in Java . Oxford University Press. p. 6. ISBN 9780195355222.
- ↑ Sullivan, John (1992). Local government and community in Java: an urban case-study. Oxford University Press. p. 25. ISBN 9780195885590.