
Irssi is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client program for Linux, FreeBSD, macOS and Microsoft Windows. It was originally written by Timo Sirainen, and released under the terms of the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later in January 1999.

A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. They are often obtained from the website of each distribution, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to servers and powerful supercomputers.

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution derived from Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in multiple editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. The operating system is developed by the British company Canonical, and a community of other developers, under a meritocratic governance model. As of April 2024, the most-recent long-term support release is 24.04.
phpLDAPadmin is a web app for administering Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers. It's written in the PHP programming language, and is licensed under the GNU General Public License. The application is available in 14 languages and supports UTF-8 encoded directory strings.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organizational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.
NX technology, commonly known as NX or NoMachine, is a remote access and remote control computer software, allowing remote desktop access and maintenance of computers. It is developed by the Luxembourg-based company NoMachine S.à r.l.. NoMachine is proprietary software and is free-of-charge for non-commercial use.

PulseAudio is a network-capable sound server program distributed via the freedesktop.org project. It runs mainly on Linux, including Windows Subsystem for Linux on Microsoft Windows and Termux on Android; various BSD distributions such as FreeBSD, OpenBSD, and macOS; as well as Illumos distributions and the Solaris operating system. It serves as a middleware in between applications and hardware and handles raw PCM audio streams.

Jami is a SIP-compatible distributed peer-to-peer softphone and SIP-based instant messenger for Linux, Microsoft Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. Jami was developed and maintained by the Canadian company Savoir-faire Linux, and with the help of a global community of users and contributors, Jami positions itself as a potential free Skype replacement.

WeeChat is a free and open-source Internet Relay Chat client that is designed to be light and fast. It is released under the terms of the GNU GPL-3.0-or-later and has been developed since 2003.
DAViCal is a server for calendar sharing. It is an implementation of the CalDAV protocol which is designed for storing calendaring resources on a remote shared server. Although the events are stored in a SQL database the information between client and server is transferred in the iCalendar format.

Plymouth is an application which provides a graphical boot experience for Linux. Plymouth supports animations using Direct Rendering Manager (DRM) and the KMS driver. Plymouth is bundled with an initial ramdisk which allows it to run before the file system is mounted. Some sources claim that Plymouth is named after Plymouth Rock, symbolizing the program's role as the first thing a user sees, but this has not been confirmed in any official capacity.

Kiwix is a free and open-source offline web browser created by Emmanuel Engelhart and Renaud Gaudin in 2007. It was first launched to allow offline access to Wikipedia, but has since expanded to include other projects from the Wikimedia Foundation, public domain texts from Project Gutenberg, many of the Stack Exchange sites, and many other resources. Available in more than 100 languages, Kiwix has been included in several high-profile projects, from smuggling operations in North Korea to Google Impact Challenge's recipient Bibliothèques Sans Frontières.

Remmina is a free and open source remote desktop client for POSIX-based computer operating systems. It supports the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), VNC, NX, XDMCP, SPICE, X2Go and SSH protocols and uses FreeRDP as foundation.

Zim is a graphical text editor designed to maintain a collection of locally stored wiki-pages, a personal wiki. It works as a personal knowledge base and note-taking software application that operates on text files using markdown. Each wiki-page can contain things like text with simple formatting, links to other pages, attachments, and images. Additional plugins, such as an equation editor and spell-checker, are also available. The wiki-pages are stored in a folder structure in plain text files with wiki formatting. Zim can be used with the Getting Things Done method.
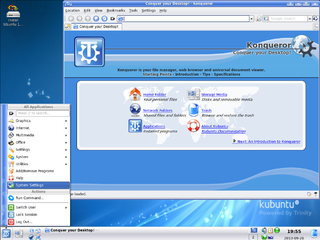
The Trinity Desktop Environment (TDE) is a complete software desktop environment designed for Linux and Unix-like operating systems, intended for computer users preferring a traditional desktop model, and is free/libre software. Born as a fork of KDE 3.5 in 2010, it was originally created by Timothy Pearson, who had coordinated Kubuntu remixes featuring KDE 3.5 after Kubuntu switched to KDE Plasma 4.

OpenZFS is an open-source implementation of the ZFS file system and volume manager initially developed by Sun Microsystems for the Solaris operating system and now maintained by the OpenZFS Project. It supports features like data compression, data deduplication, copy-on-write clones, snapshots, and RAID-Z. It also supports the creation of virtual devices, which allows for the creation of file systems that span multiple disks.

Borg is deduplicating backup software for various Unix-like operating systems.
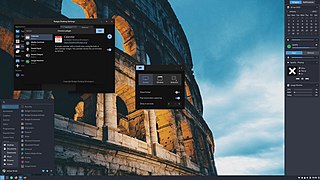
Budgie is an independent, free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that targets the desktop metaphor. Budgie is developed by the Buddies of Budgie organization, which is composed of a team of contributors from Linux distributions such as Fedora, Debian, and Arch Linux. Its design emphasizes simplicity, minimalism, and elegance, while providing the means to extend or customize the desktop in various ways. Unlike desktop environments like Cinnamon, Budgie does not have a reference platform, and all distributions that ship Budgie are recommended to set defaults that best fit their desired user experience.
Android devices have the ability to run virtual machines or emulate other operating systems. It does this either via desktop virtualization, platform virtualization, or emulation via compatibility layer.

GNOME Terminator is a free and open-source terminal emulator for Linux programmed in Python, licensed under GPL-2.0-only. The goal of the project is to produce a useful tool for arranging terminals. It is inspired by programs such as gnome-multi-term, QuadKonsole, etc. In that the main focus is arranging terminals in grids. Terminator packages exist for Arch, Debian/Ubuntu, Fedora, OpenSUSE, Gentoo, Snap, FreeBSD, OpenBSD. In 2017 took second place in voting at opensource.com, after Gnome Terminal.














