
Xavier Coppolani (1866-1905) was a French military and colonial leader, who was instrumental in the colonial occupation and creation of modern-day Mauritania.

Xavier Coppolani (1866-1905) was a French military and colonial leader, who was instrumental in the colonial occupation and creation of modern-day Mauritania.
Born to Corsican parents in French Algeria, his father was considered to be a member of the colon class of French immigrants to the country. While Coppolani was in Algeria, he grew up among local Muslims and learnt Algerian Arabic. He was intrigued by Islamic practices and studied Sufism. [1]
He was transferred to Senegal in 1899 to lead the expansion of colonial rule north of the Senegal river, where Moorish tribes held firm against French rule. [2] This was disguised as an inquiry, whereas the goal of the mission was to lead to the subjugation of the local people. [1] Local tribal rivalries provided Coppolani with an opportunity, and in 1901, he drew up a plan for moving into the territory with a combination of military and political strategies. [2]
Alliances were drawn up with two of the main marabouts of the territory, Shaykh Sidya Baba and Shaykh Saad Bouh, local leaders of Qadiriyya Sufi brotherhoods. They were promised a dominant role in the colonial administration and protection for their Zawiya tribes against the attacks of Hassane warriors. In return they would use their religious influence to persuade the local emirs to accept French rule. With military pressure applied, the strategy worked, and the emirates of Tagant, Trarza and Brakna all accepted French rule in 1903-04. The last emirate, in the northern zone of Adrar, proved combative. It was also backed by a third influential Qadiriyya marabout, shaykh Ma al-'Aynayn, himself in turn supported by the Sultan of Morocco. [2]
Coppolani was preparing to march on Adrar when he was killed in 1905, by a member of the shaykh's Gudfiyya brotherhood. [3] The emirate was eventually defeated and forcibly incorporated into Mauritania in 1912, by General Gouraud, but tribal revolts and raids persisted until 1934. [2]
The original inhabitants of Mauritania were the Bafour, presumably a Mande ethnic group, connected to the contemporary Arabized minor social group of Imraguen ("fishermen") on the Atlantic coast.

The Mouride brotherhood is a large tariqa most prominent in Senegal and The Gambia with headquarters in the city of Touba, which is a holy city for the order. Adherents are called Mourides, from the Arabic word murīd, a term used generally in Sufism to designate a disciple of a spiritual guide.The beliefs and practices of the Mourides constitute Mouridism. Mouride disciples call themselves taalibé in Wolof and must undergo a ritual of allegiance called njebbel, as it is considered highly important to have a sheikh "spiritual guide" in order to become a Mouride. The Mouride brotherhood was founded in 1883 in Senegal by Amadou Bamba. The Mouride make up around 40 percent of the total population, and their influence over everyday life can be seen throughout Senegal.
A marabout is a descendant of the Prophet Muhammad and a Muslim religious leader and teacher who historically had the function of a chaplain serving as a part of an Islamic army, notably in North Africa and the Sahara, in West Africa, and (historically) in the Maghreb. The marabout is often a scholar of the Qur'an, or religious teacher. Others may be wandering holy men who survive on alms, Sufi Murshids ("Guides"), or leaders of religious communities.
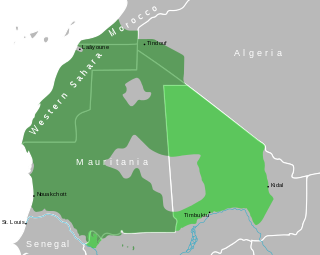
Beni Ḥassan is a Bedouin Arab tribe which inhabits Western Sahara, Mauritania, Morocco and Algeria. It is one of the four sub-tribes of the Beni Maqil who emigrated in the 11th century from South Arabia to the Maghreb with the Bani Hilal and Banu Sulaym Arab tribes. In the 13th century, they took the Sanhaja territories in the southwest of the Sahara. In Morocco, they first settled, alongside their Maqil relatives, in the area between Tadla and the Moulouya River. The Sous Almohad governor called upon them for help against a rebellion in the Sous, and they resettled in and around that region. They later moved to Mauritania, and from the 16th century onwards, they managed to push back all black Mauritanians southwards to the Senegal Valley river. The Beni Hassan and other warrior Arab tribes dominated the Sanhaja Berber tribes of the area after the Char Bouba war of the 17th century. As a result, Arabs became the dominant ethnic group in Western Sahara and Mauretania. The Bani Hassan dialect of Arabic became used in the region and is still spoken, in the form of Hassaniya Arabic. The hierarchy established by the Beni Hassan tribe gave Mauritania much of its sociological character. That ideology has led to oppression, discrimination and even enslavement of other groups in Mauritania.

A zawiya or zaouia is a building and institution associated with Sufis in the Islamic world. It can serve a variety of functions such a place of worship, school, monastery and/or mausoleum. In some regions the term is interchangeable with the term khanqah, which serves a similar purpose. In the Maghreb, the term is often used for a place where the founder of a Sufi order or a local saint or holy man lived and was buried. In the Maghreb the word can also be used to refer to the wider tariqa and its membership.
The Sahrawis, or Sahrawi people, are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Hassani Arab and Sanhaji Berber descent, as well as West African and other indigenous populations.

Spanish Sahara, officially the Spanish Possessions in the Sahara from 1884 to 1958, then Province of the Sahara between 1958 and 1976, was the name used for the modern territory of Western Sahara when it was occupied and ruled by Spain between 1884 and 1976. It had been one of the most recent acquisitions, as well as one of the last remaining holdings, of the Spanish Empire, which had once extended from the Americas to the Spanish East Indies.

Ahmad Ibn Muhammad Ibn Habiballah (Wolof: Ahmadu Bamba Mbacke, also known to followers as Khādimu 'al-Rasūl or "The Servant of the Messenger" and Serigne Touba or "Sheikh of Tuubaa", was a Sufi saint and religious leader in Senegal and the founder of the large Mouride Brotherhood.

Mohamed Mustafa Ma al-'Aynayn was a Saharan Moorish religious and political leader who fought French and Spanish colonization in North Africa. He was the son of Mohammed Fadil Mamin, and the elder brother of shaykh Saad Bouh, a prominent marabout in Mauritania.
The Tajakant is a Sahrawi tribe of Berber Sanhaja origins. They speak Hassaniya Arabic.

Islam is the predominant religion in Senegal. 97 percent of the country's population is estimated to be Muslim. Islam has had a presence in Senegal since the 11th century. Sufi brotherhoods expanded with French colonization, as people turned to religious authority rather than the colonial administration. The main Sufi orders are the Tijaniyyah, the Muridiyyah or Mourides, and to a lesser extent, the pan-Islamic Qadiriyyah and the smaller Layene order. Approximately 1% are Shiites.
The Char Bouba war, also known as the Mauritanian Thirty Years' War or the Marabout War, took place between 1644 and 1677 in the tribal areas of what is today Mauritania and Western Sahara as well as in the Senegal river valley. It was fought between the Sanhadja Berber tribes and Muslim populations in the river valley, led by Lamtuna Imam Nasr ad-Din, on one hand; and the Maqil Arab immigrant tribes, foremost of which was the Beni Hassan, as well as the traditional aristocracies of the Wolof states on the other, supported by the French.
Sheikh Saad Buh was a Moorish, Qadiriyya, Fadiliyya Sufi from Mauritania. Buh, who settled in Trarza in the 1870s, developed a following in St. Louis, and began a pattern of visits to the peanut basin and river valley. In the late 1860s, before he was 20, Buh established ties with the French administration who were at the time trying to conquer the Senegalo-Mauritanian zone, and became involved in a network of teachers, schools and zawiyas (lodges) across the Sahel and Sahara.
The Gudfiyya brotherhood was a small, militant religious organization created by the Sufi Qadiriyya shaykh Ma al-'Aynayn, in his battle against French and Spanish colonizers in the western Maghreb.

The Emirate of Trarza was a precolonial state in what is today southwest Mauritania. It has survived as a traditional confederation of semi-nomadic people to the present day. Its name is shared with the modern Region of Trarza. The population, a mixture of Berber tribes, had been there for a long time before being conquered in the 11th century by Hassaniya Arabic speakers from the north. Europeans later called these people Moors/Maures, and thus have titled this group "the Trarza Moors".

Precolonial Mauritania, lying next to the Atlantic coast at the western edge of the Sahara Desert, received and assimilated into its complex society many waves of Saharan migrants and conquerors.

The period from the mid-nineteenth to mid-twentieth centuries is the colonial period in Mauritania.

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is an Arab Maghreb country in West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Morocco in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest. It is named after the ancient Berber Kingdom of Mauretania, which later became a province of the Roman Empire, even though the modern Mauritania covers a territory far to the south of the old Berber kingdom that had no relation with it.

The people of Mauritania are overwhelmingly adherents of Sunni Islam, of the Maliki school of jurisprudence.

The Awlad Sidi Shaykh was a confederation of Arab tribes in the west and south of Algeria led by the descendants of the Sufi saint Sidi Shaykh. The Awlad had religious authority, and also owned agricultural settlements and engaged in trade. During the French occupation of Algeria they alternately cooperated with and opposed the colonialists.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)