
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target during the period when the target scene is illuminated creates the large synthetic antenna aperture. Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical or synthetic – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. For a fixed antenna size and orientation, objects which are further away remain illuminated longer - therefore SAR has the property of creating larger synthetic apertures for more distant objects, which results in a consistent spatial resolution over a range of viewing distances.
The FLuorescence EXplorer (FLEX) is a planned mission by the European Space Agency to launch a satellite to monitor the global steady-state chlorophyll fluorescence in terrestrial vegetation. FLEX was selected for funding on 19 November 2015 and will be launched on a Vega C rocket from Guiana Space Centre in mid-2025.

OpenEV is an open-source geospatial toolkit and a frontend to that toolkit. OpenEV was developed using Python and uses the GDAL library to display georeferenced images and elevation data. The application also has image editing capabilities and uses OpenGL to display elevation data in three-dimensions.

GNSS reflectometry involves making measurements from the reflections from the Earth of navigation signals from Global Navigation Satellite Systems such as GPS. The idea of using reflected GNSS signal for earth observation became more and more popular in the mid-1990s at NASA Langley Research Center and is also known as GPS reflectometry. Research applications of GNSS-R are found in

The Earth and Mission Science Division is a group of European Space Agency (ESA) staff mission scientists, contractors, research fellows, young graduates, trainees, and administrative staff working within the Science, Applications and Climate Department of the Directorate of Earth Observation Programmes. The Division is located at ESA's European Space Research and Technology Centre in Noordwijk, South Holland, The Netherlands.
Sea ice concentration is a useful variable for climate scientists and nautical navigators. It is defined as the area of sea ice relative to the total at a given point in the ocean. This article will deal primarily with its determination from remote sensing measurements.
The Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) is a space-based system developed by the University of Michigan and Southwest Research Institute with the aim of improving hurricane forecasting by better understanding the interactions between the sea and the air near the core of a storm.
The Canada Centre for Mapping and Earth Observation (CCMEO) (formerly Canada Centre for Remote Sensing (CCRS)) is a branch of Natural Resources Canada's Earth Science Sector. It was created in 1970 with Lawrence Morley as the first Director General. The department also works closely with the private sector, especially with the development of GIS software.
JoBea Way Holt is an American planetary scientist who has worked for NASA. Holt studied the carbon cycle in Earth's atmosphere. She is also a member of the Climate Project, and is the author of several books and research papers.
Frank Silvio Marzano was a professor at the Sapienza University of Rome, Italy who was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2016 for contributions to microwave remote sensing in meteorology and volcanology. He was also a Fellow of the UK Royal Meteorological Society since 2012. In 2020 Dr. Marzano was inserted in the World's Top 2% Scientists database of Stanford University (USA).
The railSAR, also known as the ultra-wideband Foliage Penetration Synthetic Aperture Radar, is a rail-guided, low-frequency impulse radar system that can detect and discern target objects hidden behind foliage. It was designed and developed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in the early 1990s in order to demonstrate the capabilities of an airborne SAR for foliage and ground penetration. However, since conducting accurate, repeatable measurements on an airborne platform was both challenging and expensive, the railSAR was built on the rooftop of a four-story building within the Army Research Laboratory compound along a 104-meter laser-leveled track.
The boomSAR is a mobile ultra-wideband synthetic aperture radar system designed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in the mid-1990s to detect buried landmines and IEDs. Mounted atop a 45-meter telescoping boom on a stable moving vehicle, the boomSAR transmits low frequency short-pulse UWB signals over the side of the vehicle to scope out a 300-meter range area starting 50 meters from the base of the boom. It travels at an approximate rate of 1 km/hour and requires a relatively flat road that is wide enough to accommodate its 18 ft-wide base.
Mahta Moghaddam is an Iranian-American electrical and computer engineer and William M. Hogue Professor of Electrical Engineering in the Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering. Moghaddam is also the president of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society and is known for developing sensor systems and algorithms for high-resolution characterization of the environment to quantify the effects of climate change. She also has developed innovative tools using microwave technology to visualize biological structures and target them in real-time with high-power focused microwave ablation.

Avik Bhattacharya is a professor at the Centre of Studies in Resources Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India. He has been working in the field of radar polarimetry theory and applications for more than a decade. His main focuses on the use of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data for land use classification, change detection and qualitative and quantitative biophysical and geophysical information estimation.

Eni G. Njoku is a Nigerian-American scientist specializing in microwave remote sensing. He worked at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), California Institute of Technology, where he was responsible for developing techniques for sea surface temperature and soil moisture remote sensing using microwave radiometers. He produced the first microwave-derived sea surface temperature maps from space, and developed the first application of deployable mesh antennas for satellite Earth observation. From 2008-2013, he served as project scientist of NASA's first soil moisture mission, the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, launched in 2015.
Land cover maps are tools that provide vital information about the Earth's land use and cover patterns. They aid policy development, urban planning, and forest and agricultural monitoring.
The Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS) is a 22-channel scanning microwave radiometer for observation of the Earth's atmosphere and surface. It is the successor to the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU) on NOAA weather satellites. ATMS units have been flown on the Suomi NPP and on the Joint Polar Satellite System.

The Earth Science Decadal Survey is a publication of the United States National Research Council that identifies key research priorities in the field of Earth Sciences with a focus on remote sensing. It is written and released at the request of three United States government agencies: the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The survey is produced by the Committee on the Decadal Survey for Earth Science and Applications from Space (ESAS) of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine (NASEM) Space Studies Board, Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences. Agencies like NASA use the recommendations from the decadal survey to prioritize funding for specific types of scientific research projects.
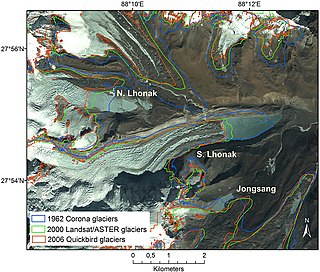
South Lhonak Lake is a glacial-moraine-dammed lake, located in Sikkim's far northwestern region. It is one of the fastest expanding lakes in the Sikkim Himalaya region, and one of the 14 potentially dangerous lakes susceptible to Glacial lake outburst flood (GLOFs).
Atmospheric correction for Interferometric Synthetic ApertureRadar (InSAR) technique is a set of different methods to remove artefact displacement from an interferogram caused by the effect of weather variables such as humidity, temperature, and pressure. An interferogram is generated by processing two synthetic-aperture radar images before and after a geophysical event like an earthquake. Corrections for atmospheric variations are an important stage of InSAR data processing in many study areas to measure surface displacement because relative humidity differences of 20% can cause inaccuracies of 10–14 cm InSAR due to varying delays in the radar signal. Overall, atmospheric correction methods can be divided into two categories: a) Using Atmospheric Phase Screen (APS) statistical properties and b) Using auxiliary (external) data such as GPS measurements, multi-spectral observations, local meteorological models, and global atmospheric models.








