Related Research Articles

A digital synthesizer is a synthesizer that uses digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to make musical sounds, in contrast to older analog synthesizers, which produce music using analog electronics, and samplers, which play back digital recordings of acoustic, electric, or electronic instruments. Some digital synthesizers emulate analog synthesizers, while others include sampling capability in addition to digital synthesis.
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a significant, and usually undesired, factor in the design of almost all communications links.
Karplus–Strong string synthesis is a method of physical modelling synthesis that loops a short waveform through a filtered delay line to simulate the sound of a hammered or plucked string or some types of percussion.

Super Audio CD (SACD) is an optical disc format for audio storage introduced in 1999. It was developed jointly by Sony and Philips Electronics and intended to be the successor to the compact disc (CD) format.

In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples". A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or space; this definition differs from the term's usage in statistics, which refers to a set of such values.

A sampler is an electronic musical instrument that records and plays back samples. Samples may comprise elements such as rhythm, melody, speech, sound effects or longer portions of music.
Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH is a German musical software and hardware company based in Hamburg. It develops software for writing, recording, arranging and editing music, most notably Cubase, Nuendo, and Dorico. It also designs audio and MIDI hardware interfaces, controllers, and iOS/Android music apps including Cubasis. Steinberg created several industry standard music technologies including the Virtual Studio Technology (VST) format for plug-ins and the ASIO protocol. Steinberg has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Yamaha since 2005.

The Roland MT-32 Multi-Timbre Sound Module is a MIDI synthesizer module first released in 1987 by Roland Corporation. It was originally marketed to amateur musicians as a budget external synthesizer with an original list price of $695. However, it became more famous along with its compatible modules as an early de facto standard in computer music. Since it was made prior to the release of the General MIDI standard, it uses its own proprietary format for MIDI file playback.
Decibels relative to full scale is a unit of measurement for amplitude levels in digital systems, such as pulse-code modulation (PCM), which have a defined maximum peak level. The unit is similar to the units dBov and decibels relative to overload (dBO).

The Yamaha TX16W is a rack-mount sampler sound module made by Yamaha.

In digital audio using pulse-code modulation (PCM), bit depth is the number of bits of information in each sample, and it directly corresponds to the resolution of each sample. Examples of bit depth include Compact Disc Digital Audio, which uses 16 bits per sample, and DVD-Audio and Blu-ray Disc, which can support up to 24 bits per sample.
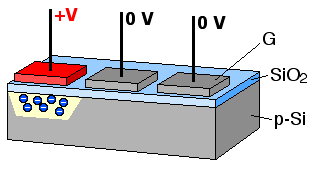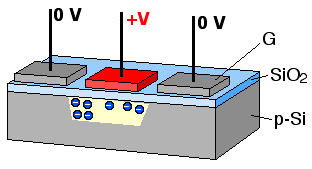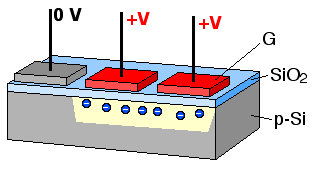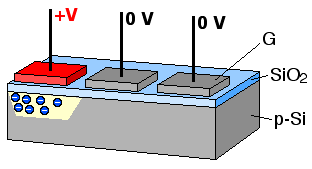
A bucket brigade or bucket-brigade device (BBD) is a discrete-time analogue delay line, developed in 1969 by F. Sangster and K. Teer of the Philips Research Labs in the Netherlands. It consists of a series of capacitance sections C0 to Cn. The stored analogue signal is moved along the line of capacitors, one step at each clock cycle. The name comes from analogy with the term bucket brigade, used for a line of people passing buckets of water.

The Korg DSS-1 is a polyphonic sampling synthesizer released by Korg in 1986. As Korg's initial entry into the sampling market, the DSS-1 combines sampling, additive synthesis, and waveform drawing with an analog signal path. The DSS-1 was released a time when major synthesizer manufacturers like Yamaha and Casio were beginning to explore sampling, an area of sound design dominated by companies like Fairlight, E-mu, and Ensoniq. Korg did not stay long in the sampling arena; the DSS-1 was the company's only sampler until 1998 when Korg introduced sampling options on their Triton and Trinity series of workstations.

aptX is a family of proprietary audio codec compression algorithms owned by Qualcomm, with a heavy emphasis on wireless audio applications.
The Yamaha YMF278B, also known as the OPL4, is a sound chip that incorporates both FM synthesis and sample-based synthesis by Yamaha.
AES67 is a technical standard for audio over IP and audio over Ethernet (AoE) interoperability. The standard was developed by the Audio Engineering Society and first published in September 2013. It is a layer 3 protocol suite based on existing standards and is designed to allow interoperability between various IP-based audio networking systems such as RAVENNA, Wheatnet, Livewire, Q-LAN and Dante.
The following is a comparison of audio over Ethernet and audio over IP audio network protocols and systems.
The Yamaha TMX is a drum trigger module that uses PCM samples. It was made in Japan in 1993. It is a 1U rackmountable unit that has a 40 X 2 LCD display.
Yamaha CP88 and Yamaha CP73 are professional stage pianos produced by Yamaha. These instruments are identical except for keyboard action and size. The instruments are designed to be played at live concerts on the stage, and are also suitable for recording studios due to their versatility of sound. As they are intended for professional use in locations with a preinstalled sound system, such as concert venues and recording studios, they do not have internal speakers, unlike the instruments intended for home use.
The OPL series are a family of sound chips developed by Yamaha. The OPL series are low-cost sound chips providing FM synthesis for use in computing, music and video game applications.
References
- ↑ "Yamaha D-1500". www.polynominal.com. Retrieved 2018-07-10.
- ↑ "Yamaha D1500 Digital Delay - Zikinf". ZIKINF (in French). Retrieved 2018-07-10.