 LRO image | |
| Coordinates | 14°36′N51°42′E / 14.6°N 51.7°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 36 km |
| Depth | None |
| Colongitude | 310° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Charles T. Yerkes |


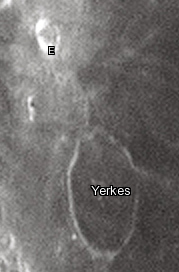
Yerkes is a lunar impact crater near the western edge of Mare Crisium. It was named after American financier Charles Yerkes. [1] To the east of Yerkes is the crater Picard, and farther to the north is Peirce.
Contents
In the past the interior of Yerkes has been almost completely inundated by lava, leaving only a shallow remnant of a rim above the mare. The rim is widest on the western and southern portions, and barely existent to the east, forming a thin curve in the surface. A low ridge runs from the north rim to Yerkes E in the north-northwest. The floor has a similar albedo to the nearby mare, so the feature is not sharply distinguished from the surroundings.