The Thermomicrobia is a group of thermophilic green non-sulfur bacteria. Based on species Thermomicrobium roseum and Sphaerobacter thermophilus, this bacteria class has the following description:

Lacticaseibacillus casei is an organism that belongs to the largest genus in the family Lactobacillaceae, a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that was previously classified as Lactobacillus casei. This bacteria has been identified as facultatively anaerobic or microaerophilic, acid-tolerant, non-spore-forming bacteria.
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) or Prokaryotic Code, formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC), governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea. It denotes the rules for naming taxa of bacteria, according to their relative rank. As such it is one of the nomenclature codes of biology.
Streptococcus equinus is a Gram-positive, nonhemolytic, nonpathogenic, lactic acid bacterium of the genus Streptococcus. It is the principal Streptococcus found in the alimentary canal of a horse, and makes up the majority of the bacterial flora in horse feces. Equivalence with Streptococcus bovis has been contested.
Agromyces is a genus in the phylum Actinomycetota (Bacteria).
Alistipes is a Gram-negative genus of rod-shaped anaerobic bacteria in the phylum Bacteroidota. When members of this genus colonize the human gastrointestinal (GI) tract, they provide protective effects against colitis, autism, and cirrhosis. However, this genus can also cause dysbiosis by contributing to anxiety, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, and hypertension. Showcasing priority effects in microbiome assembly, when infant GI tracts have bacteria of the species Staphylococcus but not the species Faecalibacterium, Alistipes species become less capable of colonization.
Yersinia aldovae is a species of bacteria that was originally described as Group X2 Yersinia enterocolitica. Its type strain is CNY 6005. Y. aldovae has been isolated from aquatic environments and soil, but it has not been associated with animal or human illnesses.
Psychrobacter is a genus of Gram-negative, osmotolerant, oxidase-positive, psychrophilic or psychrotolerant, aerobic bacteria which belong to the family Moraxellaceae and the class Gammaproteobacteria. The shape is typically cocci or coccobacilli. Some of those bacteria were isolated from humans and can cause humans infections such as endocarditis and peritonitis. This genus of bacteria is able to grow at temperatures between −10 and 42 °C. Rudi Rossau found through DNA-rRNA hybridization analysis that Psychrobacter belongs to the Moraxellaceae. The first species was described by Juni and Heym. Psychrobacter occur in wide range of moist, cold saline habitats, but they also occur in warm and slightly saline habitats.
Pontibacter is a strictly aerobic bacterial genus from the family of Cytophagaceae.
Yersinia entomophaga is a species of bacteria that was originally isolated from the diseased larvae of the New Zealand grass grub, Costelytra zealandica. The type strain is MH96. It is currently being studied for biological pest control of insect pests like the porina moth, Wiseana cervinata.
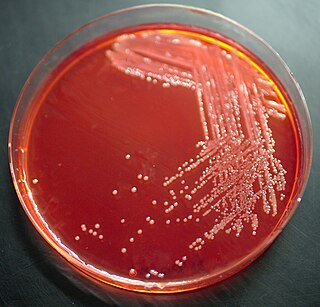
Yersinia hibernica is a species of Yersinia that was originally isolated in a pig-production environment. The type strain is CFS1934. This species has previously been misidentified as Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia kristensenii but it may be distinguished biochemically by lack of sucrose utilization. In addition to pig related environments, Y. hibernica has also been isolated from the feces of Rattus norvegicus and Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris.
Yersinia aleksiciae is a Gram-negative bacteria that is commonly isolated from the feces of warm-blooded animals such as humans, reindeers, and pigs. The type strain is Y159.
Yersinia rohdei is a Gram-negative species of Yersinia that was originally isolated from the feces of humans and dogs in addition to water surfaces. The type strain is ATCC 43380. Y. rohdei strains have also been isolated from reindeer and kelp gull from the sub-Antarctica South Georgia island.
Peribacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that exhibits Gram-positive or Gram-variable staining that belongs in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Peribacillus simplex.
Yersinia thracica is a Gram-negative species of enteric bacteria in the Yersinia genus that is closely related to Yersinia kristensenii. Reportedly, it has only been isolated in animals. The type strain, IP34646T, was isolated from diseased rainbow trout while other isolates are from birds, pig feces, and wild boars.
Yersinia vastinensis is a Gram-negative species of bacteria that has been isolated from human stools. All reported strains were isolated in France.
Yersinia proxima is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Yersiniaceae that is phylogenetically close to Yersinia enterocolitica. Members of this species has been found in human feces.
Yersinia alsatica is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Yersiniaceae that has been isolated from human stool.
Yersinia artesiana are short Gram-negative rod bacteria in the Yersiniaceae family that have been isolated from human stool.
Yersinia canariae is a Gram-negative species of Yersinia that was isolated from a human displaying symptoms of yersiniosis. Biochemically, it is similar to Yersinia enterocolitica but whole-genome sequencing data determined it is a distinct species.

