
Pedro Menéndez de Avilés was a Spanish admiral, explorer and conquistador from Avilés, in Asturias, Spain. He is notable for planning the first regular trans-oceanic convoys, which became known as the Spanish treasure fleet, and for founding St. Augustine, Florida, in 1565. This was the first successful European settlement in La Florida and the most significant city in the region for nearly three centuries.

Rene Goulaine de Laudonnière was a French Huguenot explorer and the founder of the French colony of Fort Caroline in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, a Huguenot, sent Jean Ribault and Laudonnière to explore potential sites in Florida suitable for settlement by the French Protestants.

Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June 1564, following King Charles IX's enlisting of Jean Ribault and his Huguenot settlers to stake a claim in French Florida ahead of Spain. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine in September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on 20 September. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.

San Juan del Puerto was a Spanish Franciscan mission founded before 1587 on Fort George Island, near the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. It was founded to serve the Saturiwa, a Timucua tribe who lived around the mouth of the St. Johns. It was organized by separating them into nine smaller villages. It has an important place in the study of the Timucua, as the place where Francisco Pareja undertook his work on the Timucua language.

The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River, at the head of Apalachee Bay, an area known as the Apalachee Province. They spoke a Muskogean language called Apalachee, which is now extinct.

Spanish Florida was the first major European land-claim and attempted settlement-area in northern America during the European Age of Discovery. La Florida formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and the Spanish Empire during Spanish colonization of the Americas. While its boundaries were never clearly or formally defined, the territory was initially much larger than the present-day state of Florida, extending over much of what is now the southeastern United States, including all of present-day Florida plus portions of Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Alabama, Mississippi, and the Florida Parishes of Louisiana. Spain based its claim to this vast area on several wide-ranging expeditions mounted during the 16th century. A number of missions, settlements, and small forts existed in the 16th and to a lesser extent in the 17th century; they were eventually abandoned due to pressure from the expanding English and French colonial settlements, the collapse of the native populations, and the general difficulty in becoming agriculturally or economically self-sufficient. By the 18th century, Spain's control over La Florida did not extend much beyond a handful of forts near St. Augustine, St. Marks, and Pensacola, all within the boundaries of present-day Florida.

Jacques Le Moyne de Morgues (c. 1533–1588) was a French artist and member of Jean Ribault's expedition to the New World. His depictions of Native American life and culture, colonial life, and plants are of extraordinary historical importance.
Timucua is a language isolate formerly spoken in northern and central Florida and southern Georgia by the Timucua peoples. Timucua was the primary language used in the area at the time of Spanish colonization in Florida. Differences among the nine or ten Timucua dialects were slight, and appeared to serve mostly to delineate band or tribal boundaries. Some linguists suggest that the Tawasa of what is now northern Alabama may have spoken Timucua, but this is disputed.

The Mocama were a Native American people who lived in the coastal areas of what are now northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. A Timucua group, they spoke the dialect known as Mocama, the best-attested dialect of the Timucua language. Their heartland extended from about the Altamaha River in Georgia to south of the mouth of the St. John's River, covering the Sea Islands and the inland waterways, Intracoastal. and much of present-day Jacksonville. At the time of contact with Europeans, there were two major chiefdoms among the Mocama, the Saturiwa and the Tacatacuru, each of which evidently had authority over multiple villages. The Saturiwa controlled chiefdoms stretching to modern day St. Augustine, but the native peoples of these chiefdoms have been identified by Pareja as speaking Agua Salada, which may have been a distinct dialect.

Saturiwa was chief of the Saturiwa tribe, a Timucua chiefdom centered at the mouth of the St. Johns River in Florida, during the 16th century. His main village, also known as Saturiwa, was located on the south bank of the river near its mouth, and according to French sources he was sovereign over thirty other village chiefs. Chief Saturiwa was a prominent figure in the early days of European settlement in Florida, forging friendly relations with the French Huguenot settlers, who founded Fort Caroline in his territory.

Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established a number of missions throughout La Florida in order to convert the Native Americans to Roman Catholicism, to facilitate control of the area, and to obstruct regional colonization by other Protestants, particularly, those from England and France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florida peninsula, and in the interior of Georgia and Alabama.

The Spanish missions in Georgia comprised a series of religious outposts established by Spanish Catholics in order to spread the Christian doctrine among the Guale and various Timucua peoples in southeastern Georgia.
Mayaca was the name used by the Spanish to refer to a Native American tribe in central Florida, to the principal village of that tribe and to the chief of that village in the 1560s. The Mayacas occupied an area in the upper St. Johns River valley just to the south of Lake George. According to Hernando de Escalante Fontaneda, the Mayaca language was related to that of the Ais, a tribe living along the Atlantic coast of Florida to the southeast of the Mayacas. The Mayacas were hunter-fisher-gatherers, and were not known to practice agriculture to any significant extent, unlike their neighbors to the north, the Utina, or Agua Dulce (Freshwater) Timucua. The Mayaca shared a ceramics tradition with the Freshwater Timucua, rather than the Ais.
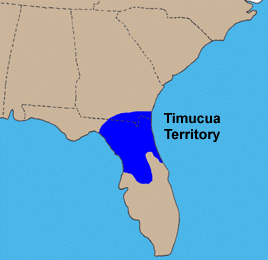
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about 19,200 square miles (50,000 km2) in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, 10.4 per square mile (4.0/km2) is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than a couple of points.

The Saturiwa were a Timucua chiefdom centered on the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. They were the largest and best attested chiefdom of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of Timucuan and lived in the coastal areas of present-day northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. They were a prominent political force in the early days of European settlement in Florida, forging friendly relations with the French Huguenot settlers at Fort Caroline in 1564 and later becoming heavily involved in the Spanish mission system.

The Agua Dulce or Agua Fresca (Freshwater) were a Timucua people of northeastern Florida. They lived in the St. Johns River watershed north of Lake George, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language also known as Agua Dulce.
Tacatacuru was a Timucua chiefdom located on Cumberland Island in what is now the U.S. state of Georgia in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was one of two chiefdoms of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of Timucuan and lived in the coastal areas of southeastern Georgia and northern Florida.

The Northern Utina, also known as the Timucua or simply Utina, were a Timucua people of northern Florida. They lived north of the Santa Fe River and east of the Suwannee River, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language known as "Timucua proper". They appear to have been closely associated with the Yustaga people, who lived on the other side of the Suwannee. The Northern Utina represented one of the most powerful tribal units in the region in the 16th and 17th centuries, and may have been organized as a loose chiefdom or confederation of smaller chiefdoms. The Fig Springs archaeological site may be the remains of their principal village, Ayacuto, and the later Spanish mission of San Martín de Timucua.
The Yustaga were a Timucua people of what is now northwestern Florida during the 16th and 17th centuries. The westernmost Timucua group, they lived between the Aucilla and Suwannee Rivers in the Florida Panhandle, just east of the Apalachee people. A dominant force in regional tribal politics, they may have been organized as a loose regional chiefdom consisting of up to eight smaller local chiefdoms.
St. Augustine, Florida, the oldest continuously occupied settlement of European origin in the continental United States, was founded in 1565 by Spanish admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés. The Spanish Crown issued an asiento to Menéndez, signed by King Philip II on March 20, 1565, granting him various titles, including that of adelantado of Florida, and expansive privileges to exploit the lands in the vast territory of Spanish Florida, called La Florida by the Spaniards. This contract directed Menéndez to explore the region's Atlantic coast and report on its features, with the object of finding a suitable location to establish a permanent colony from which the Spanish treasure fleet could be defended and Spain's claimed territories in North America protected against incursions by other European powers.














