Related Research Articles

San Juan del Puerto was a Spanish Franciscan mission founded before 1587 on Fort George Island, near the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. It was founded to serve the Saturiwa, a Timucua tribe who lived around the mouth of the St. Johns. It was organized by separating them into nine smaller villages. It has an important place in the study of the Timucua, as the place where Francisco Pareja undertook his work on the Timucua language.

Cumberland Island, in the southeastern United States, is the largest of the Sea Islands of Georgia. The long-staple Sea Island cotton was first grown here by a local family, the Millers, who helped Eli Whitney develop the cotton gin. With its unusual range of wildlife, the island has been declared a National Seashore. Little Cumberland Island is connected to the main island by a marsh.

The Icafui people were a Timucua people of southeastern Georgia, who were closely related if not synonymous with the Cascangue people. Exceptionally little is known about the Icafui, other than their general location and the fact that they spoke a dialect of Timucua called "Itafi" along with the Ibi.

The Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve is a U.S. National Preserve in Jacksonville, Florida. It comprises 46,000 acres (19,000 ha) of wetlands, waterways, and other habitats in northeastern Duval County. Managed by the National Park Service in cooperation with the City of Jacksonville and Florida State Parks, it includes natural and historic areas such as the Fort Caroline National Memorial and the Kingsley Plantation.

Utinahica was a town that was the site of a Spanish mission, Santa Isabel de Utinahica. It may have been the chief town of a Timucua tribe and chiefdom in the 17th century, but Hann says there is not enough known about it to be sure. The name means "lord's village". Utinahica, was called a "province" in one Spanish report. It was 30 leagues east of Arapaha, and 50 leagues northeast of the town of Tarihica in the Northern Utina Province. It was at or near where the Oconee and Ocmulgee rivers join to form the Altamaha River. The people of Utinahica apparently practiced a regional variant of the Lamar regional culture, unusual for a Timucuan-speaking people. Worth identifies the province of Utinahica with archaeological sites, including the Lind Landing site, Coffee Bluff site, and Bloodroot site, that have yielded artifacts of the Square Ground Lamar culture from before the 15th century until the middle of the 17th century. The Square Ground Lamar culture is otherwise associated with sites occupied by speakers of Muskogean languages. Archaeological sites identified with all other known Timucuan-speakers, with the possible exception of Guadalquini, do not have affinities with the Square Ground Lamar culture.
Guale was a historic Native American chiefdom of Mississippian culture peoples located along the coast of present-day Georgia and the Sea Islands. Spanish Florida established its Roman Catholic missionary system in the chiefdom in the late 16th century.

The Mocama were a Native American people who lived in the coastal areas of what are now northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. A Timucua group, they spoke the dialect known as Mocama, the best-attested dialect of the Timucua language. Their heartland extended from about the Altamaha River in Georgia to south of the mouth of the St. John's River, covering the Sea Islands and the inland waterways, Intracoastal. and much of present-day Jacksonville. At the time of contact with Europeans, there were two major chiefdoms among the Mocama, the Saturiwa and the Tacatacuru, each of which evidently had authority over multiple villages. The Saturiwa controlled chiefdoms stretching to modern day St. Augustine, but the native peoples of these chiefdoms have been identified by Pareja as speaking Agua Salada, which may have been a distinct dialect.

Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established a number of missions throughout Spanish Florida in order to convert the Native Americans to Roman Catholicism, to facilitate control of the area, and to obstruct regional colonization by other Protestants, particularly, those from England and France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florida peninsula, and in the interior of Georgia and Alabama.

The Spanish missions in Georgia comprised a series of religious outposts established by Spanish Catholics in order to spread the Christian doctrine among the Guale and various Timucua peoples in what is now southeastern Georgia.
San Lorenzo de Ibihica was a Spanish Franciscan mission built in the early 17th century in the southeast of the present-day U.S. state of Georgia. It was part of Spain's effort to colonize the region of Spanish Florida and convert the Timucua to Catholicism. It served the Ibi people, also known as the Yui or Ibihica, a Timucua group of the area.
Santa Catalina de Guale (1602-1702) was a Spanish Franciscan mission and town in Spanish Florida. Part of Spain's effort to convert the Native Americans to Catholicism, Santa Catalina served as the provincial headquarters of the Guale mission province. It also served various non-religious functions, such as providing food and labor for the colonial capital of St. Augustine. The mission was located on St. Catherines Island from 1602 to 1680, then on Sapelo Island from 1680 to 1684, and finally on Amelia Island from 1684 to 1702.
Francisco Pareja, OFM was a Franciscan missionary in Spanish Florida, where he was primarily assigned to Mission San Juan del Puerto. The Spaniard became a spokesman for the Franciscan community to the Spanish and colonial governments, was a leader among the missionaries, and served as custodio for the community in Florida. After the Franciscan organization was promoted to a provincia (province), Pareja was elected by his fellow missionaries as provincial in 1616.
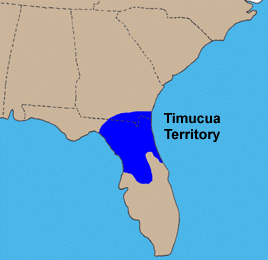
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about 19,200 square miles (50,000 km2) in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, 10.4 per square mile (4.0/km2) is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than a couple of points.

The Saturiwa were a Timucua chiefdom centered on the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. They were the largest and best attested chiefdom of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of Timucuan and lived in the coastal areas of present-day northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. They were a prominent political force in the early days of European settlement in Florida, forging friendly relations with the French Huguenot settlers at Fort Caroline in 1564 and later becoming heavily involved in the Spanish mission system.

The Agua Dulce or Agua Fresca (Freshwater) were a Timucua people of northeastern Florida. They lived in the St. Johns River watershed north of Lake George, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language also known as Agua Dulce.
Tacatacuru was a Timucua chiefdom located on Cumberland Island in what is now the U.S. state of Georgia in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was one of two chiefdoms of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of Timucuan and lived in the coastal areas of southeastern Georgia and northern Florida.

The Ibi, also known as the Yui or Ibihica, were a Timucua chiefdom in the present-day U.S. state of Georgia during the 16th and 17th centuries. They lived in southeastern Georgia, about 50 miles from the coast. Like their neighbors, the Icafui tribe, they spoke a dialect of the Timucua language called Itafi.
San Buenaventura de Guadalquini or San Buenaventura de Boadalquivi was a Spanish mission located on St. Simon's Island, Georgia, United States from between 1597 and 1609 until 1684, when pirates burned the mission and its town. The mission moved to the north side of the St. Johns River near its mouth, in present day Duval County, Florida under the name of Santa Cruz de Guadalquini or Santa Cruz y San Buenaventura de Guadalquini for a few years before merging with the mission San Juan del Puerto.

The Yufera were a Timucua people located in the present day US state of Georgia. They spoke a distinct dialect of Timucua. Little is known about the Yufera. They lived on or near the coast of Georgia near the mouths of the Satilla and St Marys Rivers. They likely participated in the Savannah or St Johns archaeological cultures.
References
- Milanich, Jerald T. (2000). "The Timucua Indians of Northern Florida and Southern Georgia". In Bonnie G. McEwan (ed.). Indians of the Greater Southeast: Historical Archaeology and Ethnohistory . University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-1778-5.