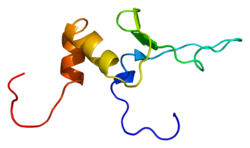
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein encoded by the SRY gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals. SRY is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).
HMGN proteins are members of the broader class of high mobility group (HMG) chromosomal proteins that are involved in regulation of transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair.

GATA-binding factor 1 or GATA-1 is the founding member of the GATA family of transcription factors. This protein is widely expressed throughout vertebrate species. In humans and mice, it is encoded by the GATA1 and Gata1 genes, respectively. These genes are located on the X chromosome in both species.
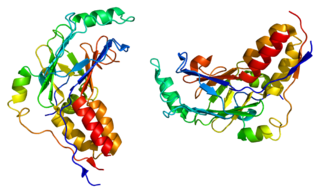
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) also known as core-binding factor subunit alpha-1 (CBF-alpha-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUNX2 gene. RUNX2 is a key transcription factor associated with osteoblast differentiation.

Antigen Kiel 67, also known as Ki-67 or MKI67, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MKI67 gene.
Chromatin remodeling is the dynamic modification of chromatin architecture to allow access of condensed genomic DNA to the regulatory transcription machinery proteins, and thereby control gene expression. Such remodeling is principally carried out by 1) covalent histone modifications by specific enzymes, e.g., histone acetyltransferases (HATs), deacetylases, methyltransferases, and kinases, and 2) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes which either move, eject or restructure nucleosomes. Besides actively regulating gene expression, dynamic remodeling of chromatin imparts an epigenetic regulatory role in several key biological processes, egg cells DNA replication and repair; apoptosis; chromosome segregation as well as development and pluripotency. Aberrations in chromatin remodeling proteins are found to be associated with human diseases, including cancer. Targeting chromatin remodeling pathways is currently evolving as a major therapeutic strategy in the treatment of several cancers.

ETS translocation variant 4 (ETV4), also known as polyoma enhancer activator 3 (PEA3), is a member of the PEA3 subfamily of Ets transcription factors.

Flap endonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FEN1 gene.

GATA3 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the GATA3 gene. Studies in animal models and humans indicate that it controls the expression of a wide range of biologically and clinically important genes.

Transcription factor GATA-6, also known as GATA-binding factor 6 (GATA6), is protein that in humans is encoded by the GATA6 gene. The gene product preferentially binds (A/T/C)GAT(A/T)(A) of the consensus binding sequence.

T-box transcription factor TBX3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX3 gene.

ID4 is a protein coding gene. In humans, it encodes for the protein known as DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-4. This protein is known to be involved in the regulation of many cellular processes during both prenatal development and tumorigenesis. This is inclusive of embryonic cellular growth, senescence, cellular differentiation, apoptosis, and as an oncogene in angiogenesis.

The LBH gene is a highly conserved human gene that produces the LBH protein, a transcription co-factor in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Upon transcriptional activation of β-catenin, LBH goes on to act as a regulator of cell proliferation and differentiation through multiple transcriptional targets. The gene is located on the p arm of chromosome 2 and is roughly 28 kb long. Current ongoing studies are examining its role in developmental and oncological settings.

Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 2 (SMC-2), also known as chromosome-associated protein E (CAP-E), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMC2 gene. SMC2 is part of the SMC protein family and is a core subunit of condensin I and II, large protein complexes involved in chromosome condensation, overall organization. Several studies have demonstrated the necessity of SMC2 for cell division and proliferation.

Transcription factor AP-2 gamma also known as AP2-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2C gene. AP2-gamma is a member of the activating protein 2 family of transcription factors.

Short-stature homeobox 2, also known as homeobox protein Og12X or paired-related homeobox protein SHOT, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHOX2 gene.
Genome instability refers to a high frequency of mutations within the genome of a cellular lineage. These mutations can include changes in nucleic acid sequences, chromosomal rearrangements or aneuploidy. Genome instability does occur in bacteria. In multicellular organisms genome instability is central to carcinogenesis, and in humans it is also a factor in some neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or the neuromuscular disease myotonic dystrophy.