A chemical database is a database specifically designed to store chemical information. This information is about chemical and crystal structures, spectra, reactions and syntheses, and thermophysical data.

In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Cheminformatics refers to the use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "in silico" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such in silico techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied.

Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.

High-throughput screening (HTS) is a method for scientific discovery especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology, materials science and chemistry. Using robotics, data processing/control software, liquid handling devices, and sensitive detectors, high-throughput screening allows a researcher to quickly conduct millions of chemical, genetic, or pharmacological tests. Through this process one can quickly recognize active compounds, antibodies, or genes that modulate a particular biomolecular pathway. The results of these experiments provide starting points for drug design and for understanding the noninteraction or role of a particular location.

Medicinal or pharmaceutical chemistry is a scientific discipline at the intersection of chemistry and pharmacy involved with designing and developing pharmaceutical drugs. Medicinal chemistry involves the identification, synthesis and development of new chemical entities suitable for therapeutic use. It also includes the study of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR).

A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.

Chemical biology is a scientific discipline between the fields of chemistry and biology. The discipline involves the application of chemical techniques, analysis, and often small molecules produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. Although often confused with biochemistry, which studies the chemistry of biomolecules and regulation of biochemical pathways within and between cells, chemical biology remains distinct by focusing on the application of chemical tools to address biological questions.

Stuart Schreiber is an American chemist who is the Morris Loeb Research Professor at Harvard University, a co-founder of the Broad Institute, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator, Emeritus, and a member of the National Academy of Sciences and National Academy of Medicine. He currently leads Arena BioWorks.

Chemogenomics, or chemical genomics, is the systematic screening of targeted chemical libraries of small molecules against individual drug target families with the ultimate goal of identification of novel drugs and drug targets. Typically some members of a target library have been well characterized where both the function has been determined and compounds that modulate the function of those targets have been identified. Other members of the target family may have unknown function with no known ligands and hence are classified as orphan receptors. By identifying screening hits that modulate the activity of the less well characterized members of the target family, the function of these novel targets can be elucidated. Furthermore, the hits for these targets can be used as a starting point for drug discovery. The completion of the human genome project has provided an abundance of potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Chemogenomics strives to study the intersection of all possible drugs on all of these potential targets.

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction.

Substructure search (SSS) is a method to retrieve from a database only those chemicals matching a pattern of atoms and bonds which a user specifies. It is an application of graph theory, specifically subgraph matching in which the query is a hydrogen-depleted molecular graph. The mathematical foundations for the method were laid in the 1870s, when it was suggested that chemical structure drawings were equivalent to graphs with atoms as vertices and bonds as edges. SSS is now a standard part of cheminformatics and is widely used by pharmaceutical chemists in drug discovery.
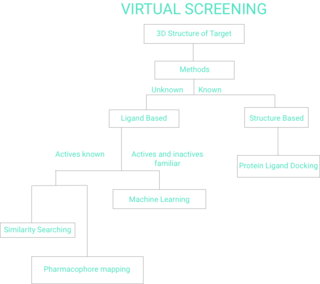
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or enzyme.
Hit to lead (H2L) also known as lead generation is a stage in early drug discovery where small molecule hits from a high throughput screen (HTS) are evaluated and undergo limited optimization to identify promising lead compounds. These lead compounds undergo more extensive optimization in a subsequent step of drug discovery called lead optimization (LO). The drug discovery process generally follows the following path that includes a hit to lead stage:
Compound management in the field of drug discovery refers to the systematic collection, storage, retrieval, and quality control of small molecule chemical compounds used in high-throughput screening and other research activities to identify hits that can be developed into candidate drugs.
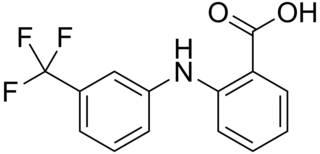
Flufenamic acid (FFA) is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Like other members of the class, it is a cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor, preventing the formation of prostaglandins. FFA is known to bind to and reduce the activity of prostaglandin F synthase and activate TRPC6.

Chemical similarity refers to the similarity of chemical elements, molecules or chemical compounds with respect to either structural or functional qualities, i.e. the effect that the chemical compound has on reaction partners in inorganic or biological settings. Biological effects and thus also similarity of effects are usually quantified using the biological activity of a compound. In general terms, function can be related to the chemical activity of compounds.
Topological inhibitors are rigid three-dimensional molecules of inorganic, organic, and hybrid compounds that form multicentered supramolecular interactions in vacant cavities of protein macromolecules and their complexes.
Pan-assay interference compounds (PAINS) are chemical compounds that often give false positive results in high-throughput screens. PAINS tend to react nonspecifically with numerous biological targets rather than specifically affecting one desired target. A number of disruptive functional groups are shared by many PAINS.











