
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and behavior, and flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and are never resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months or one month. Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood, anxiety, and substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD).

Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers to refer to reduced motivation, reduced anticipatory pleasure (wanting), reduced consummatory pleasure (liking), and deficits in reinforcement learning. In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), anhedonia is a component of depressive disorders, substance-related disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders, where it is defined by either a reduced ability to experience pleasure, or a diminished interest in engaging in previously pleasurable activities. While the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) does not explicitly mention anhedonia, the depressive symptom analogous to anhedonia as described in the DSM-5 is a loss of interest or pleasure.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Arecoline is a nicotinic acid-based mild parasympathomimetic stimulant alkaloid found in the areca nut, the fruit of the areca palm. It is an odourless oily liquid. It can bring a sense of enhanced alertness and energy along with mild feelings of euphoria and relaxation.

A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, also simply known as a muscarinic agonist or as a muscarinic agent, is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFAR1), also known as G-protein coupled receptor 40 (GPR40), is a rhodopsin-like G-protein coupled receptor that is coded by the FFAR1 gene. This gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 19 at position 13.12. G protein-coupled receptors reside on their parent cells' surface membranes, bind any one of the specific set of ligands that they recognize, and thereby are activated to trigger certain responses in their parent cells. FFAR1 is a member of a small family of structurally and functionally related GPRs termed free fatty acid receptors (FFARs). This family includes at least three other FFARs viz., FFAR2, FFAR3, and FFAR4. FFARs bind and thereby are activated by certain fatty acids.

Orexin receptor type 2 (Ox2R or OX2), also known as hypocretin receptor type 2 (HcrtR2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR2 gene. It should not be confused for the protein CD200R1 which shares the alias OX2R but is a distinct, unrelated gene located on the human chromosome 3.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

G protein-coupled receptor 119 also known as GPR119 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the GPR119 gene.

G-protein coupled receptor 139 (GPC139) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR139 gene. Research has shown that mice with loss of GCP139 experience schizophrenia-like symptomatology that is rescued with the dopamine receptor antagonist haloperidol and the μ-opioid receptor antagonist naltrexone.

Trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the TAAR1 gene.
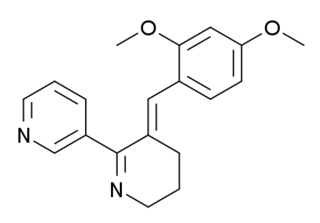
GTS-21 is a drug that has been shown to enhance memory and cognitive function. It has been studied for its potential therapeutic uses, particularly in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

Zacopride is a potent antagonist at the 5-HT3 receptor and an agonist at the 5-HT4 receptor. It has anxiolytic and nootropic effects in animal models, with the (R)-(+)-enantiomer being the more active form. It also has antiemetic and pro-respiratory effects, both reducing sleep apnea and reversing opioid-induced respiratory depression in animal studies. Early animal trials have also revealed that administration of zacopride can reduce preference for and consumption of ethanol.

F-15,599, also known as NLX-101, is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist. In addition, it displays functional selectivity, or biased agonism, by preferentially activating postsynaptic serotonin 5-HT1A receptors over somatodendritic serotonin 5-HT1A autoreceptors. The drug has been investigated for potential use as a pharmaceutical drug in the treatment of conditions including depression, schizophrenia, cognitive disorders, Rett syndrome, and fragile X syndrome.
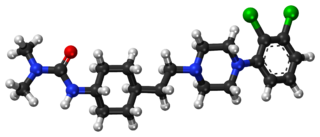
Cariprazine, sold under the brand name Vraylar among others, is an atypical antipsychotic developed by Gedeon Richter, which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is also prescribed as an add-on treatment for bipolar depression and major depressive disorder. Cariprazine acts primarily as a D3 and D2 receptor partial agonist, with a preference for the D3 receptor. It is a partial agonist at the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor and acts as an antagonist at 5-HT2B and 5-HT2A receptors. It is taken by mouth. The most prevalent side effects include nausea, mild sedation, fatigue, and dizziness. At higher dosages, there is an increased risk for restlessness, insomnia, and tremors.
Sexual anhedonia, also known as pleasure dissociative orgasmic disorder, is a condition in which an individual cannot feel pleasure from an orgasm. It is thought to be a variant of hypoactive sexual desire disorder.

A motivation-enhancing drug, also known as a pro-motivational drug, is a drug which increases motivation. Drugs enhancing motivation can be used in the treatment of motivational deficits, for instance in depression, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They can also be used in the treatment of disorders of diminished motivation (DDMs), including apathy, abulia, and akinetic mutism, disorders that can be caused by conditions like stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), and neurodegenerative diseases. Motivation-enhancing drugs are used non-medically by healthy people to increase motivation and productivity as well, for instance in educational contexts.


















