Related Research Articles

Meropeidae is a family of tiny scorpionflies within the order Mecoptera with only three living species, commonly referred to as "earwigflies". These include the North American Merope tuber, the Western Australian Austromerope poultoni, and the recently discovered South American A. brasiliensis. The biology of these species is essentially unknown, and their larvae have never been seen. The disjunct distribution suggests a common origin before the breakup of the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea. There are two undisputed extinct genera, Boreomerope antiqua known from an isolated wing found in the Middle Jurassic Itat Formation of Siberia and Burmomerope with three species from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber. As such, the extant members of this family can be considered living fossils. These insects are also of interest due to their presumed basal position in the order Mecoptera. Thaumatomerope with four described species all from the Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan has historically sometimes been included within the family, it was placed into its own monotypic family, "Thaumatomeropidae." in 2002.

Protorosaurus is a genus of lizard-like early reptiles. Members of the genus lived during the late Permian period in what is now Germany and Great Britain. Once believed to have been an ancestor to lizards, Protorosaurus is now known to be one of the oldest and most primitive members of Archosauromorpha, the group that would eventually lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs.
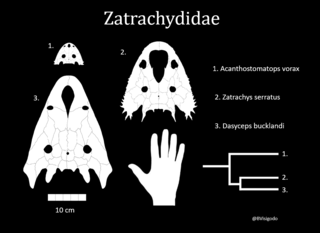
Zatracheidae is a family of Late Carboniferous and Early Permian temnospondyl amphibians known from North America and Europe. Zatracheidids are distinguished by lateral (sideways) bony protuberances of the quadratojugal bone of the skull, and a large opening in the snout called the internarial fontanelle that is bordered by enlarged premaxillae. The skull is flattened, with small orbits or eye sockets set far back. The opening in the snout may have housed a gland for producing a sticky substance so that prey would adhere to the tongue. If so, this indicates that these animals spent a large part of their time on land.

Shastasauridae is an extinct family of Triassic ichthyosaurs that includes the genera ShastasaurusShonisaurus and Himalayasaurus. Many other Triassic ichthyosaurs have been assigned to Shastasauridae in the past, but recent phylogenetic analyses suggest that these species form an evolutionary grade of early ichthyosaurs rather than a true clade or evolutionary grouping that can be called Shastasauridae. Shastasauridae was named by American paleontologist John Campbell Merriam in 1895 along with the newly described genus Shastasaurus. In 1999, Ryosuke Motani erected the clade Shastasauria to include Shastasaurus, Shonisaurus, and several other traditional shastasaurids, defining it as a stem-based taxon including "all merriamosaurians more closely related to Shastasaurus pacificus than to Ichthyosaurus communis." He also redefined Shastasauridae as a node-based taxon including "the last common ancestor of Shastasaurus pacificus and Besanosaurus leptorhynchus, and all its descendants" and Shastasaurinae, which Merriam named in 1908, as a stem taxon including "the last common ancestor of Shastasaurus and Shonisaurus, and all its descendants." In an alternative classification scheme, paleontologist Michael Maisch restricted Shastasauridae to the genus Shastasaurus and placed Shonisaurus and Besanosaurus in their own monotypic families, Shonisauridae and Besanosauridae.

Willwerathia is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of horseshoe crab-like fossil chelicerate arthropods. Willwerathia known only by one species, Willwerathia laticeps, discovered in deposits of the Devonian period from the Rhenish Slate Mountains of Germany.
The Obernkirchen Sandstein or Obernkirchen Sandstone is a geological unit in Lower Saxony, Germany whose strata date back to the Early Cretaceous. The remains of the dinosaur Stenopelix and numerous dinosaur tracks are known from the unit. The unit is a thin interval within the Bückeberg Formation As its name would suggest the lithology primarily consists of sandstone with thin intercalations of coal. This was deposited in a sandy barrier to lagoonal complex setting. The unit has historically been extensively quarried for its high quality building stone, which has been used as far away as Jakarta.

Weinbergina is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. Fossils of the single and type species, W. opitzi, have been discovered in deposits of the Devonian period in the Hunsrück Slate, Germany.
Gobiops is an extinct genus of temnospondyl from the Jurassic of Mongolia, China, and possibly Kyrgyzstan. The genus is represented by a single species, Gobiops desertus. It was named in 1991 from the Late Jurassic Shar Teeg Beds of Mongolia. Additional material was described in 2005 from the Middle Jurassic Toutunhe Formation in the Junggar Basin of China. Gobiops belongs to the family Brachyopidae. The poorly known genus Ferganobatrachus, named in 1990 from Shar Teeg, is probably synonymous with Gobiops.

Synziphosurina is a paraphyletic group of chelicerate arthropods previously thought to be basal horseshoe crabs (Xiphosura). It was later identified as a grade composed of various basal euchelicerates, eventually excluded form the monophyletic Xiphosura sensu stricto and only regarded as horseshoe crabs under a broader sense. Synziphosurines survived at least since early Ordovician to early Carboniferous in ages, with most species are known from the in-between Silurian strata.
The Balabansai Formation is a geological formation in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan whose strata date back to the Bathonian and Callovian stages of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. The lithology primarily consists of variegated sandstones, siltstones, claystones, and rare gravels and marls. Many taxa have been found in the formation, including amphibians and mammals

The Qigu Formation is a Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) geologic formation in the Southern Junggar Basin in China. Indeterminate Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, including theropod teeth and a fibula. a stegosaur dorsal vertebra and a Eusauropod tooth. Xinjiangtitan was erroneously thought to be from this formation, but it is actually from the older Qiketai Formation, which is in a different basin. The term "Qigu Formation" is also used to sediments of equivalent age in the Turpan Basin, but this might better be treated as a separate formation. It is laterally equivalent to the Shishugou Formation.
Milnererpeton is an extinct genus of branchiosaurid temnospondyl amphibian from the Late Carboniferous of New Mexico. The genus was originally described in 1996 under the name Milneria, but since the name Milneria is preoccupied by a genus of mollusks, the name Milnererpeton was proposed as a replacement in 2002. The only species is Milnererpeton huberi.
This list, 2013 in molluscan paleontology, is a list of new taxa of ammonites and other fossil cephalopods, as well as fossil gastropods, bivalves and other molluscs that have been described during the year 2013.

The Bückeberg Formation is a geologic formation and Lagerstätte in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Berriasian of the Cretaceous period. The Bückeberg Formation has previously been considered to constitute the "German Wealden" in reference to its similarity to the Wealden Group in the United Kingdom. More recently it has been considered a group, containing the Isterberg and Deister Formations. The plesiosaur Brancasaurus, an indeterminate ankylosaur referred to Hylaeosaurus, the turtle Dorsetochelys are known from the formation.

Lyelliceratidae is a family of ammonites belonging to the superfamily Acanthoceratoidea.
Chromatogenys is an extinct genus of Scincomorph lizard from the Santonian of Hungary, containing the species C. tiliquoides. It is known from the Csehbánya Formation with the remains consisting of a partial right mandible, the name coming from the vibrant colours on the preserved specimen. The dentition is durophagous, and the animal likely ate hard shelled prey.
Varavudh Suteethorn, or Warawut Suteethorn is a Thai geologist and palaeontologist. He is the current director of the Palaeontological Research and Education Centre, Mahasarakham University. He is best known for his work on vertebrate palaeontology in northeastern Thailand, having contributed to the discovery of many fossil taxa and dig sites in the Khorat Plateau, as a part of a long-standing collaboration between Thai and French scientists.
Glaurung is an extinct genus of weigeltisaurid reptile from the Upper Permian of Germany. The only known species is Glaurung schneideri. Originally considered a specimen of Coelurosauravus, a later study named it as a new genus after noting that it had several unique characteristics relative to other weigeltisaurids. These characteristics included a low skull, small eyes, smooth parietal and squamosal bones, and spiny jugal bones.
Parelasmotherium is an extinct genus of rhinos that lived in Northern China about 11.1 million years ago in the late Miocene. With its large body and its grazing teeth, it belonged to the subfamily Elasmotheriini and was a relative of the later Elasmotherium, which was widespread over large parts of northern Asia in the Pleistocene.
References
- ↑ Kennedy, W. J.; Klinger, H. C. (1993). "On the affinities of Zuluscaphites van Hoepen 1955 (Cretaceous Ammonoidea) from the Albian of Zululand, South Africa". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 67 (1–2): 63–67. doi:10.1007/BF02985870. ISSN 0031-0220. S2CID 130869806.
- ↑ "Zuluscaphites". fossilworks.org. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ↑ "Zuluscaphites orycteropusi". fossilworks.org. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ↑ Kennedy, W. J.; Klinger, H. C. (1993-06-01). "On the affinities ofZuluscaphites van Hoepen 1955 (Cretaceous Ammonoidea) from the Albian of Zululand, South Africa". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 67 (1): 63–67. doi:10.1007/BF02985870. ISSN 0031-0220. S2CID 130869806.