Related Research Articles
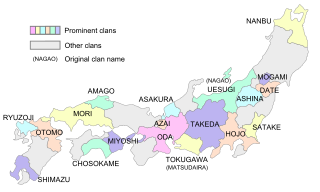
Daimyo were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the kuge. In the term, dai (大) means 'large', and myō stands for myōden (名田), meaning 'private land'.
The Hosokawa clan is a Japanese Samurai kin group or clan.

Akechi Mitsuhide, first called Jūbei from his clan and later Koretō Hyūga no Kami (惟任日向守) from his title, was a Japanese samurai general of the Sengoku period. He is best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later, one of the trusted general under daimyō Oda Nobunaga during his war of political unification in Japan.

The Nanboku-chō period, spanning from 1336 to 1392, was a period that occurred during the formative years of the Muromachi (Ashikaga) shogunate of Japanese history.

The Ōnin War, also known as the Upheaval of Ōnin and Ōnin-Bunmei war, was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. Ōnin refers to the Japanese era during which the war started; the war ended during the Bunmei era. A dispute between a high official, Hosokawa Katsumoto, and a regional lord, Yamana Sōzen, escalated into a nationwide civil war involving the Ashikaga shogunate and a number of daimyō in many regions of Japan.

Hosokawa Katsumoto was one of the Kanrei, the Deputies to the Shōgun, during Japan's Muromachi period. He is famous for his involvement in the creation of Ryōan-ji, a temple famous for its rock garden, and for his involvement in the Ōnin War, which sparked the 130-year Sengoku period. His childhood name was Sumiakamaru (聡明丸).

Yamana Sōzen was originally Yamana Mochitoyo before becoming a monk. Due to his red complexion, he was sometimes known as Aka-nyūdō, "the Red Monk". He was one of the daimyōs who fought against Hosokawa Katsumoto during the Ōnin War in Heian-kyō.

Hosokawa Sumimoto was a samurai commander in the Muromachi period during the 16th century of Japan.

Hosokawa Takakuni was the most powerful military commander in the Muromachi period under Ashikaga Yoshiharu, the twelfth shōgun. His father was Hosokawa Masaharu, a member of the branch of the Hosokawa clan. His childhood name was Rokuro (六郎).

Ashikaga Yoshimi was the brother of Shōgun Ashikaga Yoshimasa, and a rival for the succession in a dispute that would lead to the Ōnin War.

Ōuchi clan was one of the most powerful and important families in Western Japan during the reign of the Ashikaga shogunate in the 12th to 14th centuries. Their domains, ruled from the castle town of Yamaguchi, comprised six provinces at their height, and the Ōuchi played a major role in supporting the Ashikaga in the Nanboku-cho Wars against the Imperial Court. The Ōuchi remained powerful up until the 1550s, when they were eclipsed by their vassals, the Mōri clan.

Hosakawa Masamoto was a deputy-shōgun of the Hosokawa clan of Japan, and son of Hosokawa Katsumoto. Masamoto was appointed to this rank during 1486. For a brief period this title was lost by Hatakeyama Masanaga but was regained in time. When Ashikaga Yoshihisa died childless during the year of 1489, Masamoto supported the nomination of Ashikaga Yoshizumi as successor in opposition to Ashikaga Yoshitane. Masamoto thought that the post of deputy-shogun would return to Hosokawa Masanaga due to Yoshitane's closeness with Hatakeyama Masanaga and his own objections to Yoshitane's rise. During Masanaga's struggle with a rival branch of the Hatakeyama clan, Yoshitane led troops to the assistance of Masanaga. Masamoto then assisted his force to the Hatakeyama, ultimately defeating those of Masanaga and Yoshitane. Masanaga killed himself during the battle and Yoshitane became a prisoner at Kyoto. His childhood name was Sumiakamaru (聡明丸).

Ōuchi Yoshioki became a sengoku daimyō of Suō Province and served as the 15th head of the Ōuchi clan. Yoshioki was born early in the Sengoku period, the son of Ōuchi Masahiro, shugo of Suō Province and the 14th head of the Ōuchi clan. The first character in Yoshioki's name originated from Ashikaga Yoshihisa, the ninth shōgun in the Muromachi bakufu. In 1492, Masahiro ordered Yoshioki to join the battle against Rokkaku Takayori, a sengoku daimyō from southern Ōmi Province. In the midst of this engagement in 1493, an incident known as the Meiō no seihen occurred, by which Hosokawa Masamoto, a kanrei, or deputy, held the shōgun, Ashikaga Yoshiki, in confinement. Yoshioki withdrew his men from the battle to Hyōgo in Settsu Province to wait for the outcome of the event, which resulted in Yoshiki being deposed and replaced by Ashikaga Yoshizumi. Yoshioki's younger sister was abducted while staying in Kyōto in an area under the control of Takeda Motonobu, an ally of Hosokawa Masamoto. Masamoto took her hostage as leverage against Masahiro in his support for Yoshiki. Masahiro then ordered close associates of Yoshioki to commit seppuku. This may have been as retribution for what he viewed as Yoshioki's tepid response to the pressure exerted upon him by Masamoto and his retainers. Nevertheless, Yoshioki's decision to withdraw his forces was well-received by the hikan, or administrators, in his birthplace of Kyōto, building relationships that benefit him later at the time of his succession to Masahiro.

Kusunoki Masanori was a samurai who fought for the Southern Court in Japan's Nanboku-chō Wars, and is famed for his skills as a leader and military strategist, though he later sought a diplomatic solution and was regarded a traitor by many of his comrades. He was the brother of Kusunoki Masatsura and Kusunoki Masatoki, and son of Kusunoki Masashige.

Hosokawa Yoriyuki was a samurai of the Hosokawa clan, and prominent government minister under the Ashikaga shogunate, serving as Kyoto Kanrei from 1367 to 1379. The first to hold this post, he solidified the power of the shogunate, as well as elements of its administrative organization. He was also Constable (Shugo) of the provinces of Sanuki, Tosa, and Settsu. His childhood name was Yakuro (弥九郎).

Miyoshi clan is a Japanese family descended from Emperor Seiwa (850–880) and the Minamoto clan (Seiwa-Genji). They were a cadet branch of the Ogasawara clan and the Takeda clan.
The Ningbo Incident was a 1523 brawl between trade representatives of two Japanese daimyō clans — the Ōuchi and the Hosokawa — in the Ming Chinese city of Ningbo. The Ōuchi pillaged and harmed local residents, causing massive damage. The turmoil resulted in the interruption of the Ming-Japanese trade and led to a surge in piratical (wokou) activity on the Chinese coast. The episode is also known by the names Ningbo Tribute Conflict (寧波争貢事件), Mingzhou Incident (明州之亂), or the Sōsetsu Incident (宗設之亂).

Ashikaga Mitsukane (1378–1409) was a Nanboku-chō period warrior, and the Kamakura-fu's third Kantō kubō,. Being the eldest son, he succeeded his father Ujimitsu in 1398 at the age of 21 when he died during an epidemic. Like his father, Mitsukane aspired more or less openly to the shogunate and, like him and his successors, failed to obtain it. He died suddenly at the age of 32.
Hino Tomiko was a prominent figure during the Muromachi period and the beginning of the Sengoku period. She was daughter to Hino Shigemasa and was the official wife of Ashikaga Yoshimasa, the eighth shōgun of the Ashikaga shogunate, and the mother of Ashikaga Yoshihisa, the ninth shōgun. Her efforts during the succession dispute are seen as one of the causes of the Ōnin War and led to the beginning of the Sengoku period.

Kagamiyama Castle was a yamajiro-style Japanese castle located in what is today part of the city of Higashihiroshima in Hiroshima Prefecture. Its ruins have been protected by the central government as a National Historic Site since 1957.
References
- ↑ Sansom, George (1961). A History of Japan, 1334–1615. Stanford University Press. pp. 223–228. ISBN 0804705259.