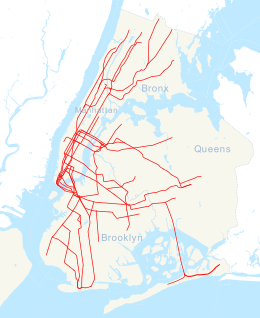
The Dual Contracts, also known as the Dual Subway System, were contracts for the construction and/or rehabilitation and operation of rapid transit lines in the City of New York. The contracts were signed on March 19, 1913, by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company. As part of the Dual Contracts, the IRT and BRT would build or upgrade several subway lines in New York City, then operate them for 49 years.

The Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) was the private operator of New York City's original underground subway line that opened in 1904, as well as earlier elevated railways and additional rapid transit lines in New York City. The IRT was purchased by the city in June 1940, along with the younger BMT and IND systems, to form the modern New York City Subway. The former IRT lines are now the A Division or IRT Division of the Subway.

The St. Lawrence Avenue station is a local station on the IRT Pelham Line of the New York City Subway. The station, served by the 6 train at all times, is located at the intersection of St. Lawrence Avenue and Westchester Avenue in the Parkchester neighborhood of the Bronx.

The Woodlawn station is the northern terminal of the New York City Subway's IRT Jerome Avenue Line. The station is located at the intersection of Bainbridge and Jerome Avenues, outside Woodlawn Cemetery. Despite the station name, this intersection is in the Norwood neighborhood of the Bronx, and not in Woodlawn. It is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1918.

The Mosholu Parkway station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Mosholu Parkway and Jerome Avenue in the Bedford Park and Norwood neighborhoods of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times.

The Bedford Park Boulevard–Lehman College station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Bedford Park Boulevard immediately west of Jerome Avenue in the Bedford Park neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. It is also the only station on the Jerome Avenue Line north of 170th Street that is not located above Jerome Avenue. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1918.

The Kingsbridge Road station is a local station on the elevated IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Kingsbridge Road and Jerome Avenue in the Kingsbridge Heights neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The Fordham Road station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Fordham Road and Jerome Avenue in the University Heights and Fordham Heights neighborhoods of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The 183rd Street station is a local station on the elevated IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 183rd Street and Jerome Avenue in the Univeristy Heights and Fordham Heights neighborhoods of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The Burnside Avenue station is an express station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Burnside and Jerome Avenues in the Morris Heights and Unniversity Heights neighborhoods of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. It also serves as a rush hour short turn northern terminal for select 4 trains from Crown Heights–Utica Avenue.

The 176th Street station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 176th Street and Jerome Avenue in the Morris Heights neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The Mount Eden Avenue station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of Mount Eden and Jerome Avenues in the Highbridge neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The 170th Street station is a local station on the IRT Jerome Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 170th Street and Jerome Avenue in the Highbridge neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 4 train at all times. This station was constructed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company as part of the Dual Contracts and opened in 1917.

The IRT Ninth Avenue Line, often called the Ninth Avenue Elevated or Ninth Avenue El, was the first elevated railway in New York City. It opened in July 1868 as the West Side and Yonkers Patent Railway, as an experimental single-track cable-powered elevated railway from Battery Place, at the south end of Manhattan Island, northward up Greenwich Street to Cortlandt Street. By 1879 the line was extended to the Harlem River at 155th Street. It was electrified and taken over by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company in 1903.

The 149th Street–Grand Concourse station is a New York City Subway station complex shared by the IRT Jerome Avenue Line and the IRT White Plains Road Line. It is located at East 149th Street and Grand Concourse in Mott Haven, Melrose and Concourse in the Bronx. The complex is served by the 2 and 4 trains at all times, and by the 5 train at all times except late nights.

The White Plains Road Line is a rapid transit line of the A Division of the New York City Subway serving the central Bronx. It is mostly elevated and served both subway and elevated trains until 1952. The original part of the line, the part opened as part of the first subway was called the West Farms Division, and the extension north to 241st Street as part of the Dual Contracts was called the White Plains Road Line. Eventually, however, the two parts came to be known as the White Plains Road Line.
The IRT Jerome Avenue Line, also unofficially known as IRT Woodlawn Line, is an A Division New York City Subway line mostly along Jerome Avenue in the Bronx. Originally an Interborough Rapid Transit Company-operated route, it was built as part of the Dual Contracts expansion and opened in 1917 and 1918. It is both elevated and underground, with 161st Street–Yankee Stadium being the southernmost elevated station. The line has three tracks from south of the Woodlawn station to the 138th Street–Grand Concourse station. The Woodlawn Line also has a connection to the Jerome Yard, where 4 trains are stored, just north of the Bedford Park Boulevard–Lehman College station.

The 161st Street–Yankee Stadium station is a New York City Subway station complex shared by the elevated IRT Jerome Avenue Line and the underground IND Concourse Line. It is located at the intersection of 161st Street and River Avenue in the Highbridge and Concourse neighborhoods of the Bronx. It is generally served by the 4 train at all times; the D train at all times except rush hours in the peak direction ; and the B train during rush hours.