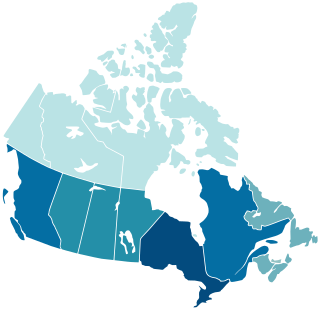
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area are also its most populous; together they account for 86.5 percent of the country's population. The territories account for over a third of Canada's area but are home to only 0.32 percent of its population, which skews the national population density value.

Flin Flon is a mining city, located on a correction line on the border of the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan, with the majority of the city located within Manitoba. Residents thus travel southwest into Saskatchewan, and northeast into Manitoba. The city is incorporated in and is jointly administered by both provinces.

Lloydminster is a city in Canada which has the unusual geographic distinction of straddling the provincial border between Alberta and Saskatchewan. The city is incorporated by both provinces as a single city with a single municipal administration.

Wetaskiwin is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. The city is located 70 kilometres (43 mi) south of the provincial capital of Edmonton. The city name comes from the Cree word wītaskiwinihk, meaning "the hills where peace was made".

Okotoks is a town in the Calgary Region of Alberta, Canada. It is on the Sheep River, approximately 38 km (24 mi) south of Downtown Calgary. Okotoks has emerged as a bedroom community of Calgary. According to the 2021 Federal Census, the town has a population of 30,214, making it the largest town in Alberta.

Strathmore is a town located in southern Alberta, Canada that is surrounded by Wheatland County. It is along the Trans-Canada Highway approximately 50 kilometres (30 mi) east of Calgary.
The 1911 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census was started on June 1, 1911. All reports had been received by February 26, 1912. The total population count of Canada was 7,206,643. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315.

Mankota is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Mankota No. 45 and Census Division No. 3. The village is located on Highway 18, about 150 kilometres (93 mi) southeast of the city of Swift Current.
According to the 2021 census, the City of Edmonton had a population of 1,010,899 residents, compared to 4,262,635 for all of Alberta, Canada. The total population of the Edmonton census metropolitan area (CMA) was 1,418,118, making it the sixth-largest CMA in Canada.
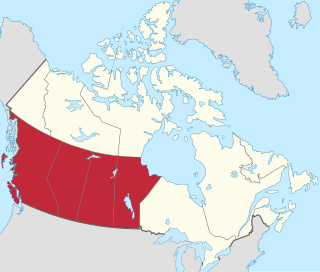
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada–United States border namely British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The people of the region are often referred to as "Western Canadians" or "Westerners", and though diverse from province to province are largely seen as being collectively distinct from other Canadians along cultural, linguistic, socioeconomic, geographic and political lines. They account for approximately 32% of Canada's total population.
The Canada 1921 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census count was taken as at June 1, 1921. The total population count was 8,788,483 representing a 22% increase over the 1911 census population count of 7,206,643. The 1921 census was the sixth comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867. The previous census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1916 census and the following census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1926 census.
The 1926 Canadian census was the third of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946. This census was conducted as at June 1, 1926.
The 1936 Canadian census was the fourth of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946. This census was conducted as at June 1, 1936.
The 1946 Canadian census was the fifth, and last, of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946, and ceased when the nationwide census switched from decennial to quinquennial in 1956. This census was conducted as of June 1, 1946.
The Canada 1931 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census count was taken as at June 1, 1931. The total population count was 10,376,379 representing a 17.9% increase over the 1911 census population count of 8,800,249. The 1931 census was the seventh comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867.
The 1951 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The total population count was 14,009,429, representing a 21.8% increase over the 1941 census population count of 11,506,655. The 1951 census was the ninth comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867.







