
James Strom Thurmond Sr. was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to shortly before his death in 2003. Prior to his 48 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South Carolina from 1947 to 1951. Thurmond was a member of the Democratic Party until 1964 when he joined the Republican Party for the remainder of his legislative career. He also ran for president in 1948 as the Dixiecrat candidate, receiving over a million votes and winning four states.

The States' Rights Democratic Party was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition to the regular Democratic Party. After President Harry S. Truman, the leader of the Democratic Party, ordered integration of the military in 1948 and other actions to address civil rights of African Americans, including the first presidential proposal for comprehensive civil and voting rights, many Southern white politicians who objected to this course organized themselves as a breakaway faction. They wished to protect the ability of states to maintain racial segregation. Its members were referred to as "Dixiecrats", a portmanteau of "Dixie", referring to the Southern United States, and "Democrat".
Southern Democrats are affiliates of the U.S. Democratic Party who reside in the Southern United States.

The 1984 United States Senate elections were held on November 6, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of President Ronald Reagan in the presidential election. In spite of the lopsided presidential race, Reagan's Republican Party suffered a net loss of two Senate seats to the Democrats, although it retained control of the Senate with a reduced 53–47 majority. Democrats defeated incumbents in Illinois and Iowa, and won an open seat in Tennessee, while Republicans defeated an incumbent in Kentucky.

The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1966 United States Senate elections were elections on November 8, 1966, for the United States Senate which occurred midway through the second term of President Lyndon B. Johnson. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. With divisions in the Democratic base over the Vietnam War, and with the traditional mid-term advantage of the party not holding the presidency, the Republicans took three Democratic seats, thereby breaking Democrats' 2/3rds supermajority. Despite Republican gains, the balance remained overwhelmingly in favor of the Democrats, who retained a 64–36 majority. Democrats were further reduced to 63–37, following the death of Robert F. Kennedy in June 1968.

The 1962 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate. Held on November 6, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They occurred in the middle of President John F. Kennedy's term. His Democratic Party made a net gain of four seats from the Republicans, increasing their control of the Senate to 68–32. However, this was reduced to 67–33 between the election and the next Congress, as on November 18, 1962, Democrat Dennis Chávez, who was not up for election that year, died. He was replaced on November 30, 1962, by Republican appointee Edwin L. Mechem. Additionally, Democrat Strom Thurmond became a Republican in 1964, further reducing Democrats to 66–34. This was the first time since 1932 that Democrats gained seats in this class of Senators.
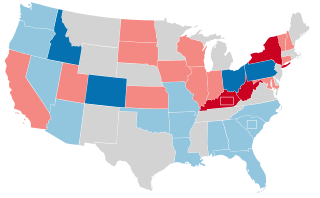
The 1956 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. Although Democrats gained two seats in regular elections, the Republicans gained two seats in special elections, leaving the party balance of the chamber unchanged.

The 1954 United States Senate elections was a midterm election in the first term of Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidency. The 32 Senate seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and six special elections were held to fill vacancies. Eisenhower's Republican party lost a net of two seats to the Democratic opposition. This small change was just enough to give Democrats control of the chamber with the support of an Independent who agreed to caucus with them, he later officially joined the party in April 1955.

The South Carolina Republican Party (SCGOP) is the state affiliate of the national Republican Party in South Carolina. It is one of two major political parties in the state, along with the South Carolina Democratic Party, and is the dominant party. Incumbent governor Henry McMaster, as well as senators Tim Scott and Lindsey Graham, are Republicans. Graham has served since January 3, 2003, having been elected in 2002 and re-elected in 2008, 2014, and 2020; Tim Scott was appointed in 2013 by then-governor Nikki Haley, who is also a Republican.

The 2002 United States Senate election in South Carolina was held on November 5, 2002. Longtime Republican incumbent Strom Thurmond decided to retire at the age of 100, becoming the first centenarian to ever serve in Congress. At that time, Thurmond was the longest-serving Senator in U.S. history, but his record was later surpassed by West Virginia's Robert Byrd. Thurmond died at age 100 on June 26, 2003, a little under six months after leaving the Senate.

The 1966 South Carolina United States Senate election was held on November 8, 1966 to select the U.S. Senator from the state of South Carolina simultaneously with the special election to fill out the remainder of Olin D. Johnston's term.
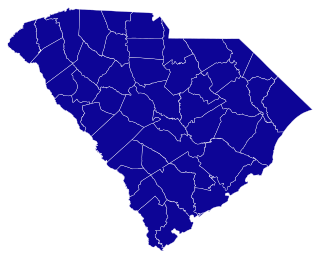
The 1956 South Carolina United States Senate special election was held on November 6, 1956 to select the U.S. Senator from the state of South Carolina simultaneously with the regular Senate election. The election resulted from the resignation of Senator Strom Thurmond on April 4, 1956, who was keeping a campaign pledge he had made in the 1954 election. Thurmond was unopposed in his bid to complete the remaining four years of the term.
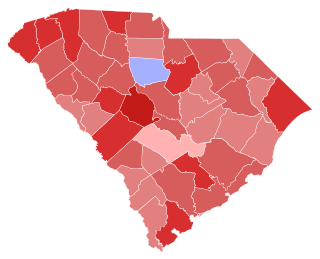
The 1984 South Carolina United States Senate election was held on November 6, 1984 to select the U.S. Senator from the state of South Carolina. Popular incumbent Republican Senator Strom Thurmond cruised to re-election against Democratic challenger Melvin Purvis.

The 1972 South Carolina United States Senate election was held on November 7, 1972 to select the U.S. Senator from the state of South Carolina. Popular incumbent Republican Senator Strom Thurmond easily defeated Democratic challenger Eugene N. Zeigler. This marked the first time that a Republican was re-elected Senator from the state, and the first time since 1872 when that person won consecutive elections.

The 1978 South Carolina United States Senate election was held on November 7, 1978, to select the U.S. senator from the state of South Carolina. Popular incumbent Republican Senator Strom Thurmond defeated Democratic challenger Charles D. Ravenel.

The 1950 South Carolina United States Senate election was held on November 7, 1950, to select the U.S. Senator from the state of South Carolina. Incumbent Democratic Senator Olin D. Johnston defeated Strom Thurmond in a bitterly contested Democratic primary on July 11 and was unopposed in the general election.

The 1948 United States presidential election in Florida was held on November 2, 1948. Voters chose eight electors, or representatives to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1948 United States presidential election in South Carolina took place on November 2, 1948, as part of the 1948 United States presidential election. State voters chose eight electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

On August 28, 1957, Strom Thurmond, then a Democratic United States senator from South Carolina, began a filibuster intended to prevent the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1957. The filibuster—an extended speech designed to stall legislation—began at 8:54 p.m. and lasted until 9:12 p.m. the following day, a duration of 24 hours and 18 minutes. This made the filibuster the longest single-person filibuster in United States Senate history, a record that still stands as of 2023. The filibuster focused primarily on asserting that the bill in question, which provided for expanded federal protection of African American voting rights, was both unnecessary and unconstitutional, and Thurmond recited from documents including the election laws of each U.S. state, Supreme Court decisions, and George Washington's Farewell Address. Thurmond focused on a particular provision in the bill that dealt with certain court cases, but opposed the entirety of the bill.



















