| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
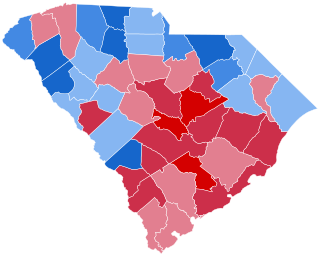
All 8 South Carolina votes to the Electoral College | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
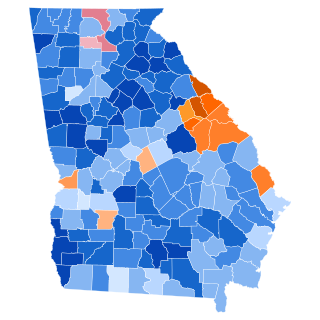
 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in South Carolina |
|---|
 |
The 1960 United States presidential election in South Carolina took place on November 8, 1960, as part of the 1960 United States presidential election. South Carolina voters chose eight [2] representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Contents
For six decades up to 1950 South Carolina was a one-party state dominated by the Democratic Party. The Republican Party had been moribund due to the disfranchisement of blacks and the complete absence of other support bases as the Palmetto State completely lacked upland or German refugee whites opposed to secession. [3] Between 1900 and 1948, no Republican presidential candidate ever obtained more than seven percent of the total presidential vote [4] – a vote which in 1924 reached as low as 6.6 percent of the total voting-age population [5] (or approximately 15 percent of the voting-age white population).
Following Harry S. Truman’s To Secure These Rights in 1947, the following year South Carolina’s small electorate overwhelmingly rejected him in favour of state Governor Strom Thurmond, who won 71 percent of the state’s limited electorate and every county except poor white industrial Anderson and Spartanburg. [6] During the 1950s, the state’s wealthier and more urbanized whites became extremely disenchanted with the national Democratic Party and to a lesser extent with the federal administration of Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower. [7] However, the state’s abolition of its poll tax in 1950 allowed increasing white voter registration and the poor white upcountry provided enough support to national Democrat Adlai Stevenson II to, aided by substantial majorities amongst the small but increasing number of blacks able to vote, [8] keep the state Democratic in the 1952 and 1956 elections.
During the 1950s, wealthy textile mill owners in the upcountry developed a grassroots state Republican Party dedicated to the tenets of the John Birch Society. This group nominated the most conservative delegation at the party’s 1960 convention. [9] These wealthy businessmen would merge with hardline segregationists to draft Barry Goldwater for the Republican nomination in 1960, and at the same time, the “Independents” in the lowcountry moved to support GOP nominees Richard Nixon and Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. as they had in 1952. [9] At the same time, Protestant clergymen in the state were quite outspoken against the nomination of Catholic Massachusetts Senator John F. Kennedy by the Democratic Party. [10]
Both candidates toured the state in October, when James F. Byrnes, former governor, criticized severely the Kennedy platform as economically unaffordable and injurious to the states’ independence. [11] In September and October polls, the state was considered likely to go for Nixon, [12] and even on election night Nixon was leading until quite late when Kennedy overtook him. [13] Kennedy ultimately won the state by 2.48 percentage points, [14] [15] being aided by an exceptional turnout for him amongst the state’s seventy-five thousand or so black voters, [16] and by the loyalty of the pro-Stevenson upcountry despite its distaste for his Catholicism. [17] Nixon won a narrow majority of the state’s white voters, and a strong majority amongst the wealthier whites of the growing Columbia and Charleston metropolitan areas.
This was the second to last time South Carolina voted Democratic. Had Gerald Ford won the state in 1976, the Palmetto State would have the nation's longest Republican streak. This was the first time Barnwell County, home of the influential “Barnwell Ring” of the state legislature, voted Republican since Ulysses S. Grant in 1872. [18]