Related Research Articles
In finance, a derivative is a contract that derives its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the underlying. Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements (hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets.
The derivatives market is the financial market for derivatives, financial instruments like futures contracts or options, which are derived from other forms of assets.
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a "linear" IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs).
In finance, a forward rate agreement (FRA) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). In particular it is a linear IRD with strong associations with interest rate swaps (IRSs).
In finance, an interest rate cap is a type of interest rate derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price. An example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the LIBOR rate exceeds 2.5%.
A swaption is an option granting its owner the right but not the obligation to enter into an underlying swap. Although options can be traded on a variety of swaps, the term "swaption" typically refers to options on interest rate swaps.
In finance, a swap is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments, cashflows, or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.
In finance, an interest rate derivative (IRD) is a derivative whose payments are determined through calculation techniques where the underlying benchmark product is an interest rate, or set of different interest rates. There are a multitude of different interest rate indices that can be used in this definition.
An equity swap is a financial derivative contract where a set of future cash flows are agreed to be exchanged between two counterparties at set dates in the future. The two cash flows are usually referred to as "legs" of the swap; one of these "legs" is usually pegged to a floating rate such as LIBOR. This leg is also commonly referred to as the "floating leg". The other leg of the swap is based on the performance of either a share of stock or a stock market index. This leg is commonly referred to as the "equity leg". Most equity swaps involve a floating leg vs. an equity leg, although some exist with two equity legs.
In finance, leverage, also known as gearing, is any technique involving borrowing funds to buy an investment.
Fixed-income arbitrage is a group of market-neutral-investment strategies that are designed to take advantage of differences in interest rates between varying fixed-income securities or contracts. Arbitrage in terms of investment strategy, involves buying securities on one market for immediate resale on another market in order to profit from a price discrepancy.
The notional amount on a financial instrument is the nominal or face amount that is used to calculate payments made on that instrument. This amount generally does not change and is thus referred to as notional.
In finance, a currency swap is an interest rate derivative (IRD). In particular it is a linear IRD, and one of the most liquid benchmark products spanning multiple currencies simultaneously. It has pricing associations with interest rate swaps (IRSs), foreign exchange (FX) rates, and FX swaps (FXSs).
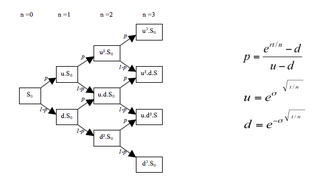
In finance, a lattice model is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where a discrete time model is required. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at "all" times before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black–Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, where because of path dependence in the payoff, Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, though methods now exist for solving this problem.
In finance, inflation derivative refers to an over-the-counter and exchange-traded derivative that is used to transfer inflation risk from one counterparty to another. See Exotic derivatives.
The term notional principal contract (NPC) is a term of art used by U.S. federal income tax professionals for contracts based on an underlying notional amount. The reason the underlying amount is "notional" is that neither party to the NPC is required to actually hold the property comprising the underlying amount. NPCs involve two parties who agree contractually to pay each other amounts at specified times, based on the underlying notional amount. The simplest example of an NPC is a so-called interest rate swap, in which one party pays the other party an amount each quarter determined by multiplying a floating, market-determined interest rate by the notional amount; and Party B pays Party A on the same date an amount determined by multiplying a fixed interest rate by the notional amount.
A dual-currency note (DC) pays coupons in the investor's domestic currency with the notional in the issuer's domestic currency. A reverse dual-currency note (RDC) is a note which pays a foreign interest rate in the investor's domestic currency. A power reverse dual-currency note (PRDC) is a structured product where an investor is seeking a better return and a borrower a lower rate by taking advantage of the interest rate differential between two economies. The power component of the name denotes higher initial coupons and the fact that coupons rise as the foreign exchange rate depreciates. The power feature comes with a higher risk for the investor, which characterizes the product as leveraged carry trade. Cash flows may have a digital cap feature where the rate gets locked once it reaches a certain threshold. Other add-on features include barriers such as knockouts and cancel provision for the issuer. PRDCs are part of the wider Structured Notes Market.
An asset swap refers to an exchange of tangible for intangible assets, in accountancy, or, in finance, to the exchange of the flow of payments from a given security for a different set of cash flows.
An inflation swap is an agreement between two counterparties to swap fixed rate payments on a notional principal amount for floating rate payments linked to an inflation index, such as the consumer price index.
In finance, a zero coupon swap (ZCS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). In particular it is a linear IRD, that in its specification is very similar to the much more widely traded interest rate swap (IRS).
References
Sources
- ↑ Frank J. Fabozzi, 2018. The Handbook of Financial Instruments, Wiley ISBN 978-1-119-52296-6
Further reading
- Mark Rubinstein Rubinstein on Derivatives. Futures, Options and Dynamic Strategies 1999 ISBN 1-899332-53-7