Related Research Articles

In finance, a derivative is a contract that derives its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the "underlying". Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements (hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Some of the more common derivatives include forwards, futures, options, swaps, and variations of these such as synthetic collateralized debt obligations and credit default swaps. Most derivatives are traded over-the-counter (off-exchange) or on an exchange such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, while most insurance contracts have developed into a separate industry. In the United States, after the financial crisis of 2007–2009, there has been increased pressure to move derivatives to trade on exchanges.

A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.

The derivatives market is the financial market for derivatives, financial instruments like futures contracts or options, which are derived from other forms of assets.

In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.

A futures exchange or futures market is a central financial exchange where people can trade standardized futures contracts defined by the exchange. Futures contracts are derivatives contracts to buy or sell specific quantities of a commodity or financial instrument at a specified price with delivery set at a specified time in the future. Futures exchanges provide physical or electronic trading venues, details of standardized contracts, market and price data, clearing houses, exchange self-regulations, margin mechanisms, settlement procedures, delivery times, delivery procedures and other services to foster trading in futures contracts. Futures exchanges can be organized as non-profit member-owned organizations or as for-profit organizations. Futures exchanges can be integrated under the same brand name or organization with other types of exchanges, such as stock markets, options markets, and bond markets. Non-profit member-owned futures exchanges benefit their members, who earn commissions and revenue acting as brokers or market makers. For-profit futures exchanges earn most of their revenue from trading and clearing fees.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.

The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) is a global derivatives marketplace based in Chicago and located at 20 S. Wacker Drive. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board, an agricultural commodities exchange. Originally, the exchange was a non-profit organization. The Merc demutualized in November 2000, went public in December 2002, and merged with the Chicago Board of Trade in July 2007 to become a designated contract market of the CME Group Inc., which operates both markets. The chairman and chief executive officer of CME Group is Terrence A. Duffy, Bryan Durkin is president. On August 18, 2008, shareholders approved a merger with the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and COMEX. CME, CBOT, NYMEX, and COMEX are now markets owned by CME Group. After the merger, the value of the CME quadrupled in a two-year span, with a market cap of over $25 billion.
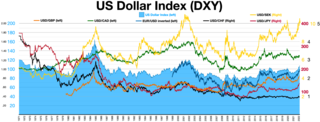
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.

Over-the-counter (OTC) or off-exchange trading or pink sheet trading is done directly between two parties, without the supervision of an exchange. It is contrasted with exchange trading, which occurs via exchanges. A stock exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity, providing transparency, and maintaining the current market price. In an OTC trade, the price is not necessarily publicly disclosed.
An energy derivative is a derivative contract based on an underlying energy asset, such as natural gas, crude oil, or electricity. Energy derivatives are exotic derivatives and include exchange-traded contracts such as futures and options, and over-the-counter derivatives such as forwards, swaps and options. Major players in the energy derivative markets include major trading houses, oil companies, utilities, and financial institutions.
The Dalian Commodity Exchange (DCE) is a Chinese futures exchange based in Dalian, Liaoning province, China. It is a non-profit, self-regulating and membership legal entity established on February 28, 1993.
Foreign exchange risk is a financial risk that exists when a financial transaction is denominated in a currency other than the domestic currency of the company. The exchange risk arises when there is a risk of an unfavourable change in exchange rate between the domestic currency and the denominated currency before the date when the transaction is completed.

StoneX Group Inc. is a financial services organization. The company operates in six areas: commercial hedging, global payments, securities, physical commodities, foreign exchange and clearing and execution services (CES). The company ranked No. 58 in the 2021 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. In July 2020, the company rebranded and changed its name to StoneX Group Inc.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:

Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. (ICE) is an American company formed in 2000 that operates global financial exchanges and clearing houses and provides mortgage technology, data and listing services. Listed on the Fortune 500, S&P 500, and Russell 1000, the company owns exchanges for financial and commodity markets, and operates 12 regulated exchanges and marketplaces. This includes ICE futures exchanges in the United States, Canada and Europe, the Liffe futures exchanges in Europe, the New York Stock Exchange, equity options exchanges and OTC energy, credit and equity markets.
Weather risk management is a type of risk management done by organizations to address potential financial losses caused by unusual weather.

An exchange, bourse, trading exchange or trading venue is an organized market where (especially) tradable securities, commodities, foreign exchange, futures, and options contracts are bought and sold.
LCH is a British clearing house group that serves major international exchanges, as well as a range of OTC markets. The LCH Group consists of two subsidiaries: LCH Ltd and LCH SA. Based on 2012 figures, LCH cleared approximately 50% of the global interest rate swap market, and was the second largest clearer of bonds and repos in the world, providing services across 13 government debt markets. In addition, LCH clears a broad range of asset classes including: commodities, securities, exchange traded derivatives, credit default swaps, energy contracts, freight derivatives, interest rate swaps, foreign exchange and Euro and Sterling denominated bonds and repos.

Richard L. Sandor is an American businessman, economist, and entrepreneur. He is chairman and CEO of the American Financial Exchange (AFX) established in 2015, which is an electronic exchange for direct interbank/financial institution lending and borrowing. The AFX flagship product, the AMERIBOR benchmark index, reflects the actual borrowing costs of thousands of regional and community banks across the U.S. and is one of the short-term borrowing rates, along with the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, vying to replace U.S. dollar Libor as a benchmark in the U.S.
Indonesia Commodity and Derivatives Exchange (ICDX) is the commodity and derivatives based exchange in Indonesia.
References
- ↑ Management. Arihant Publications. p. 395. ISBN 9326193527.
- ↑ Julian Gaspar; James Kolari; Richard Hise; Leonard Bierman; L. Murphy Smith (2016). Introduction to Global Business: Understanding the International Environment & Global Business Functions. Cengage Learning. p. 99. ISBN 9781305856226.
- ↑ Julian Roche (2014). The International Rice Trade. Elsevier Science. p. 193. ISBN 9781845692841.
- ↑ House of Commons Trade and Industry Committee (2005). Fuel Prices; Twelfth Report of Session 2004-05; Report, Together with Formal Minutes, Oral and Written Evidence. Stationery Office. ISBN 9780215024992.
- ↑ Risk Management in Commodity Markets; From Shipping to Agriculturals and Energy. Wiley. 2009. pp. 26–27. ISBN 9780470740811.
- ↑ Suk Hi Kim; Kenneth A Kim (2014). Global Corporate Finance: A Focused Approach (2nd ed.). World Scientific Publishing Company. pp. 98–100. ISBN 9789814618021.
- ↑ Alexander Davidson (2009). How the Global Financial Markets Really Work. Kogan Page. p. 150. ISBN 9780749458218.
- ↑ Jeff Madura (2015). International Financial Management. Cengage Learning. p. 73. ISBN 9781305840577.
- ↑ Vyuptakesh Sharan (2008). Fundamentals of Financial Management. Pearson Education. p. 457. ISBN 9788131723975.