
Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan Siddiqi also known as Chin Qilich Qamaruddin Khan, Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah and Nizam I, was the first Nizam of Hyderabad. He was married to the daughter of a Syed nobleman of Gulbarga. He began his career as a favourite of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, who made him a general. Following the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, Asaf Jah refused to favour any one of Aurangzeb's warring sons and as such remained neutral. When Aurangzeb's third son Bahadur Shah ultimately emerged victorious, Asaf Jah was rotated as governor of multiple Mughal provinces until 1714, when he was created Viceroy of the Deccan with authority over six Mughal provinces in southern India from 1714 to 1719. From 1719 onwards he was involved in combating the intrigues of the Sayyid brothers. From 1720 to 1722 he helped the new Mughal emperor Muhammad Shah eliminate the Sayyid brothers and was rewarded by being elevated to the grand viziership from 1722 to 1724.

Aurangabad, officially known as Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, also spelt Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar, is a city in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarters of Aurangabad district and is the largest city in the Marathwada region. Located on a hilly upland terrain in the Deccan Traps, Aurangabad is the fifth-most populous urban area in Maharashtra after Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur and Nashik with a population of 1,175,116. The city is known as a major production center of cotton textile and artistic silk fabrics. Several prominent educational institutions, including Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, are located in the city. The city is also a popular tourism hub, with tourist destinations like the Ajanta and Ellora caves lying on its outskirts, both of which have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1983. Other tourist attractions include the Aurangabad Caves, Devagiri Fort, Grishneshwar Temple, Jama Mosque, Bibi Ka Maqbara, Himayat Bagh, Panchakki and Salim Ali Lake. Historically, there were 52 Gates in Aurangabad, some of them extant, because of which Aurangabad is nicknamed as the "City of Gates". In 2019, the Aurangabad Industrial City (AURIC) became the first greenfield industrial smart city of India under the country's flagship Smart Cities Mission.

Secunderabad, also spelled as Sikandarabad, is a twin city of Hyderabad and one of the six zones of the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) in the Indian state of Telangana. It is the headquarters of the South Central Railway zone. Named after the Mir Akbar Ali Khan Sikander Jah, Asaf Jah III, Nizam of the Asaf Jahi dynasty, Secunderabad was established in 1806 as a British cantonment. Although both the cities are together referred to as the twin cities, Hyderabad and Secunderabad have different histories and cultures, with Secunderabad having developed directly under British rule until 1948, and Hyderabad as the capital of the Nizams' princely state of Hyderabad.

The City and Industrial Development Corporation of Maharashtra (CIDCO) is an Indian city planning agency and richest government authority in India which is formed and controlled by the Government of Maharashtra. CIDCO was formed on 17 March 1970 under the Indian Companies Act of 1956; its purpose at the time of its creation was to develop a satellite town to Mumbai, Maharashtra, and now functioning as New Town Development Authority (NTDA) and Special Planning Authority (SPA) of Government of Maharashtra for development of new towns by planning and developing entire urban infrastructure, providing municipal services, executing large scale infrastructure projects including Navi Mumbai International Airport and the Navi Mumbai Metro. CIDCO also launched India's first smart city project. CIDCO has ownership of all plots in new cities, underutilised funds about Rs 40,000 crore and reserved Land Bank; which makes CIDCO richest Government Authority.
A cantonment is a military quarters. In Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and other parts of South Asia, a cantonment refers to a permanent military station. In United States military parlance, a cantonment is, essentially, "a permanent residential section of a fort or other military installation," such as Fort Cavazos.

Delhi Cantonment is a Class I Cantonment Board established in 1914. The area of the Cantonment is 10,452 acres (42.30 km2) and the population of the Cantonment as per the 2011 census is 110,351.

Mir Nizam Ali Khan Siddiqi, Asaf Jah II was the 5th Nizam of Hyderabad State in South India between 1762 and 1803. He was born on 7 March 1734 as fourth son to Asaf Jah I and Umda Begum. His official name is Asaf Jah II, Nizam ul-Mulk, Nizam ud-Daula, Nawab Mir Nizam 'Ali Khan Siddiqi, Fateh Jang, Sipah Salar, Nawab Subedar of the Deccan. Sawānih-i-Deccan, a Persian work compiled by Munim Khan, a military commander during the era of Asaf Jah II gave more insight about administration of Asaf Jahis.

Cantonments in Pakistan are permanent military bases of the Pakistan Army, which are administered by Cantonment Boards under the control of the Military Lands & Cantonments Department (ML&C), Ministry of Defence, Government of Pakistan. Cantonments are established under and governed by the Cantonments Act 1924.

The Mughal–Maratha Wars was a conflict between the Mughal Empire and the descendants of the Maratha ruler Shivaji from the time of Shivaji's death in 1680 until the death of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. Shivaji was a central figure in what has been called "the Maratha insurgency" against the Mughal state. Both he and his son, Sambhaji, or Shambuji, typically, alternated between rebellion against the Mughal state and service to the Mughal sovereign in an official capacity. It was common practice in late 17th-century India for members of a ruling family of a small principality to both collaborate with the Mughals and rebel.

Rawalpindi is a tehsil - an administrative subdivision - of Rawalpindi District in the western part of the Punjab province, Pakistan, it contains the district capital - the city of Rawalpindi.

Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) is the civic body that oversees Hyderabad, the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It is the local government for the city of Hyderabad. It is one of the largest municipal corporations in India with a population of 7.9 million and an area of 650 km².
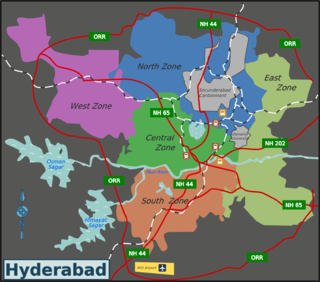
Secunderabad Cantonment Board is the civic administrative agency of Secunderabad cantonment area. Geographically, it lies in the twin cities of Hyderabad-Secunderabad. Secunderabad Cantonment Board is India’s second largest cantonment board, after Bathinda Cantonment. There are eight civilian wards in Secunderabad Cantonment Board, with a population of four lakh. Being primarily a military area, the Secunderabad cantonment comes under the administrative purview of the union defence ministry of the government of India. It is overseeing an area of 40.1 km2 (15.5 sq mi), where there are several military camps. Secunderabad Cantonment has a huge land bank, which has been protected since the British era.
A cantonment board is a civic administration body in India under control of the Ministry of Defence. The board comprises elected members besides ex-officio and nominated members as per the Cantonments Act, 2006. The term of office of a member of a board is five years. A cantonment board consists of eight elected members, three nominated military members, three ex-officio members, and one representative of the district magistrate.
Aurangabad is a medieval Indian town named after Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, who established this town during his tenure as the Viceroy of the Deccan (Dakhin), a geographical region comprising parts of modern-day Maharashtra, Telangana and Karnataka.
The Government of Delhi, officially the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (GNCTD) is the governing body of the Union Territory of Delhi, whose urban area is the seat of the Government of India. It also governs the city or local governments in the area as per the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act.

Pune Cantt, also known as Camp, is a military cantonment located in the city of Pune, India. It was established in 1817 for accommodating troops of the Indian Army. The cantonment houses many military establishments. It is also known for its shopping locations, MG Road and East Street. The headquarters of Indian Army's Southern Command is located in Pune Cantonment. The National War Memorial Southern Command which commemorates the sacrifice of soldiers of the Indian Armed Forces is also situated in the cantonment.
Kanpur Cantonment is a military cantonment in Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. The Kanpur Cantonment was established in the year 1811 and is situated on the right bank of river Ganges and is bound by Kanpur city area on the remaining three sides. Kanpur Cantonment is the largest cantonment in India, by population. The area of the Cantonment is approx. 4243.0084 acres (17 km2) out of which the Bungalow Area is 3899.1784 acres and the Civil Area is 334.83 acres. As per 2011 Census, the population of Cantonment is 108,035 which is 453rd largest city of India.
The Indian Defence Estates Service is a Civil Service in the Government of India. Its Cadre Controlling Authority (CCA) is the Ministry of Defence. Civil Services Examination conducted every year by Union Public Service Commission provides a gateway for entry into this service. The Service traces its origin to 16 December 1926 and has been constantly evolving since then. The service was initially known as the Military Lands and Cantonment Service (1926-1983), and then Defence Lands and Cantonment Service (1983-1985). In 1985, it was renamed as the Indian Defence Estates Service. The service is governed by the Indian Defence Estates Service Rules, 2013, where 75% intake is by direct recruitment and 25% by promotion.















