Related Research Articles

Papillomaviridae is a family of non-enveloped DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected mammals, but also other vertebrates such as birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Infection by most papillomavirus types, depending on the type, is either asymptomatic or causes small benign tumors, known as papillomas or warts. Papillomas caused by some types, however, such as human papillomaviruses 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous.
Polyomaviridae is a family of viruses whose natural hosts are primarily mammals and birds. As of 2020, there are six recognized genera and 117 species, five of which are unassigned to a genus. 14 species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified in humans to a lesser extent. Most of these viruses are very common and typically asymptomatic in most human populations studied. BK virus is associated with nephropathy in renal transplant and non-renal solid organ transplant patients, JC virus with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and Merkel cell virus with Merkel cell cancer.
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
Microviridae is a family of bacteriophages with a single-stranded DNA genome. The name of this family is derived from the ancient Greek word μικρός (mikrós), meaning "small". This refers to the size of their genomes, which are among the smallest of the DNA viruses. Enterobacteria, intracellular parasitic bacteria, and spiroplasma serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this family, divided among seven genera and two subfamilies.
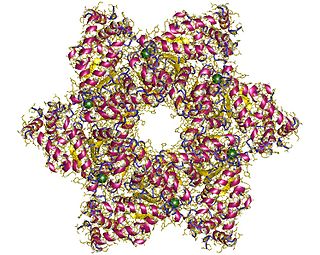
SV40 large T antigen is a hexamer protein that is a dominant-acting oncoprotein derived from the polyomavirus SV40. TAg is capable of inducing malignant transformation of a variety of cell types. The transforming activity of TAg is due in large part to its perturbation of the retinoblastoma (pRb) and p53 tumor suppressor proteins. In addition, TAg binds to several other cellular factors, including the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP, which may contribute to its transformation function.
Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) is a retrovirus and is the first oncovirus to have been described. It causes sarcoma in chickens.

Bovine papillomaviruses (BPV) are a paraphyletic group of DNA viruses of the subfamily Firstpapillomavirinae of Papillomaviridae that are common in cattle. All BPVs have a circular double-stranded DNA genome. Infection causes warts of the skin and alimentary tract, and more rarely cancers of the alimentary tract and urinary bladder. They are also thought to cause the skin tumour equine sarcoid in horses and donkeys.

The Western barred bandicoot, also known as the Marl, is a small species of bandicoot; now extinct across most of its former range, the western barred bandicoot only survives on offshore islands and in fenced sanctuaries on the mainland.
Visna-maedi virus from the genus Lentivirus and subfamily Orthoretrovirinae, is a retrovirus that causes encephalitis and chronic pneumonitis in sheep. It is known as visna when found in the brain, and maedi when infecting the lungs. Lifelong, persistent infections in sheep occur in the lungs, lymph nodes, spleen, joints, central nervous system, and mammary glands; The condition is sometimes known as ovine progressive pneumonia (OPP), particularly in the United States, or Montana sheep disease. White blood cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage are the main target of the virus.

Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC20A1 gene.

A viral disease occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.

Vpu is an accessory protein that in HIV is encoded by the vpu gene. Vpu stands for "Viral Protein U". The Vpu protein acts in the degradation of CD4 in the endoplasmic reticulum and in the enhancement of virion release from the plasma membrane of infected cells. Vpu induces the degradation of the CD4 viral receptor and therefore participates in the general downregulation of CD4 expression during the course of HIV infection. Vpu-mediated CD4 degradation is thought to prevent CD4-Env binding in the endoplasmic reticulum to facilitate proper Env assembly into virions. It is found in the membranes of infected cells, but not the virus particles themselves.

Transmissible gastroenteritis virus or Transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV) is a coronavirus which infects pigs. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. The virus is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus, subgenus Tegacovirus, species Alphacoronavirus 1.
Alphasatellites are a single-stranded DNA family of satellite viruses that depend on the presence of another virus to replicate their genomes. As such, they have minimal genomes with very low genomic redundancy. The genome is a single circular single strand DNA molecule. The first alphasatellites were described in 1999 and were associated with cotton leaf curl disease and Ageratum yellow vein disease. As begomoviruses are being characterised at the molecular level an increasing number of alphasatellites are being described.
Rhinolophus bat coronavirus HKU2 is a novel enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus species in the Alphacoronavirus, or Group 1, genus with a corona-like morphology.
Agnoprotein is a protein expressed by some members of the polyomavirus family from a gene called the agnogene. Polyomaviruses in which it occurs include two human polyomaviruses associated with disease, BK virus and JC virus, as well as the simian polyomavirus SV40.
A kinetic class, also known as a temporal class, is a grouping of genes in a viral genome that are expressed at the same time during the viral replication cycle. Five of the human DNA viral families have multiple kinetic classes: Poxviridae, Herpesviridae, Adenoviridae, Papillomaviridae, and Polyomaviridae. All of the genes in a particular kinetic class are activated by the same mechanism: either by the process of the virus entering the cell and uncoating, or by the products of an earlier kinetic class in what is known as a transcriptional cascade. Generally speaking, earlier kinetic classes code for enzymes that direct the viral replication process, and later kinetic classes code for structural proteins to be packaged into virions

Monodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all single-stranded DNA viruses that encode an endonuclease of the HUH superfamily that initiates rolling circle replication of the circular viral genome. Viruses descended from such viruses are also included in the realm, including certain linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses and circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses. These atypical members typically replicate through means other than rolling circle replication.
ORF3c is a gene found in coronaviruses of the subgenus Sarbecovirus, including SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. It was first identified in the SARS-CoV-2 genome and encodes a 41 amino acid non-structural protein of unknown function. It is also present in the SARS-CoV genome, but was not recognized until the identification of the SARS-CoV-2 homolog.
Kanyana Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre is a not-for-profit organisation and establishment located in Lesmurdie, Western Australia, dedicated to wildlife conservation by caring for sick, injured, orphaned and displaced native animals, breeding threatened native species, animal care training, research, and education through schools and local communities.
References
- ↑ Bennett MD, Woolford L, Stevens H, Van Ranst M, Oldfield T, Slaven M, O'Hara AJ, Warren KS, Nicholls PK (2008) Genomic characterization of a novel virus found in papillomatous lesions from a southern brown bandicoot (Isoodon obesulus) in Western Australia. Virology 376(1):173-182
- ↑ Bennett MD, Reiss A, Stevens H, Heylen E, Van Ranst M, Wayne A, Slaven M, Mills JN, Warren KS, O'Hara AJ, Nicholls PK (2010) The first complete papillomavirus genome characterized from a marsupial host: a novel isolate from Bettongia penicillata. J Virol 84(10):5448-5453
- ↑ Woolford L, Rector A, Van Ranst M, Ducki A, Bennett MD, Nicholls PK, Warren KS, Swan RA, Wilcox GE, O'Hara AJ (2007) A novel virus detected in papillomas and carcinomas of the endangered western barred bandicoot (Perameles bougainville) exhibits genomic features of both the Papillomaviridae and Polyomaviridae. J Virol 81(24):13280-13290