
Gibbons are apes in the family Hylobatidae. The family historically contained one genus, but now is split into four extant genera and 20 species. Gibbons live in subtropical and tropical forests from eastern Bangladesh to Northeast India to southern China and Indonesia.

Apes are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, which together with its sister group Cercopithecidae form the catarrhine clade, cladistically making them monkeys. Apes do not have tails due to a mutation of the TBXT gene. In traditional and non-scientific use, the term ape can include tailless primates taxonomically considered Cercopithecidae, and is thus not equivalent to the scientific taxon Hominoidea. There are two extant branches of the superfamily Hominoidea: the gibbons, or lesser apes; and the hominids, or great apes.

The hoolock gibbons are three primate species of genus Hoolock in the gibbon family, Hylobatidae, native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.

Lohit is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. The district headquarters is located at Tezu. As of 2011 it is the third most populous district of Arunachal Pradesh, after Papum Pare and Changlang.

The genus Hylobates is one of the four genera of gibbons. Its name means "forest walker", from the Greek hūlē and bates.

Nomascus is the second-most speciose genus of the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. Originally, this genus was a subgenus of Hylobates, with all individuals considered to be one species, H. concolor.
Endangered mammals of India are the mammal species in India that are listed as threatened in the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Animals

The Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary, formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserved Forest, is an isolated protected area of evergreen forest located in Assam, India. The sanctuary was officially constituted and renamed in 1997. Set aside initially in 1881, its forests used to extend to the foothills of the Patkai mountain range.

The eastern hoolock gibbon is a primate from the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. It is one of three species of hoolock gibbon. This species is found in east of the Chindwin River, such as the Mahamyaing Wildlife Sanctuary, and in south west Yunnan of China. Recent study published in April, 2021, in International Journal of Primatology confirmed that this species is not found in India as it was thought to be.

The western hoolock gibbon is a primate from the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. The species is found in Assam, Mizoram, and Meghalaya in India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar west of the Chindwin River.

Ficus neriifolia is a species of fig (Ficus). It is native to Asia, including Bhutan, Burma, China, India, and Nepal.
Rakhine Yoma Elephant Range is a protected area in Myanmar's Rakhine Yoma mountains, covering about 1,756 km2 (678 sq mi) of evergreen and mixed deciduous forest at an elevation of 20–1,270 m (66–4,167 ft).

Lawachara National Park is a national park and nature reserve in Bangladesh, located at Kamalganj Upazila and Moulvibazar District in the northeastern region of the country. It is located within the 2,740 ha (27.4 km2) West Bhanugach Reserved Forest.

People Resources and Conservation Foundation (PRCF) is an international non-governmental organization that helps local people in developing countries protect their natural environment. Its headquarters are in the United States but its conservation fieldwork is carried out in a number of Southeast Asian countries. PRCF has joined collaborative research projects on new animal species in Southeast Asia, such as the Myanmar/Burmese snub-nosed monkey. The organization also sets up programs to help native cultures retain their cultural identity through projects such as basket and fabric weaving.

The Mishmi Hills are located at the northeastern tip of India, in northeastern Arunachal Pradesh. On the Chinese side, they form the southern parts of Nyingchi Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region.

The phylogenetic split of the superfamily Hominoidea (apes) into the Hylobatidae (gibbons) and Hominidae families is dated to the early Miocene, roughly 20 to 16 million years ago.
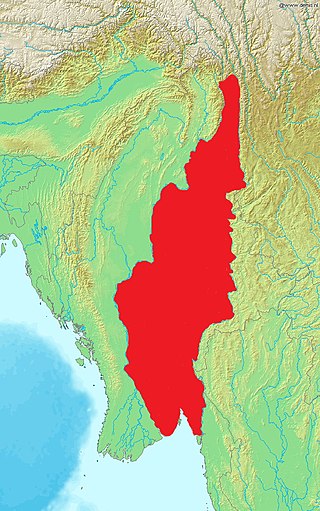
The Skywalker hoolock gibbon or Gaoligong hoolock gibbon is an arboreal primate in the gibbon family Hylobatidae. It is one of three species of hoolock gibbon and was first described in January 2017 in the American Journal of Primatology. The Skywalker hoolock gibbon is one of two species of Eastern hoolocks: H. tianxing and H. leuconedys. Researchers estimate H. tianxing diverged from H. leuconedys roughly 490,000 years ago. The Eastern hoolock is vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, with a population of 310,000–370,000 individuals. Of this population, H. tianxing makes up less than 150 individuals, making the Skywalker hoolock gibbon an endangered species.
Mahamyaing Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Myanmar's Sagaing Region, covering an area of 1,181 km2 (456 sq mi). It ranges in elevation from 145 to 590 m and was established in 2002 in Kalay and Mawlaik Townships.
Pablakhali Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary at the northern end of the Kaptai reservoir in the Chittagong Hill Tracts region of Bangladesh. The area of the sanctuary is 42,087 ha, and it is located on the eastern and northern hills of Bangladesh. The nearest town is Rangamati (Bengali: রাঙ্গামাটি which is 112 km from the sanctuary. The western boundary of the sanctuary is formed by the Kassalong River.

















