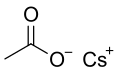
 Structural formula | |||
 Unit cell of anhydrous caesium acetate. | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Caesium acetate | |||
| Other names Cesium acetate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.226 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H3CsO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 191.949 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colourless, hygroscopic | ||
| Density | 2.423 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 194 °C (381 °F; 467 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 945 °C (1,733 °F; 1,218 K) | ||
| 945.1 g/100 g (−2.5 °C) 1345.5 g/100 ml (88.5 °C) | |||
| Structure [2] | |||
| Primitive hexagonal | |||
| P6/m, No. 175 | |||
Lattice volume (V) | 76.542 cm3·mol−1 | ||
Formula units (Z) | 6 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: [3] | |||
  | |||
| Warning | |||
| H302, H319, H361f, H373 | |||
| P203, P260, P264, P264+P265, P270, P280, P301+P317, P305+P351+P338, P318, P319, P330, P337+P317, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions | Caesium formate | ||
Other cations | Lithium acetate Sodium acetate Potassium acetate Rubidium acetate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Caesium acetate or cesium acetate is an ionic caesium compound with the molecular formula CH3COOCs. It is a white solid that may be formed by the reaction of caesium hydroxide or caesium carbonate with acetic acid. [4]

