
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology.

Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.

Climate change in Sri Lanka is an important issue, and its effects threaten to impact both human and natural systems in Sri Lanka. Roughly 50 percent of its 22 million citizens live in low-lying coastal areas in the west, south, and south-west of the island, and are at risk of future sea level rise. Climate change also threatens the island's biodiversity, including its marine ecosystem and coastal coral reef environments. Sea-level rise due to climate change has the potential to affect the overall abundance of endemic species. Sri Lanka's coastal regions, such as the Northern Province and the Northern Western Province, are considered major hotspots and extremely vulnerable to climate change. These maritime provinces are the most densely populated. In addition to being a threat to Sri Lanka's biodiversity, climate change may cause disastrous consequences on various levels in such areas. Such consequences include: Affecting agricultural productivity, causing natural disasters like floods and droughts, increasing the spread of infectious illnesses, and finally undermining the living standards.

Climate change in Bangladesh is a critical issue as the country is one of the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it ranked seventh in the list of countries most affected by climate calamities during the period 1999–2018. Bangladesh's vulnerability to climate change impacts is due to a combination of geographical factors, such as its flat, low-lying, and delta-exposed topography, and socio-economic factors, including its high population density, levels of poverty, and dependence on agriculture.

Climate change in Africa is an increasingly serious threat as Africa is among the most vulnerable continents to the effects of climate change. Some sources even classify Africa as "the most vulnerable continent on Earth". This vulnerability is driven by a range of factors that include weak adaptive capacity, high dependence on ecosystem goods for livelihoods, and less developed agricultural production systems. The risks of climate change on agricultural production, food security, water resources and ecosystem services will likely have increasingly severe consequences on lives and sustainable development prospects in Africa. With high confidence, it was projected by the IPCC in 2007 that in many African countries and regions, agricultural production and food security would probably be severely compromised by climate change and climate variability. Managing this risk requires an integration of mitigation and adaptation strategies in the management of ecosystem goods and services, and the agriculture production systems in Africa.

Climate change in Pakistan is a major issue for the country. Pakistan is highly vulnerable to climate change. As with the changing climate in South Asia as a whole, the climate of Pakistan has changed over the past several decades, with significant impacts on the environment and people. In addition to increased heat, drought and extreme weather in parts of the country, the melting of glaciers in the Himalayas has impacted some of the important rivers of Pakistan. Between 1999 and 2018, Pakistan ranked 5th in the countries affected by extreme weather caused by climate change.

The effects of climate change on agriculture can result in lower crop yields and nutritional quality due to drought, heat waves and flooding as well as increases in pests and plant diseases. The effects are unevenly distributed across the world and are caused by changes in temperature, precipitation and atmospheric carbon dioxide levels due to global climate change. In 2019, millions were already suffering from food insecurity due to climate change. Further, the predicted decline in global crop production is 2% - 6% with each decade. In 2019 it was predicted that food prices would rise by 80% by 2050. This will likely lead to increased food insecurity, disproportionally affecting poorer communities. A 2021 study estimated that the severity of heatwave and drought impacts on crop production tripled over the last 50 years in Europe – from losses of 2.2% during 1964–1990 to losses of 7.3% in 1991–2015.

The effect of climate change on small island countries can be extreme because of low-lying coasts, relatively small land masses, and exposure to extreme weather. The effects of climate change, particularly sea level rise and increasingly intense tropical cyclones, threaten the existence of many island countries, island peoples and their cultures, and will alter their ecosystems and natural environments. Several Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are among the most vulnerable nations to climate change.

Climate change in the Philippines is having serious impacts such as increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, sea level rise, extreme rainfall, resource shortages, and environmental degradation. All of these impacts together have greatly affected the Philippines' agriculture, water, infrastructure, human health, and coastal ecosystems and they are projected to continue having devastating damages to the economy and society of the Philippines.
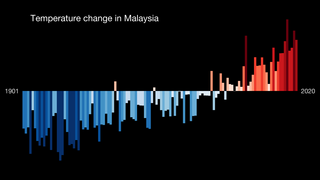
Climate change is having a considerable impact in Malaysia. Increasing temperatures are likely to greatly increase the number of heatwaves occurring annually. Variations in precipitation may increase the frequency of droughts and floods in various local areas. Sea level rise may inundate some coastal areas. These impacts are expected to have numerous environmental and socioeconomic effects, exacerbating existing environmental issues and reinforcing inequality.

Climate change in Tanzania is affecting the natural environment and residents of Tanzania. Temperatures in Tanzania are rising with a higher likelihood of intense rainfall events and of dry spells.
Climate change in Somalia refers to changes in the climate in Somalia and the subsequent response, adaption and mitigation strategies of the country.

Climate change in Senegal will have wide reaching impacts on many aspects of life in Senegal. Climate change will cause an increase in average temperatures over west Africa by between 1.5 and 4 °C by mid-century, relative to 1986–2005. Projections of rainfall indicate an overall decrease in rainfall and an increase in intense mega-storm events over the Sahel. The sea level is expected to rise faster in West Africa than the global average. Although Senegal is currently not a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, it is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change.

Climate change in Morocco is expected to significantly impact Morocco on multiple dimensions, just like for other countries in the MENA region.

Climate change is a significant threat to Madagascar's environment and people. Climate change has raised temperatures, made the dry season longer and has resulted in more intense tropical storms. The country's unique ecosystems, animal and plant life are being impacted.

Climate change is posing an increasing threat to global socio-economic development and environmental sustainability. Developing countries with low adaptive capacity and high vulnerability to the phenomenon are disproportionately affected. Climate change in Kenya is increasingly impacting the lives of Kenya's citizens and the environment. Climate Change has led to more frequent extreme weather events like droughts which last longer than usual, irregular and unpredictable rainfall, flooding and increasing temperatures.

Climate change in Vietnam is having considerable environmental, economic and social impacts. Vietnam is among the most affected countries by global climate change. A large number of studies show that Vietnam is experiencing climate change and will be severely negatively affected in coming decades. These negative effects include sea level rise, salinity intrusion and other hydrological problems like floods, river mouth evolution and sedimentation. Natural hazards such as cold waves, storm surges will increase in frequency, with negative effects on the country's development, infrastructure and economy.

Climate change in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) refers to changes in the climate of the MENA region and the subsequent response, adaption and mitigation strategies of countries in the region. In 2018, the MENA region emitted 3.2 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide and produced 8.7% of global greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) despite making up only 6% of the global population. These emissions are mostly from the energy sector, an integral component of many Middle Eastern and North African economies due to the extensive oil and natural gas reserves that are found within the region. The region of Middle East is one of the most vulnerable to climate change. The impacts include increase in drought conditions, aridity, heatwaves and sea level rise.
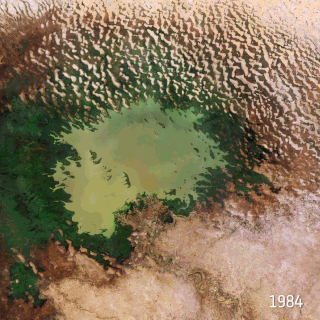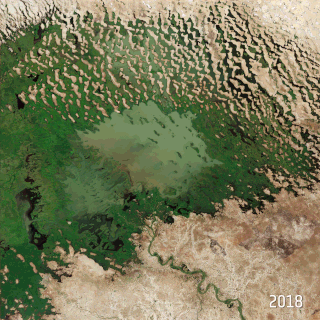
Climate change in Nigeria is evident from temperature increase, rainfall variability. It also reflects in drought, desertification, rising sea levels, erosions, floods, thunderstorms, burning of fossil fuels, bush fires, landslides, land degradation, more frequent extreme weather conditions and loss of biodiversity. All of which continues to negatively affect human and animal life and also the ecosystems in Nigeria. Although depending on the location, regions experience climate change with significant higher temperatures during the dry seasons while rainfalls during rainy seasons help keep the temperature at milder levels.

Climate change in Fiji is an exceptionally pressing issue for the country - as an island nation, Fiji is particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels, coastal erosion and extreme weather. These changes, along with temperature rise, will displace Fijian communities and will prove disruptive to the national economy - tourism, agriculture and fisheries, the largest contributors to the nation's GDP, will be severely impacted by climate change causing increases in poverty and food insecurity. As a party to both the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Climate Agreement, Fiji hopes to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 which, along with national policies, will help to mitigate the impacts of climate change.





















