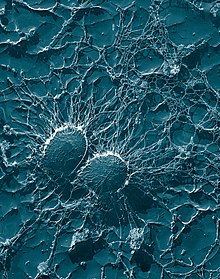
Staphylococcus lugdunensis is a coagulase-negative member of the genus Staphylococcus, consisting of Gram-positive bacteria with spherical cells that appear in clusters.

Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS. Infections can be localized or systemic, and are often associated with the insertion of medical devices. The highly antibiotic-resistant phenotype and ability to form biofilms make S. haemolyticus a difficult pathogen to treat. Its most closely related species is Staphylococcus borealis.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is a Gram-positive coccus belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. S. saprophyticus is a common cause of community-acquired urinary tract infections.
Staphylococcus caprae is a Gram-positive, coccus bacteria and a member of the genus Staphylococcus. S. caprae is coagulase-negative. It was originally isolated from goats, but members of this species have also been isolated from human samples.
Staphylococcus hominis is a coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus, consisting of Gram-positive, spherical cells in clusters. It occurs very commonly as a harmless commensal on human and animal skin and is known for producing thioalcohol compounds that contribute to body odour. Like many other coagulase-negative staphylococci, S. hominis may occasionally cause infection in patients whose immune systems are compromised, for example by chemotherapy or predisposing illness.

Staphylococcus xylosus is a species of bacteria belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is a Gram-positive bacterium that forms clusters of cells. Like most staphylococcal species, it is coagulase-negative and exists as a commensal on the skin of humans and animals and in the environment.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.

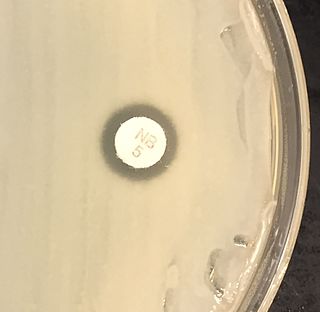
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. It contains a high concentration of salt (NaCl) which is inhibitory to most bacteria - making MSA selective against most Gram-negative and selective for some Gram-positive bacteria that tolerate high salt concentrations. It is also a differential medium for mannitol-fermenting staphylococci, containing the sugar alcohol mannitol and the indicator phenol red, a pH indicator for detecting acid produced by mannitol-fermenting staphylococci. Staphylococcus aureus produces yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas other coagulase-negative staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no colour change to the medium. If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that causes the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow. It is used for the selective isolation of presumptive pathogenic (pp) Staphylococcus species.
Lysostaphin is a Staphylococcus simulans metalloendopeptidase. It can function as a bacteriocin (antimicrobial) against Staphylococcus aureus.
Clumping factor A, or ClfA, is a virulence factor from Staphylococcus aureus that binds to fibrinogen.

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.
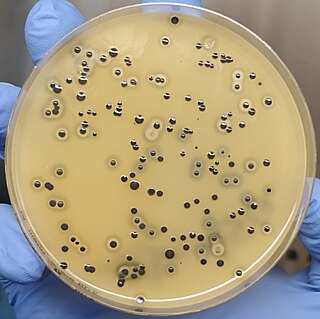
Baird-Parker agar is a type of agar used for the selective isolation of gram-positive Staphylococci species. It contains lithium chloride and tellurite to inhibit the growth of alternative microbial flora, while the included pyruvate and glycine promote the growth of Staphylococci. Staphylococcus colonies show up black in colour with clear zones produced around them.

Staphylococcus capitis is a coagulase-negative species (CoNS) of Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal flora of the skin of the human scalp, face, neck, scrotum, and ears and has been associated with prosthetic valve endocarditis, but is rarely associated with native valve infection.

Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms.

Staphylococcus cohnii is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. The species commonly lives on human skin; clinical isolates have shown high levels of antibiotic resistance. A strain of S. cohnii was found to contain a mobile genetic element very similar to the staphylococcal cassette chromosome encoding methicillin resistance element seen in Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus carnosus is a bacterium from the genus Staphylococcus that is both Gram-positive and coagulase-negative. It was originally identified in dry sausage and is an important starter culture for meat fermentation. Unlike other members of its genus, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. carnosus is nonpathogenic and safely used in the food industry.
Staphylococcus intermedius is a Gram-positive, catalase positive member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. Strains of this species were originally isolated from the anterior nares of pigeons, dogs, cats, mink, and horses. Many of the isolated strains show coagulase activity. Clinical tests for detection of methicillin-resistant S. aureus may produce false positives by detecting S. intermedius, as this species shares some phenotypic traits with methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains. It has been theorized that S. intermedius has previously been misidentified as S. aureus in human dog bite wound infections, which is why molecular technologies such as MALDI-TOF and PCR are preferred in modern veterinary clinical microbiology laboratories for their more accurate identifications over biochemical tests. S. intermedius is largely phenotypically indiscriminate from Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Staphylococcus delphini, and therefore the three organisms are considered to be included in the more general 'Staphylococcus intermedius group'.
Staphylococcus schleiferi is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium of the family Staphylococcaceae. It is facultatively anaerobic, coagulase-variable, and can be readily cultured on blood agar where the bacterium tends to form opaque, non-pigmented colonies and beta (β) hemolysis. There exists two subspecies under the species S. schleiferi: Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. schleiferi and Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well. S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.

In microbiology, colonial morphology refers to the visual appearance of bacterial or fungal colonies on an agar plate. Examining colonial morphology is the first step in the identification of an unknown microbe. The systematic assessment of the colonies' appearance, focusing on aspects like size, shape, colour, opacity, and consistency, provides clues to the identity of the organism, allowing microbiologists to select appropriate tests to provide a definitive identification.